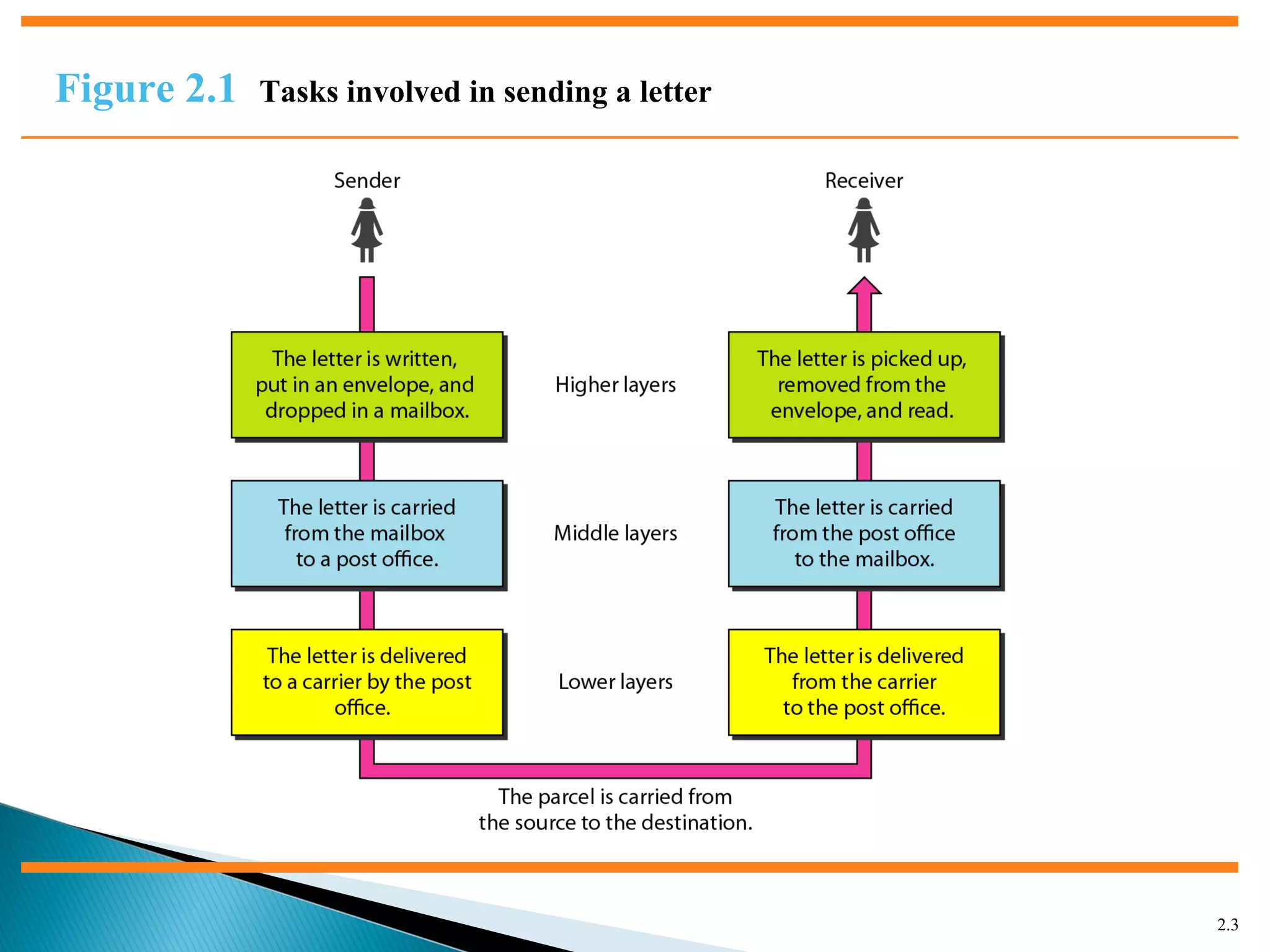
