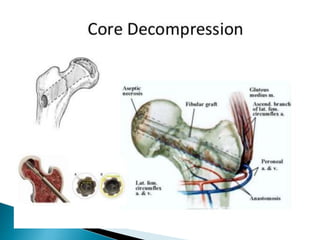
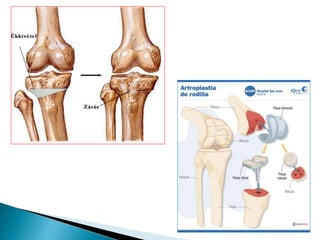
Osteonecrosis is a condition caused by loss of blood supply to the bone, which can lead to bone tissue death and joint collapse. It is often caused by long term steroid use or heavy alcohol use. Symptoms may include joint pain that worsens with weight bearing. Diagnosis involves x-rays, MRI, or biopsy. Treatment options range from medications and reduced activity to core decompression surgery or joint replacement depending on severity. Preventing osteonecrosis involves limiting steroid use, alcohol, and smoking.