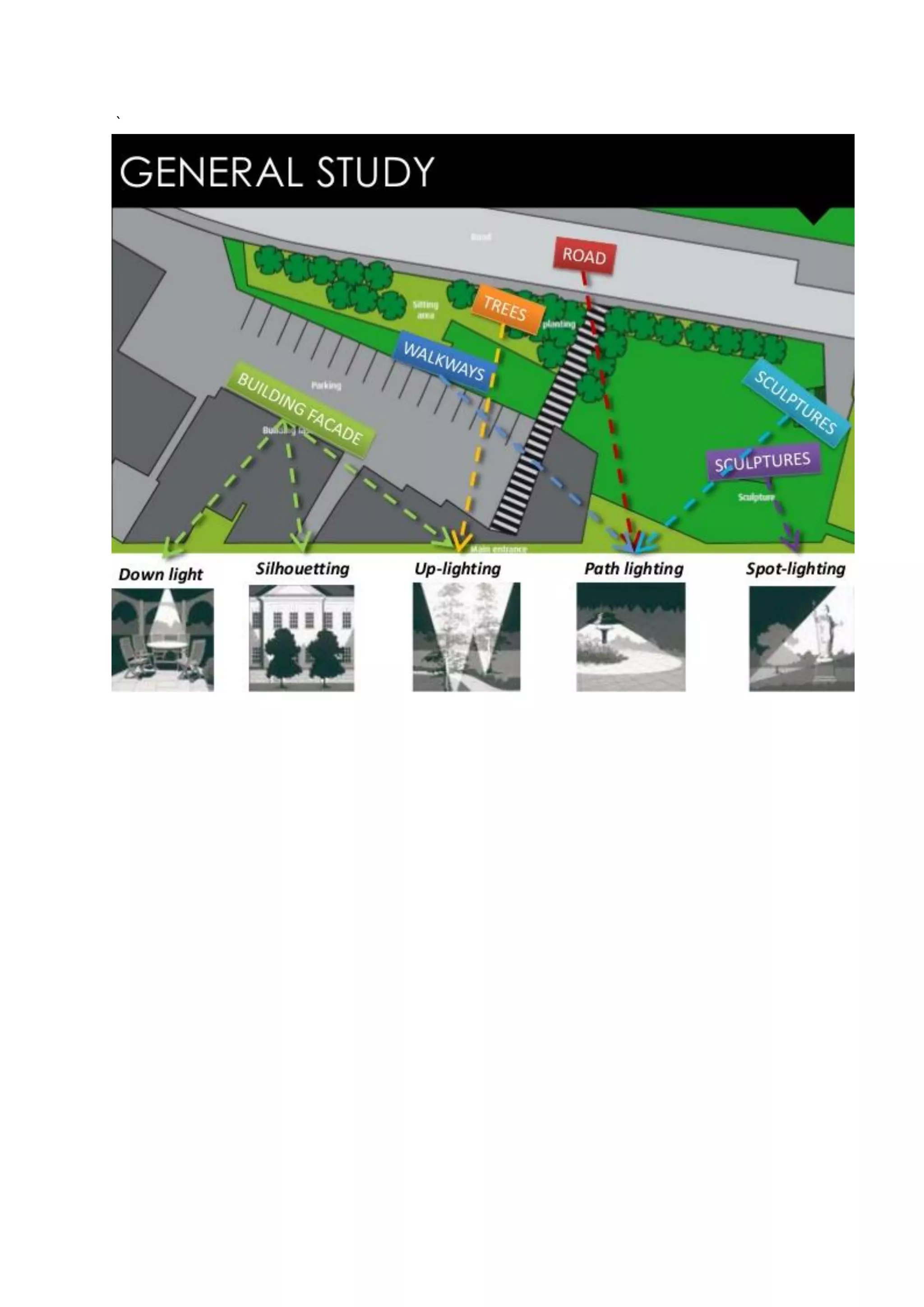
The document provides a comprehensive overview of outdoor lighting, including classifications such as street lighting, park lighting, and techniques for enhancing visibility while minimizing glare. It details various types of outdoor bulbs like halogen, metal halide, high- and low-pressure sodium, and LEDs, focusing on their applications, efficiency, and environmental concerns. Additionally, it discusses specific lighting techniques for safety and aesthetics in public spaces, emphasizing the importance of maintaining appropriate light levels to improve visibility and reduce light pollution.