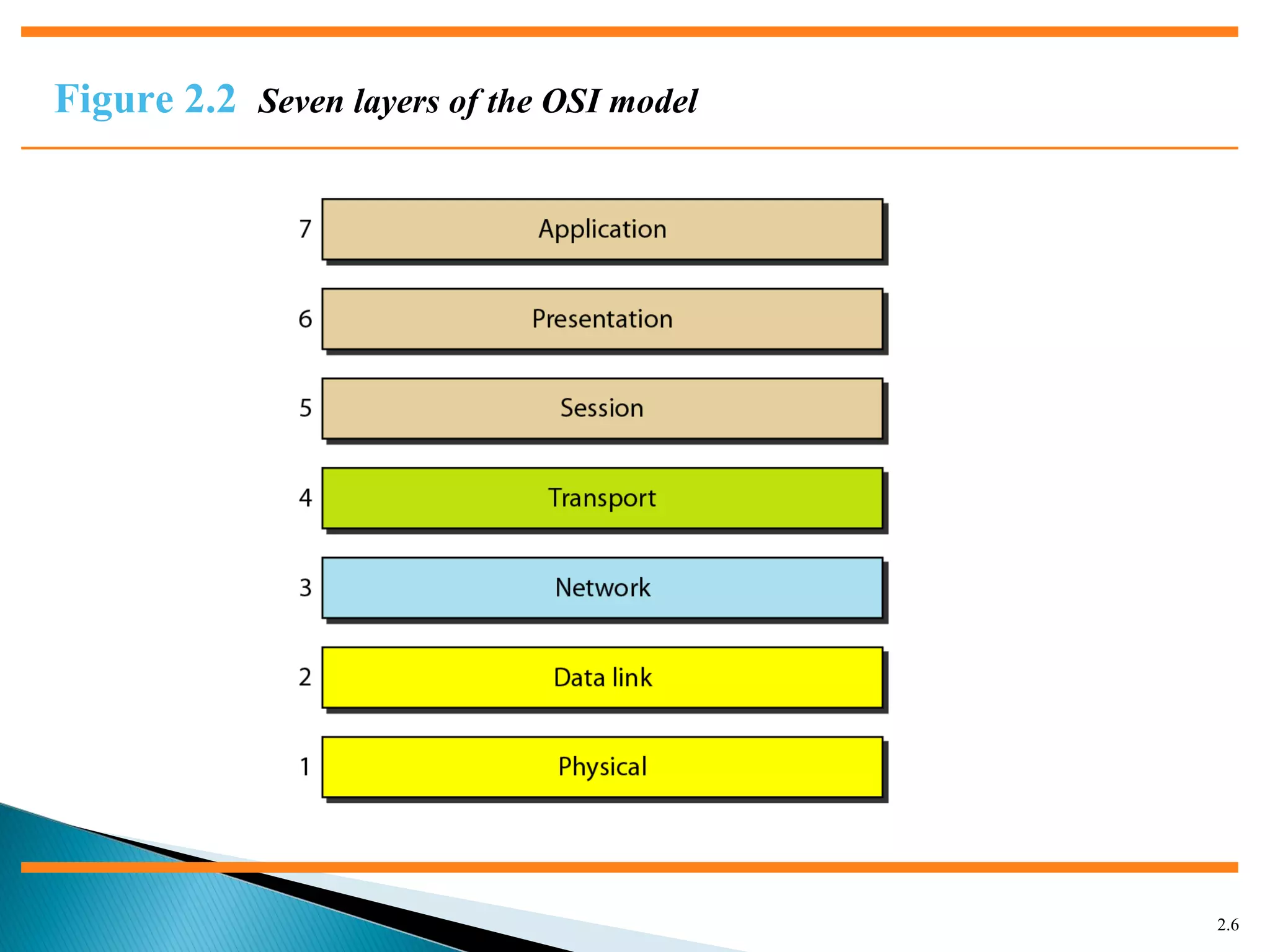
