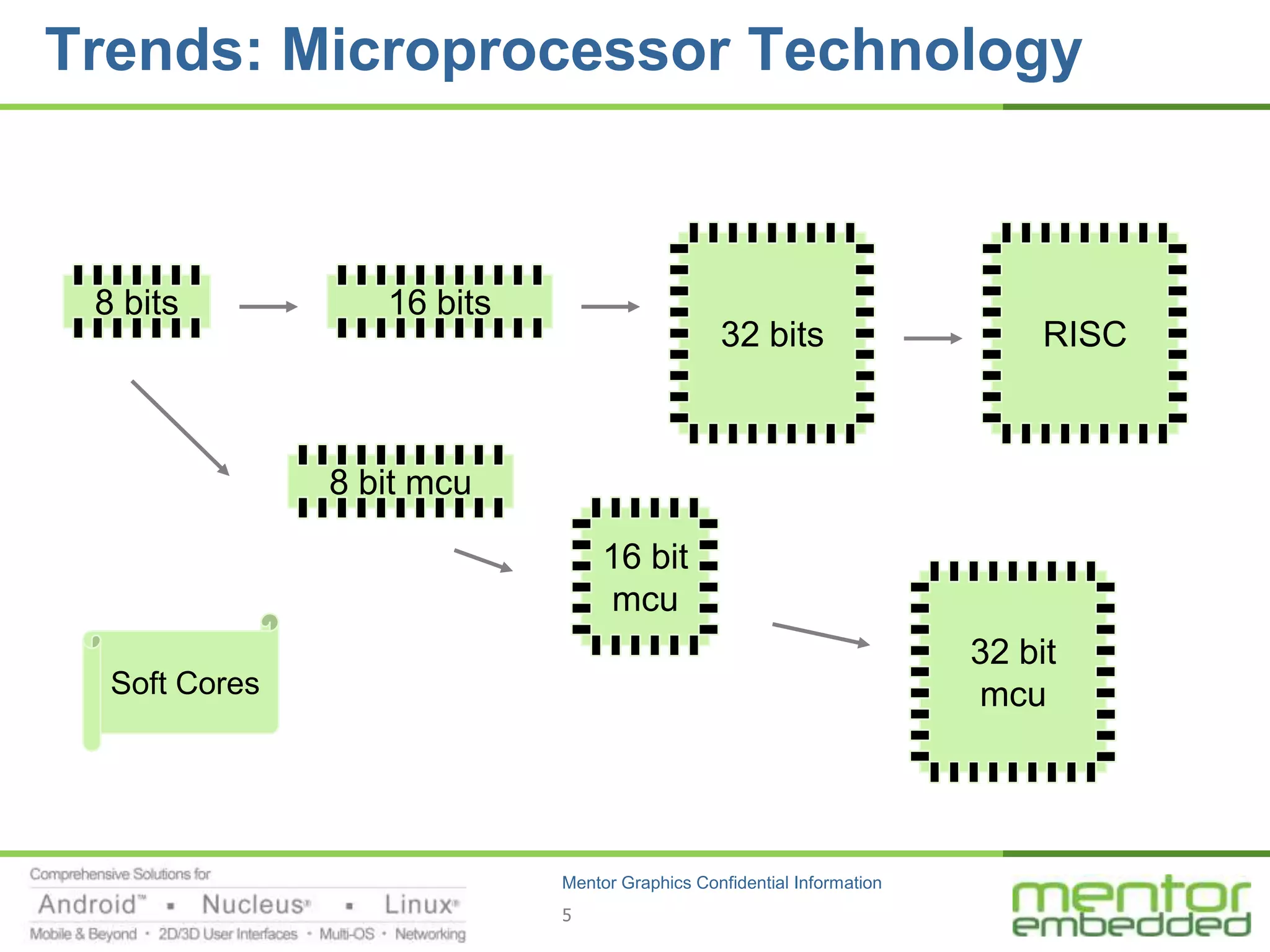
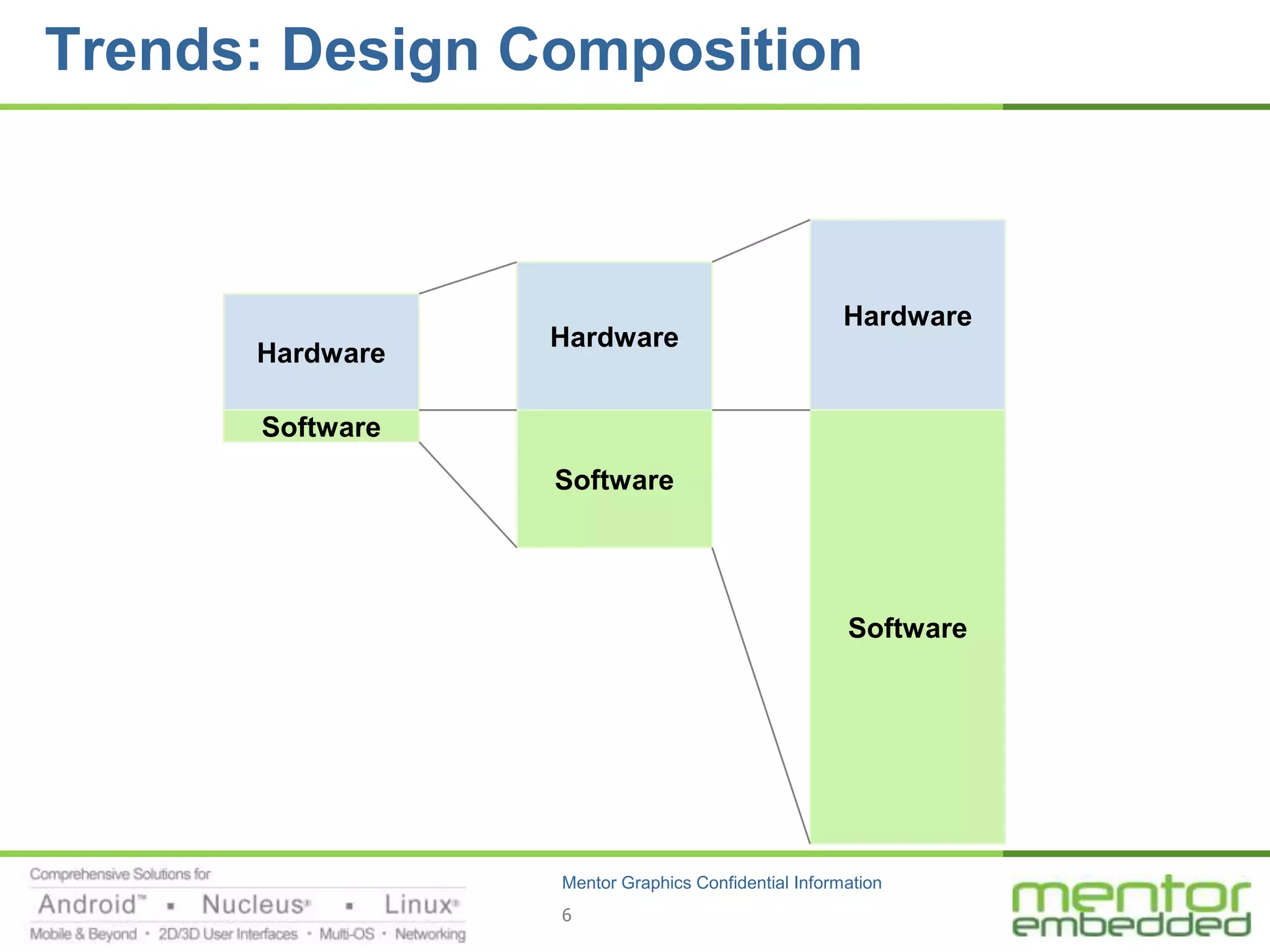
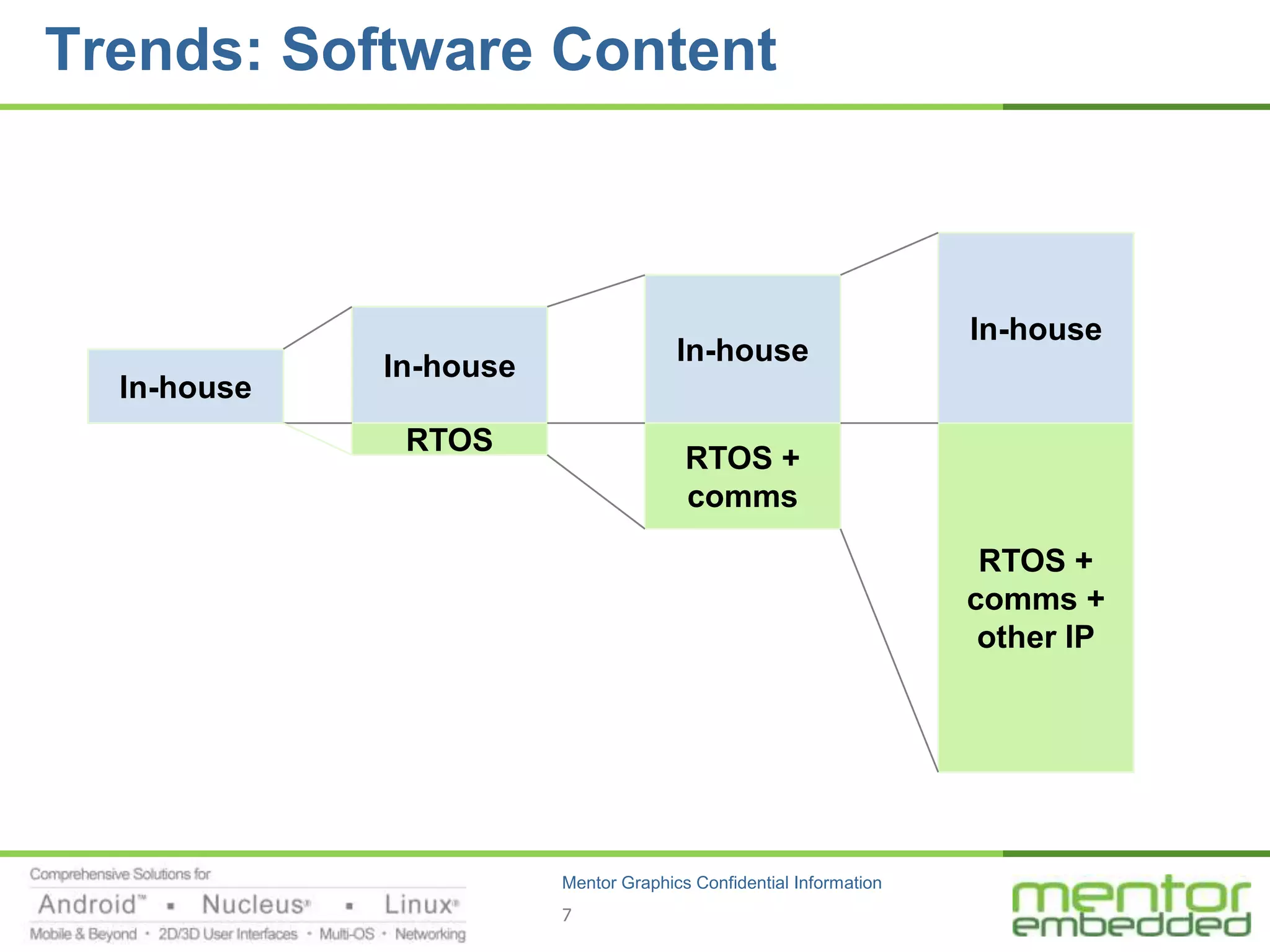
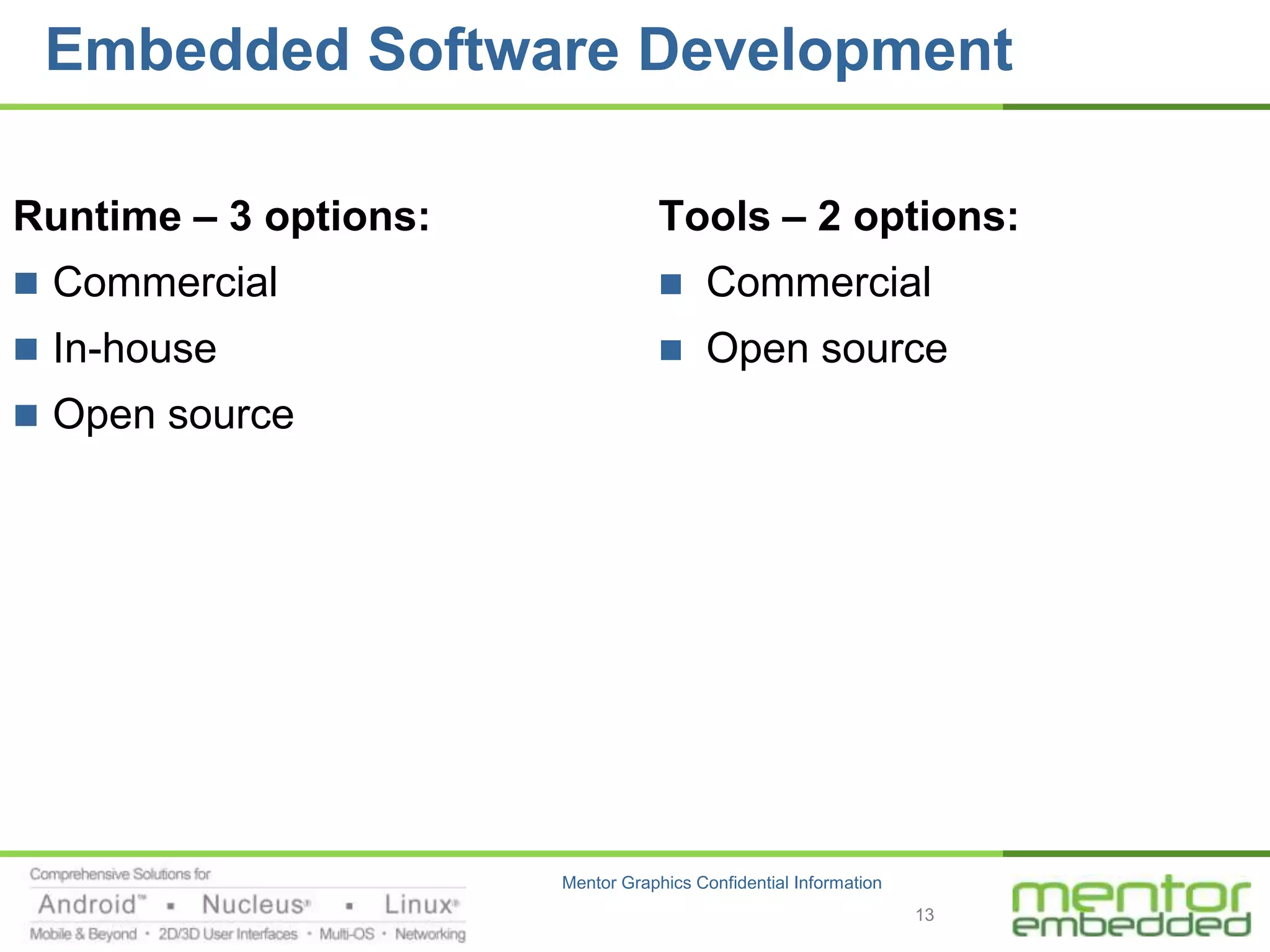
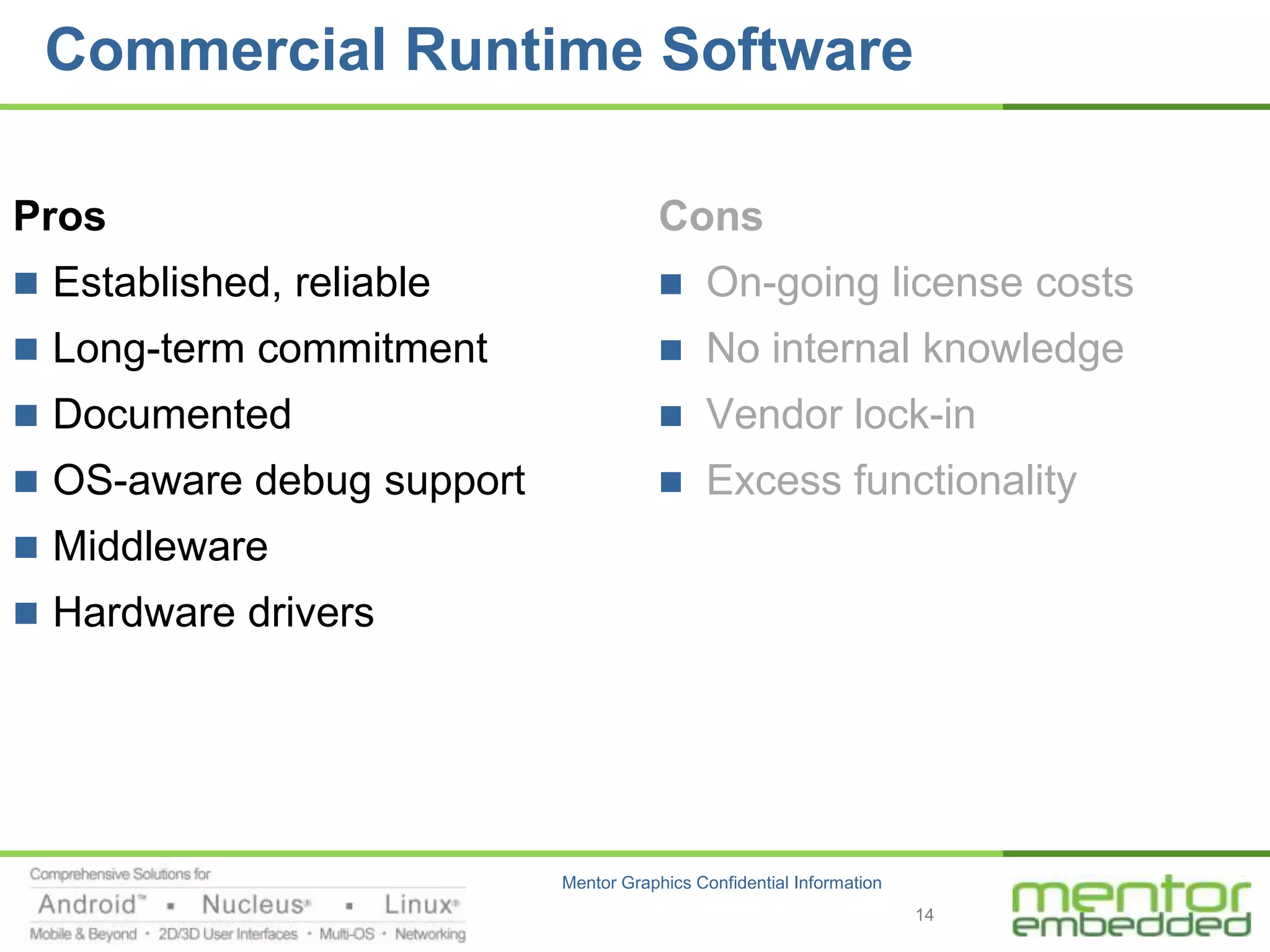
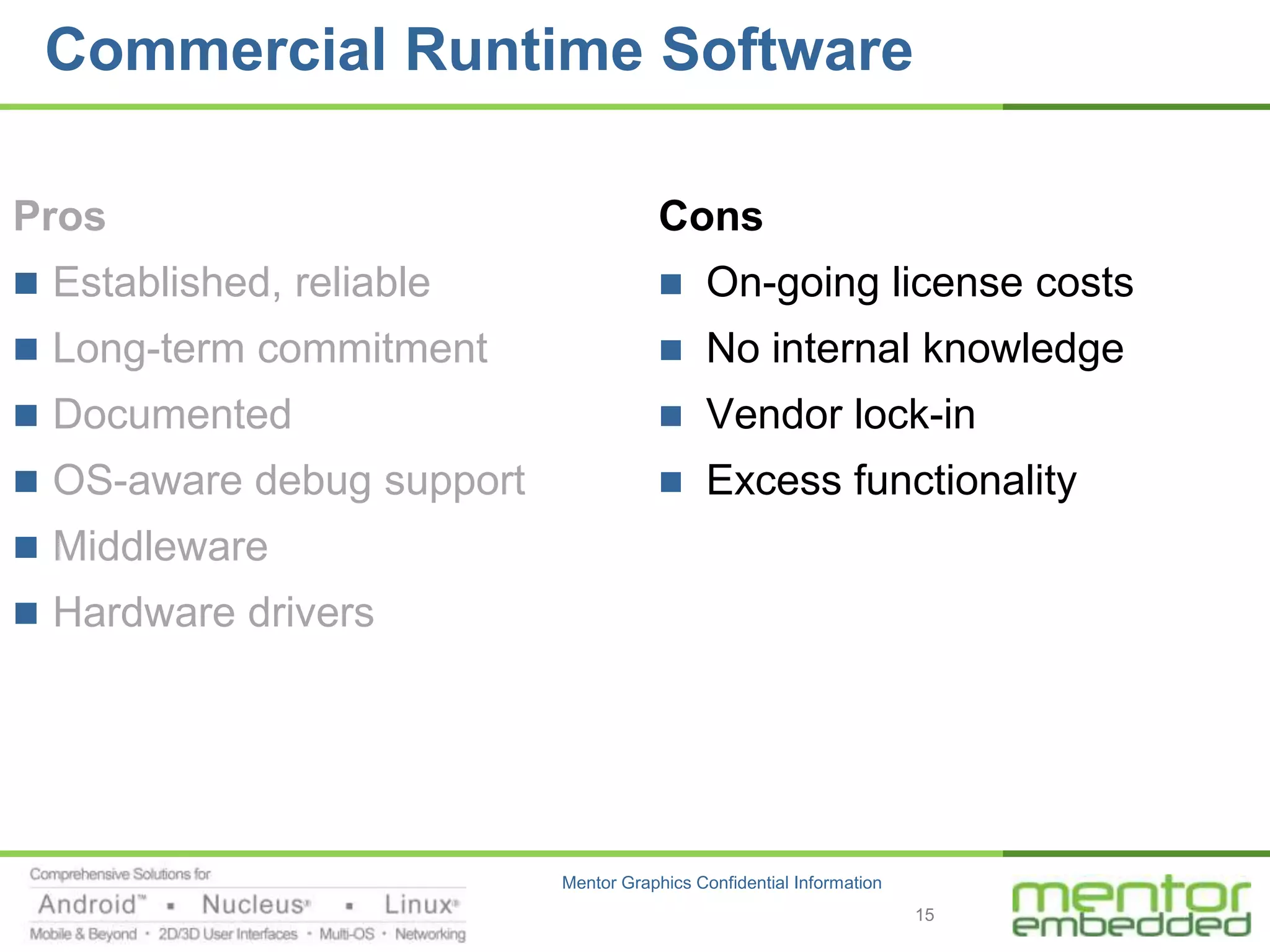