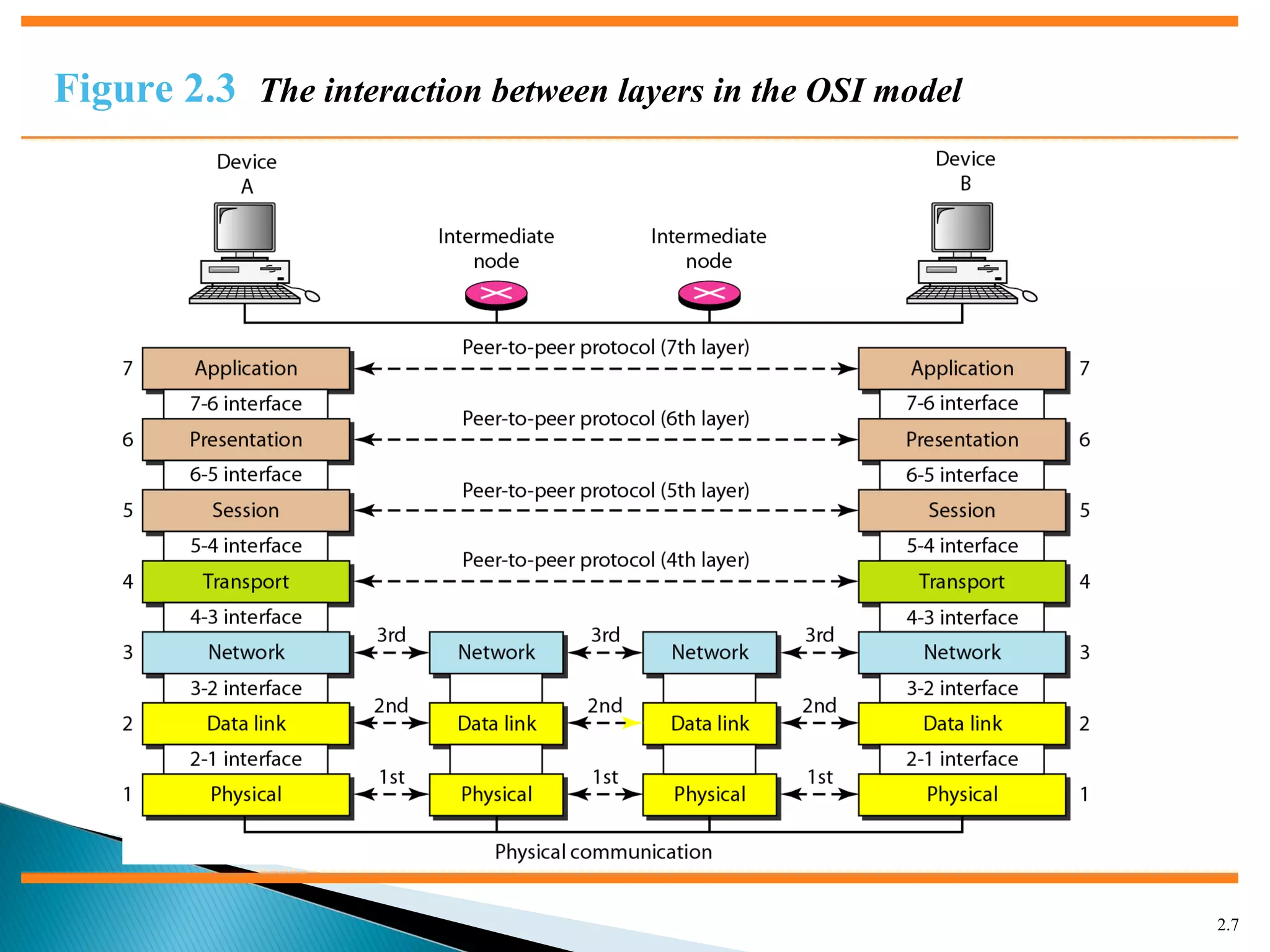
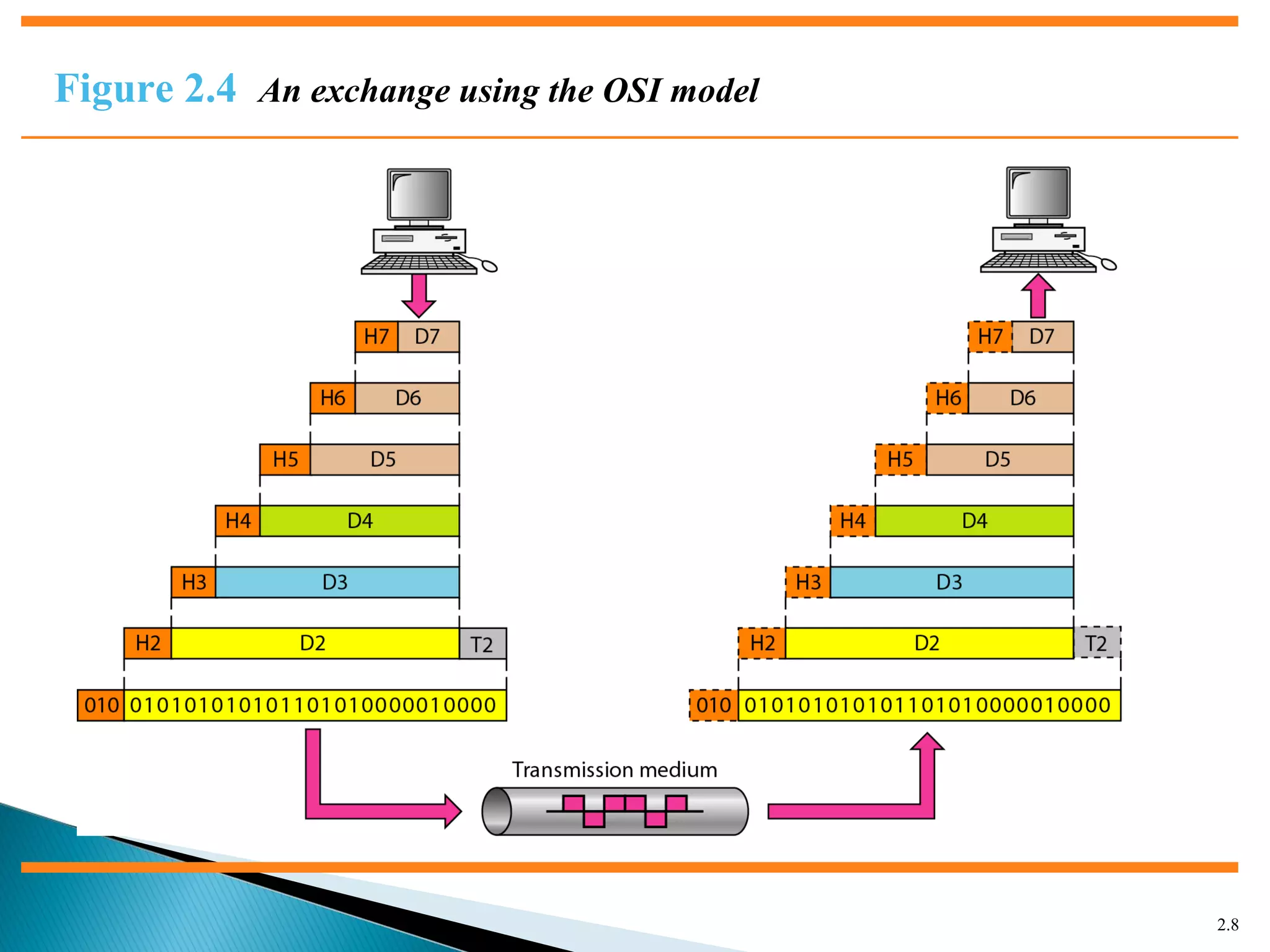