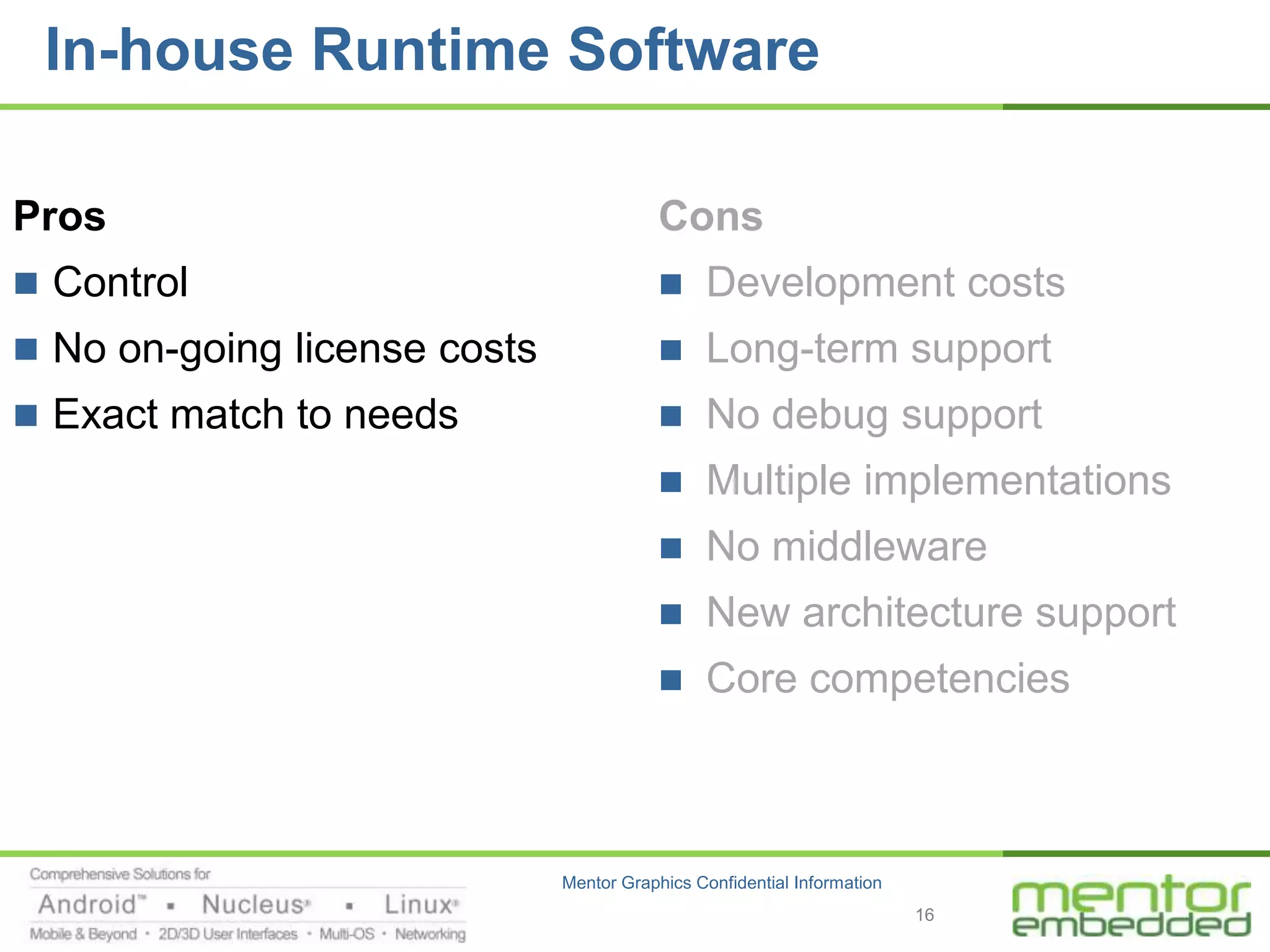
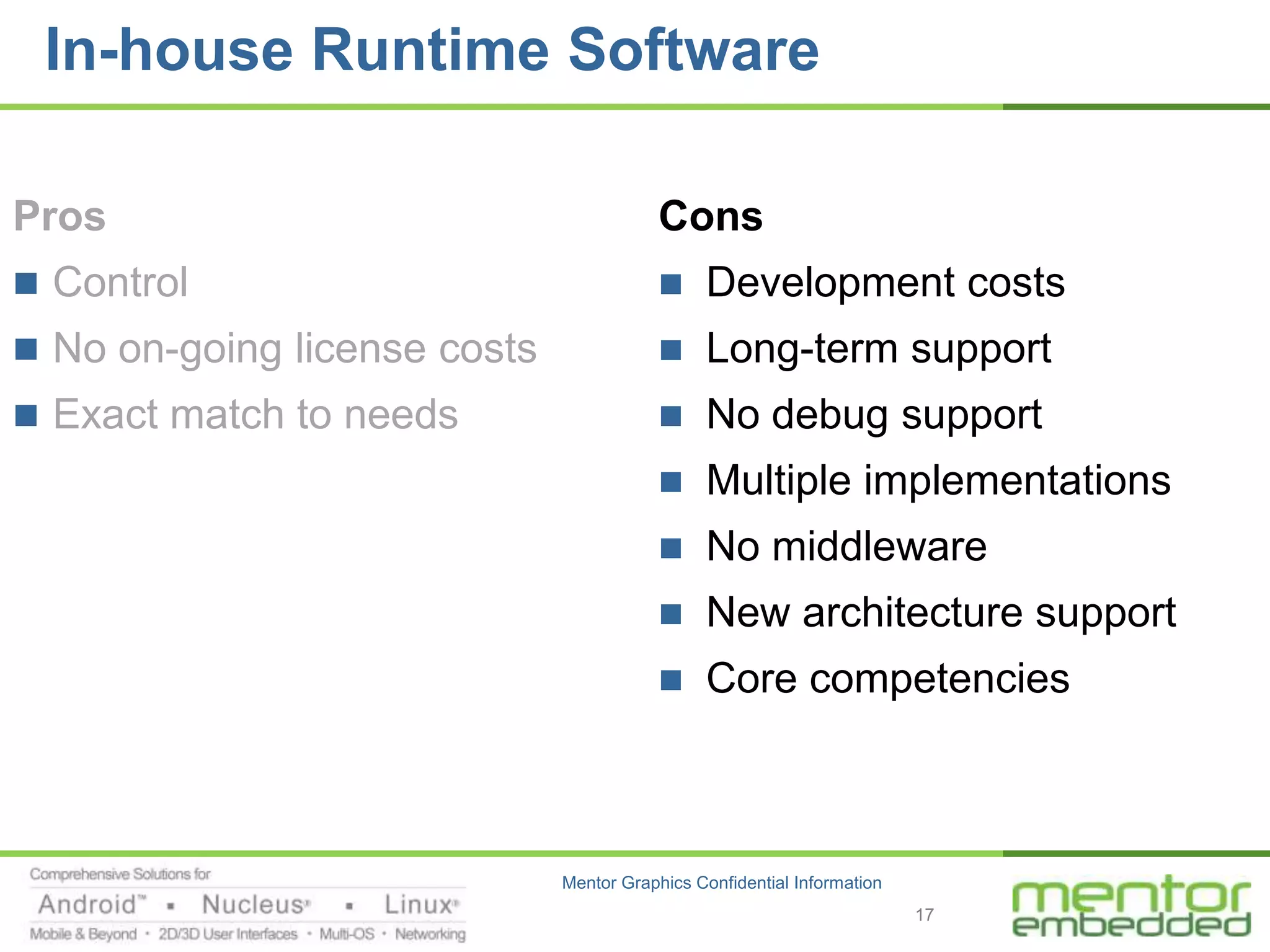
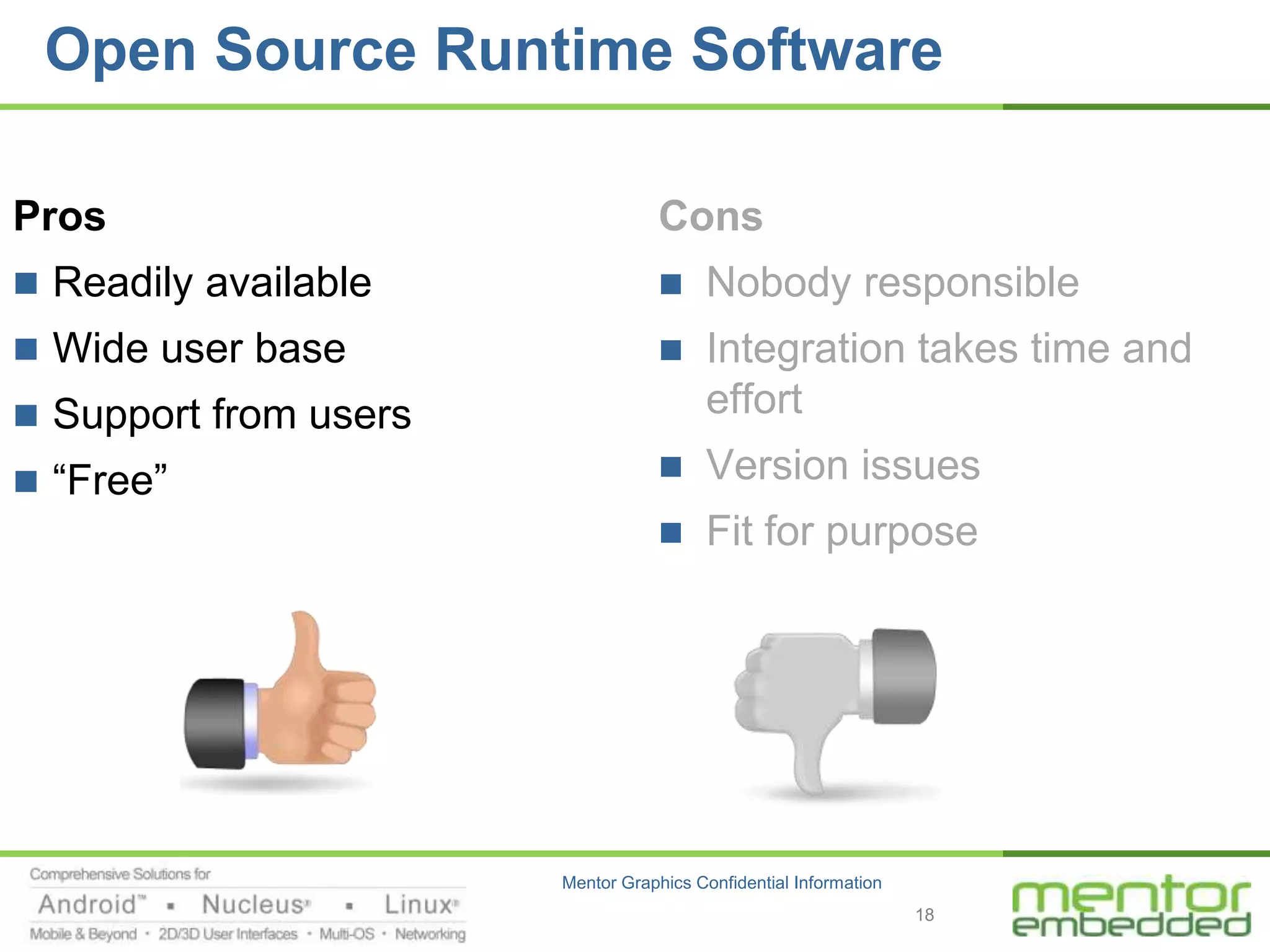
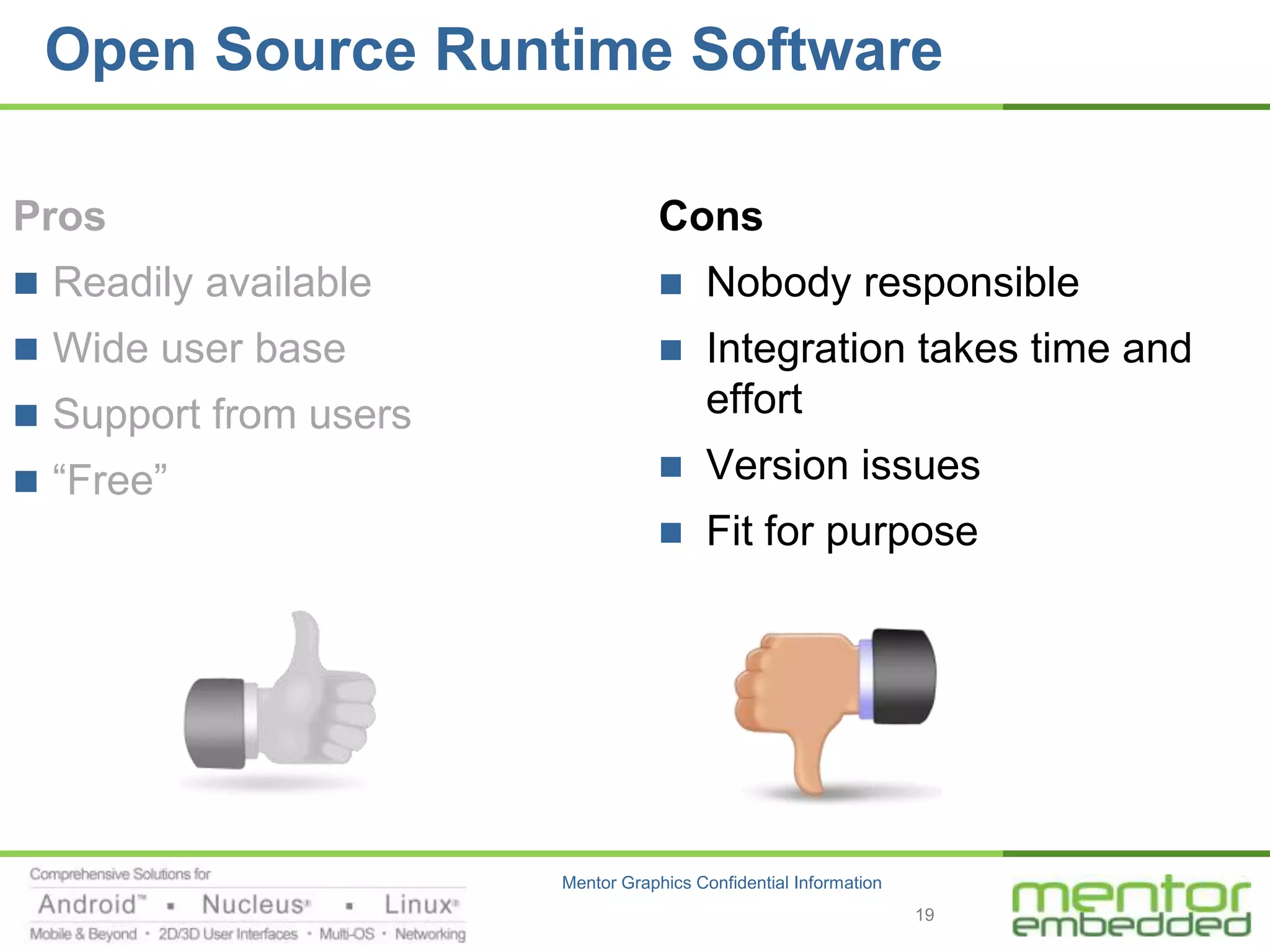
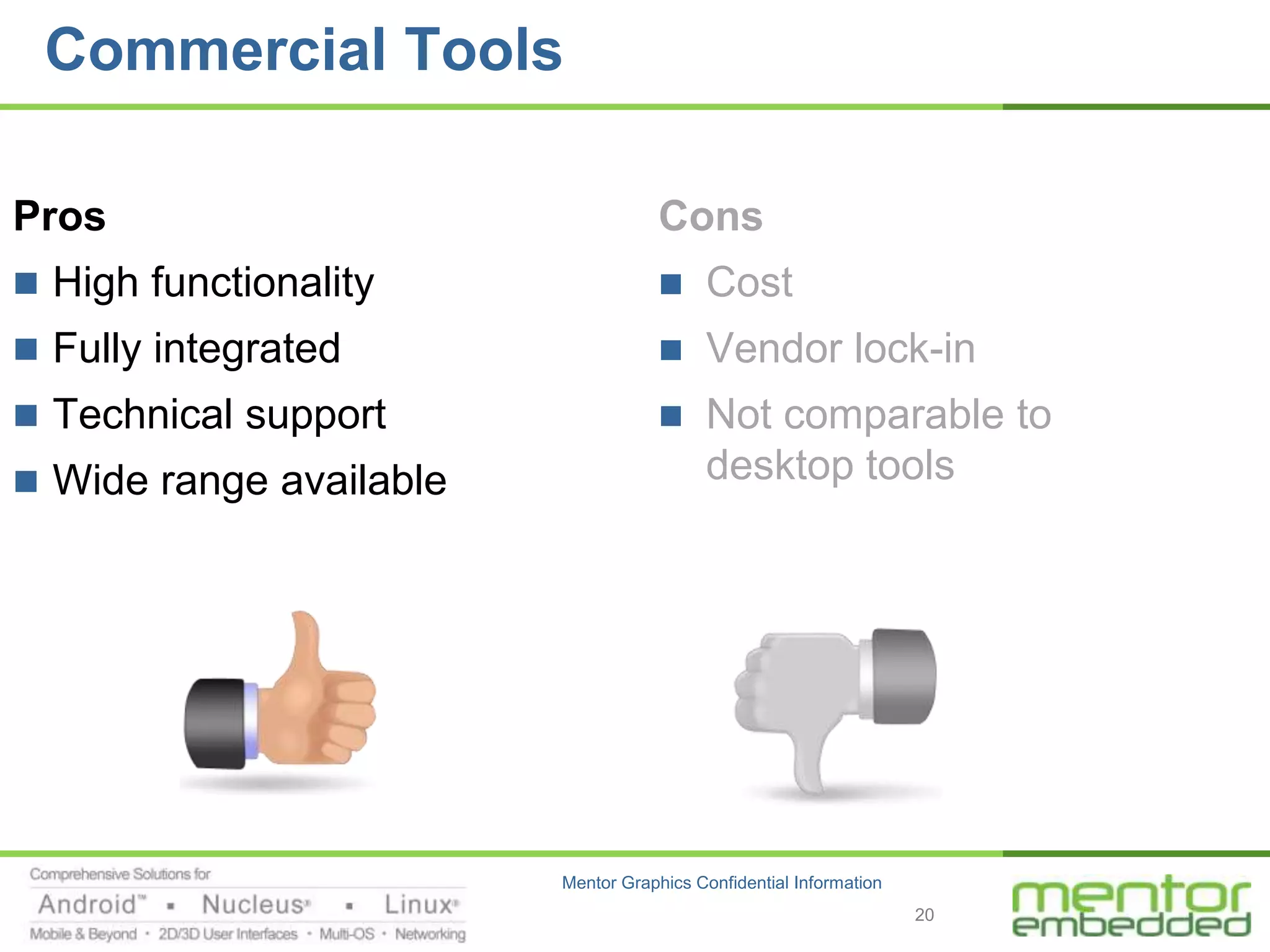
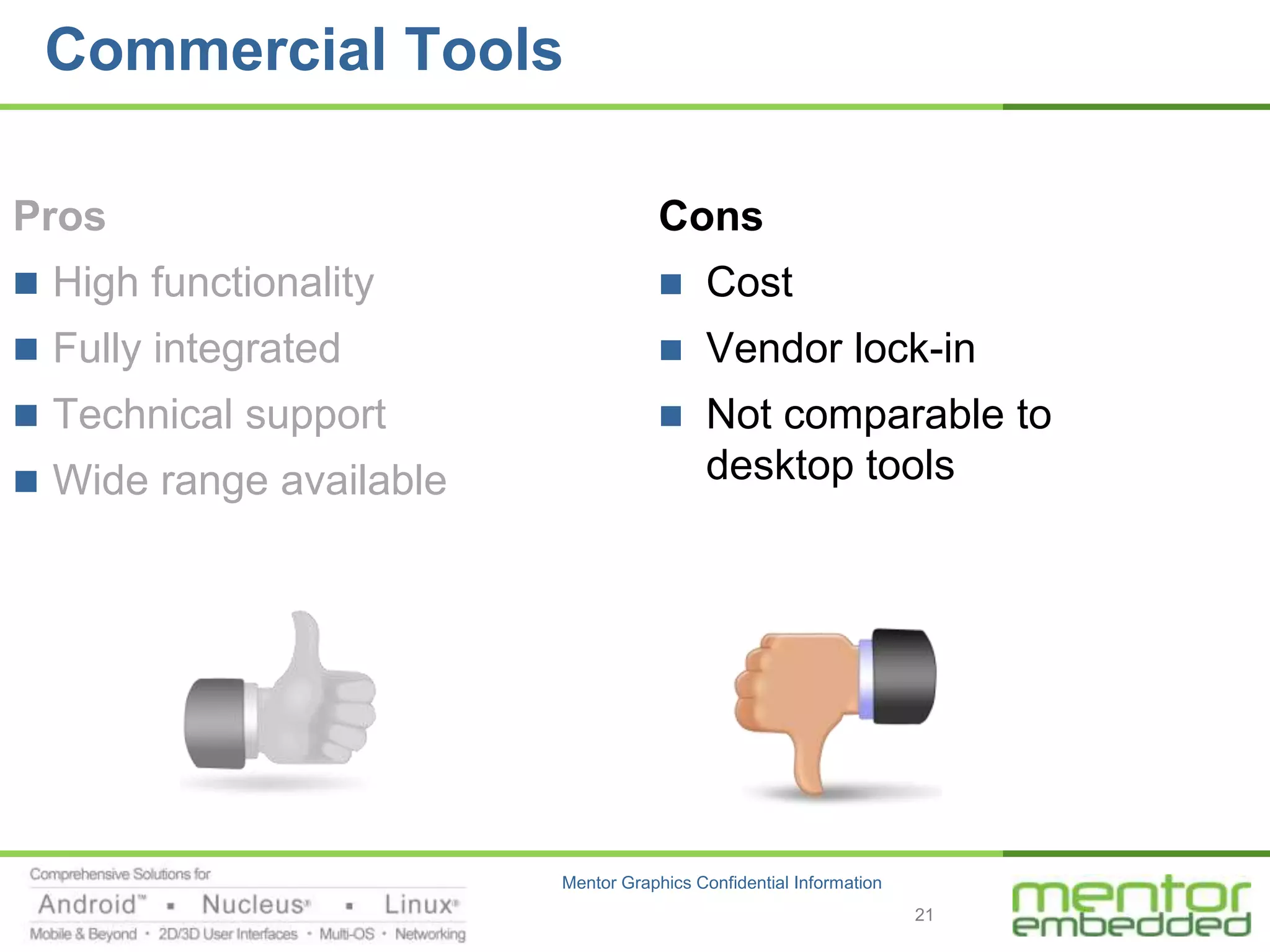