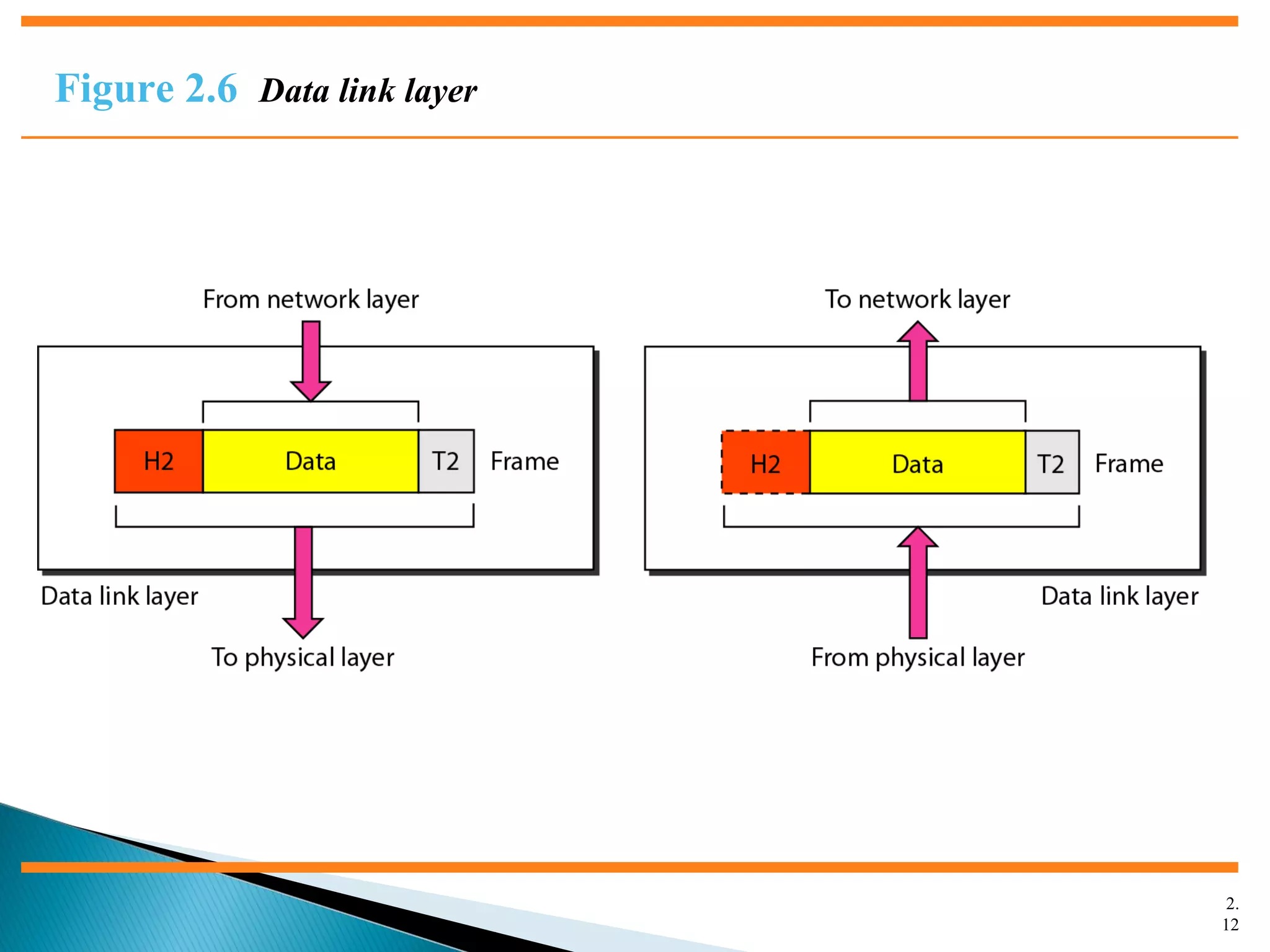
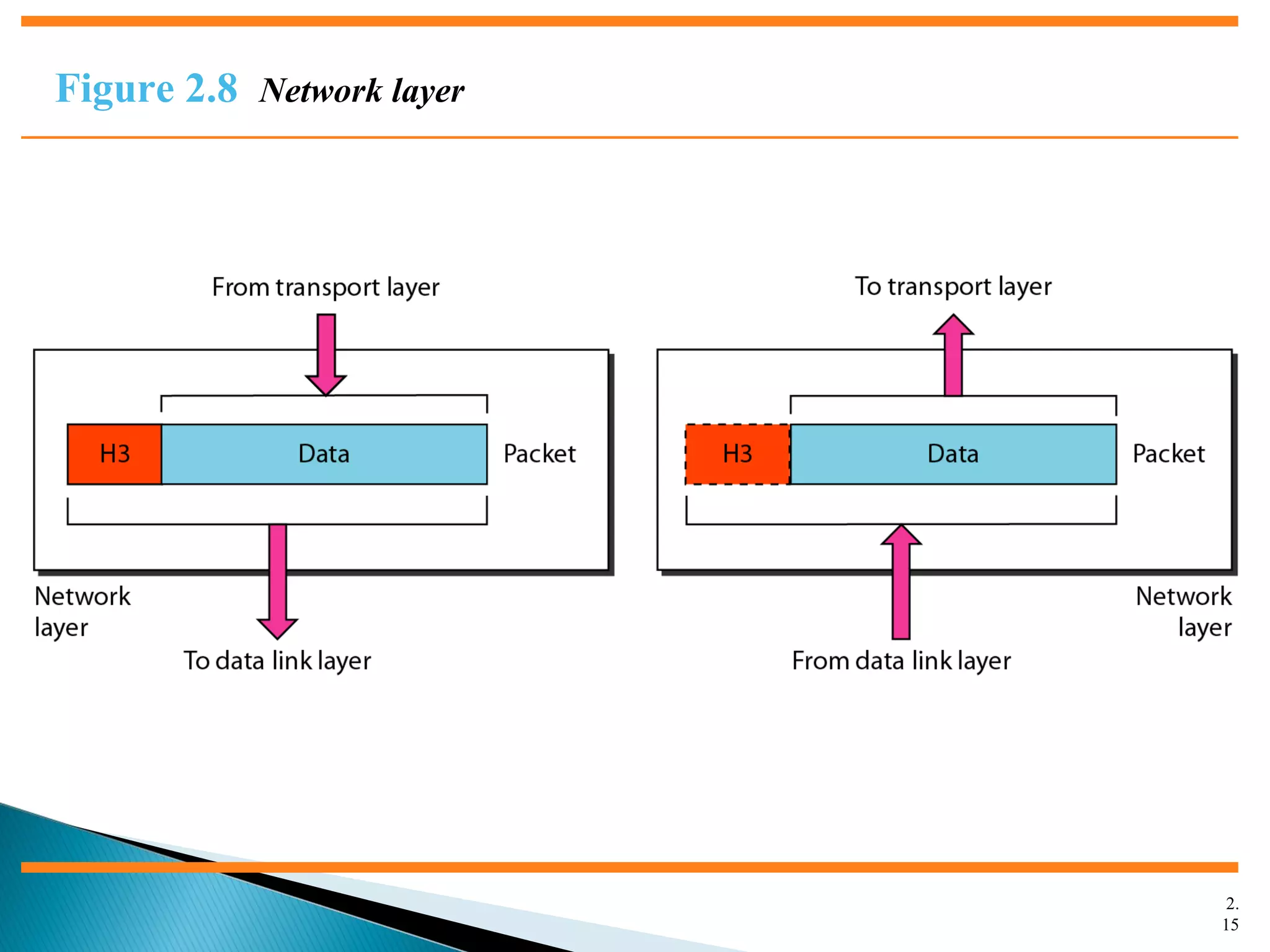
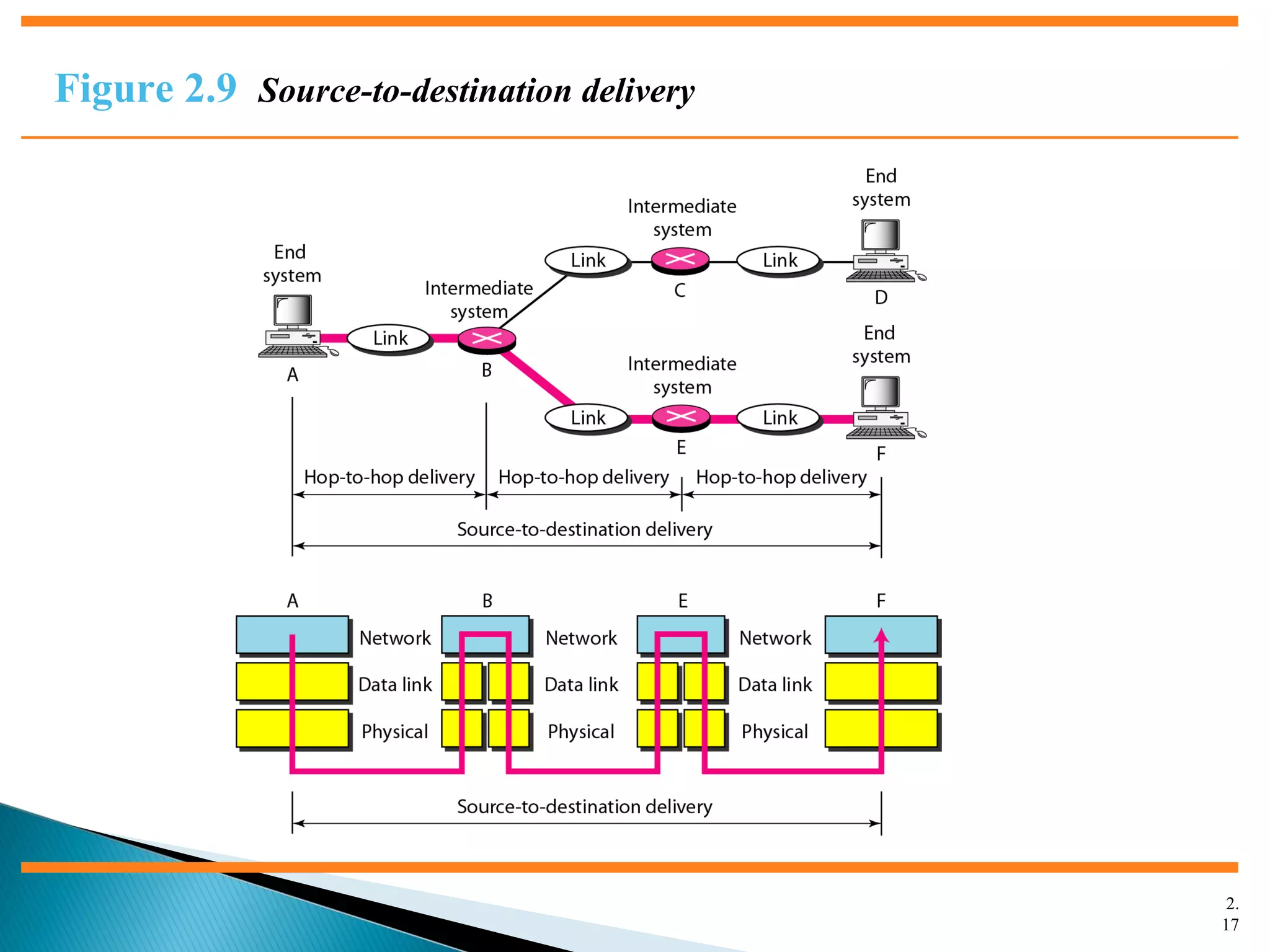