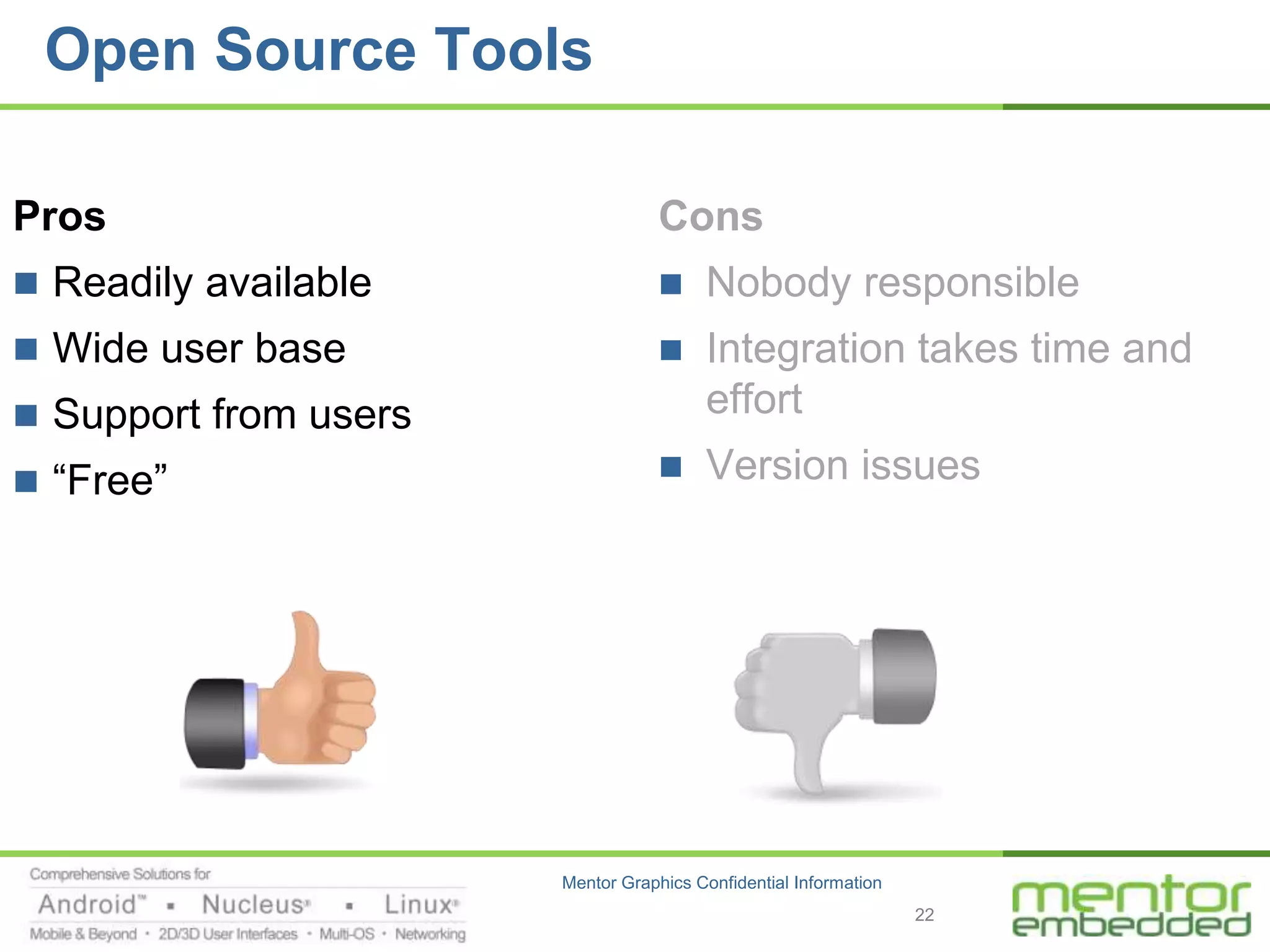
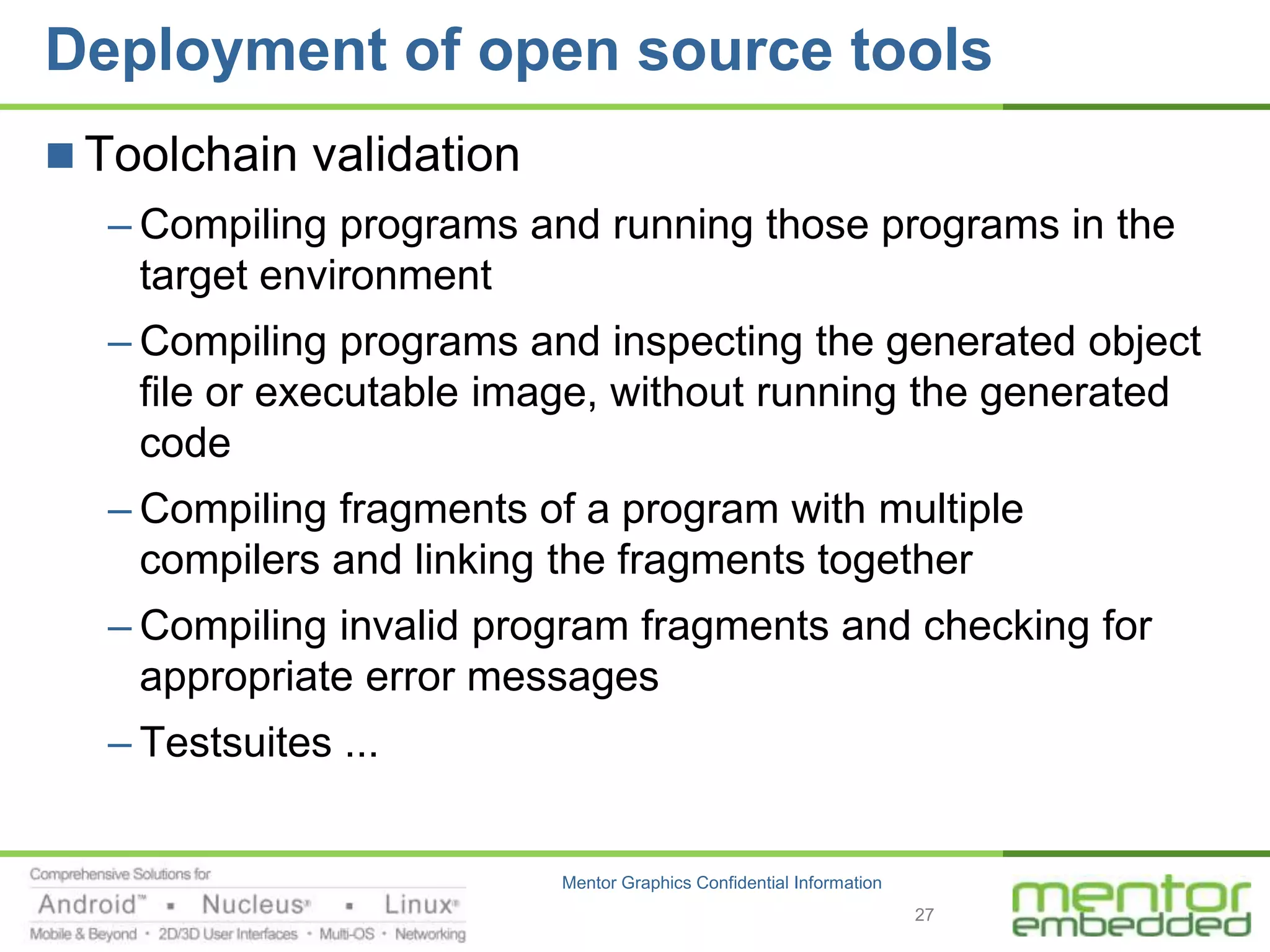
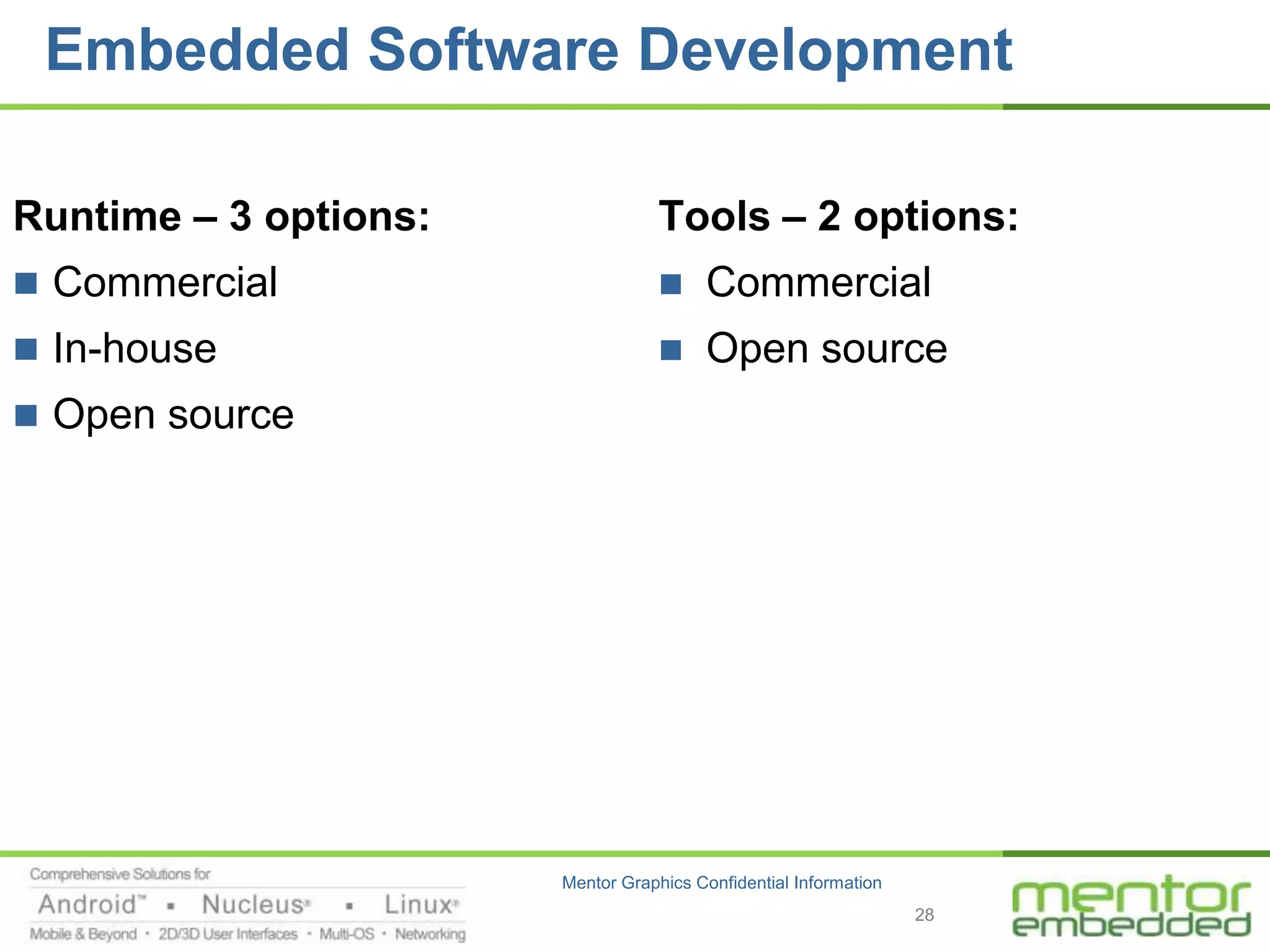
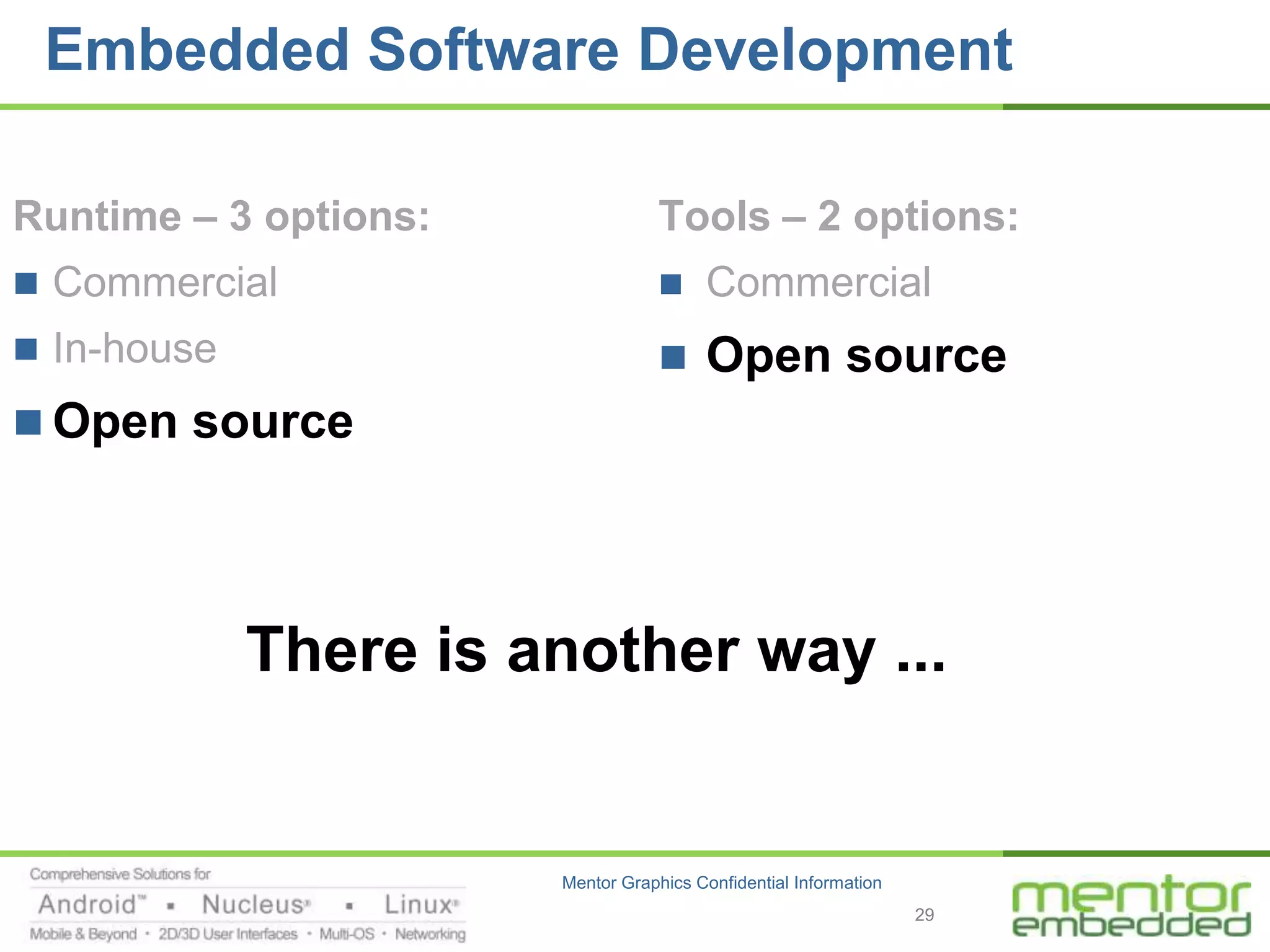
The document discusses options for embedded software development, including commercial runtime software, in-house runtime software, and open source runtime software. It also discusses commercial tools versus open source tools. Commercial runtime software and tools provide benefits like being established, reliable, and having technical support, but have downsides like ongoing costs and vendor lock-in. In-house runtime has benefits like control and customization but has high development costs. Open source has advantages of being freely available but has issues like lack of long-term support and responsibility.






![Embedded Software Development
Recognize that open source does not mean “free”
Do not underestimate the configuration and
deployment challenges [= costs]
Consider using a specialist vendor
– Tools [and OS] packaged and ready to use
– Costs well defined and contained
– Additional support [with open source community there
for you as well]
– Additional value-added components
This if The Third Way
Mentor Graphics Confidential Information
30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/over20yearsofembeddedsoftwaredevelopment-athirdwayemerges-120120095513-phpapp01/75/Over-20-years-of-embedded-software-development-a-third-way-emerges-30-2048.jpg)