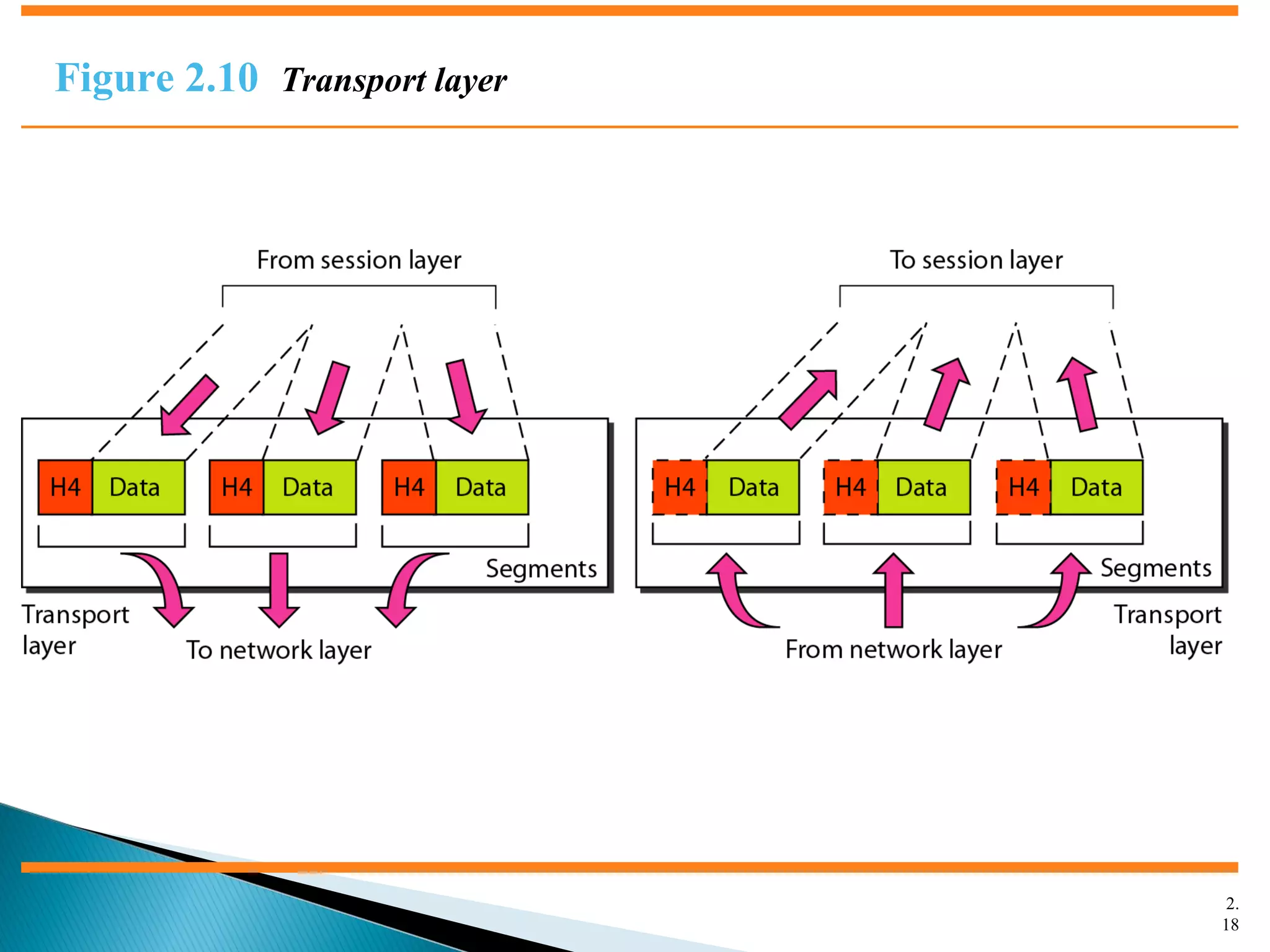
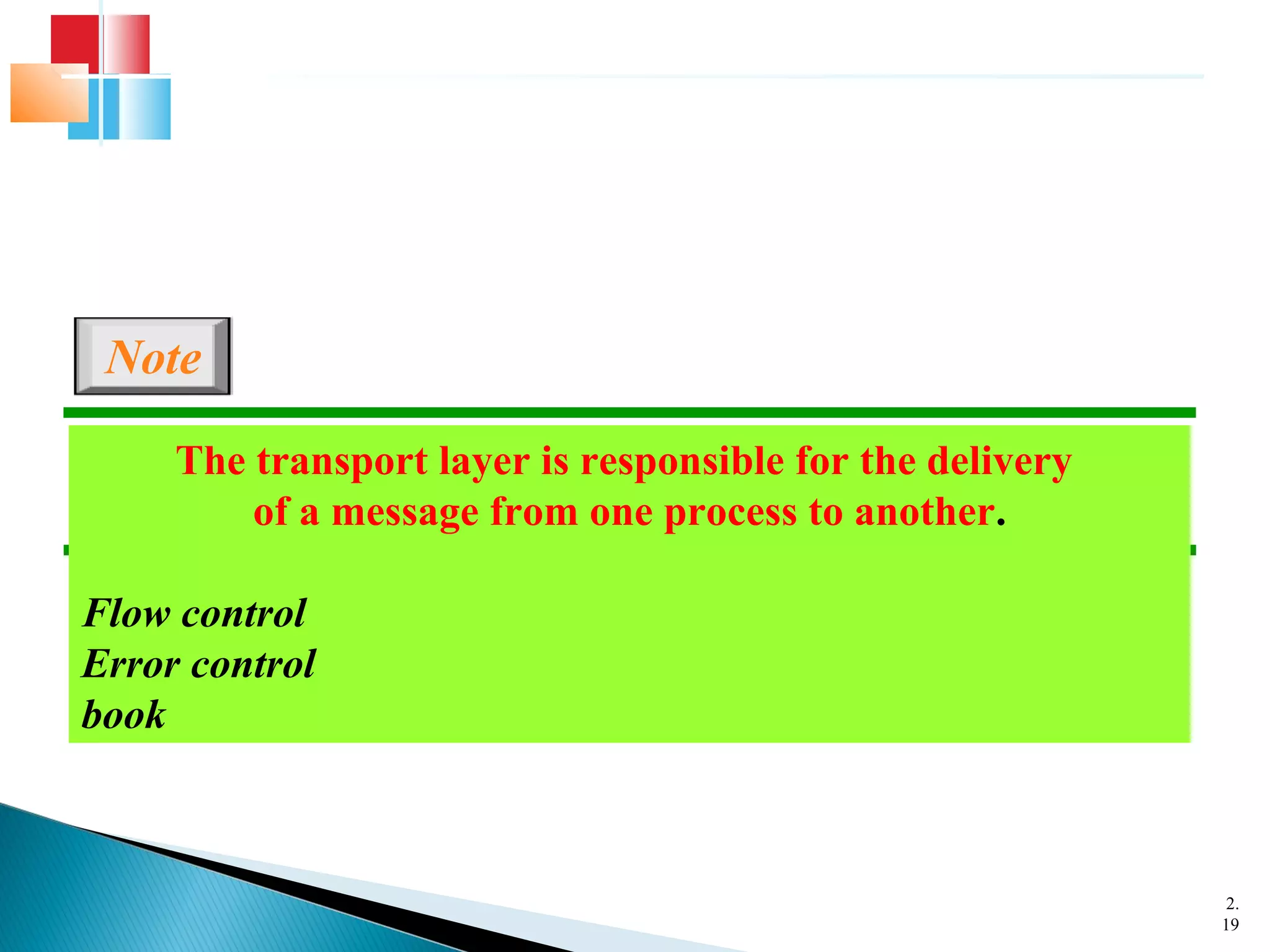
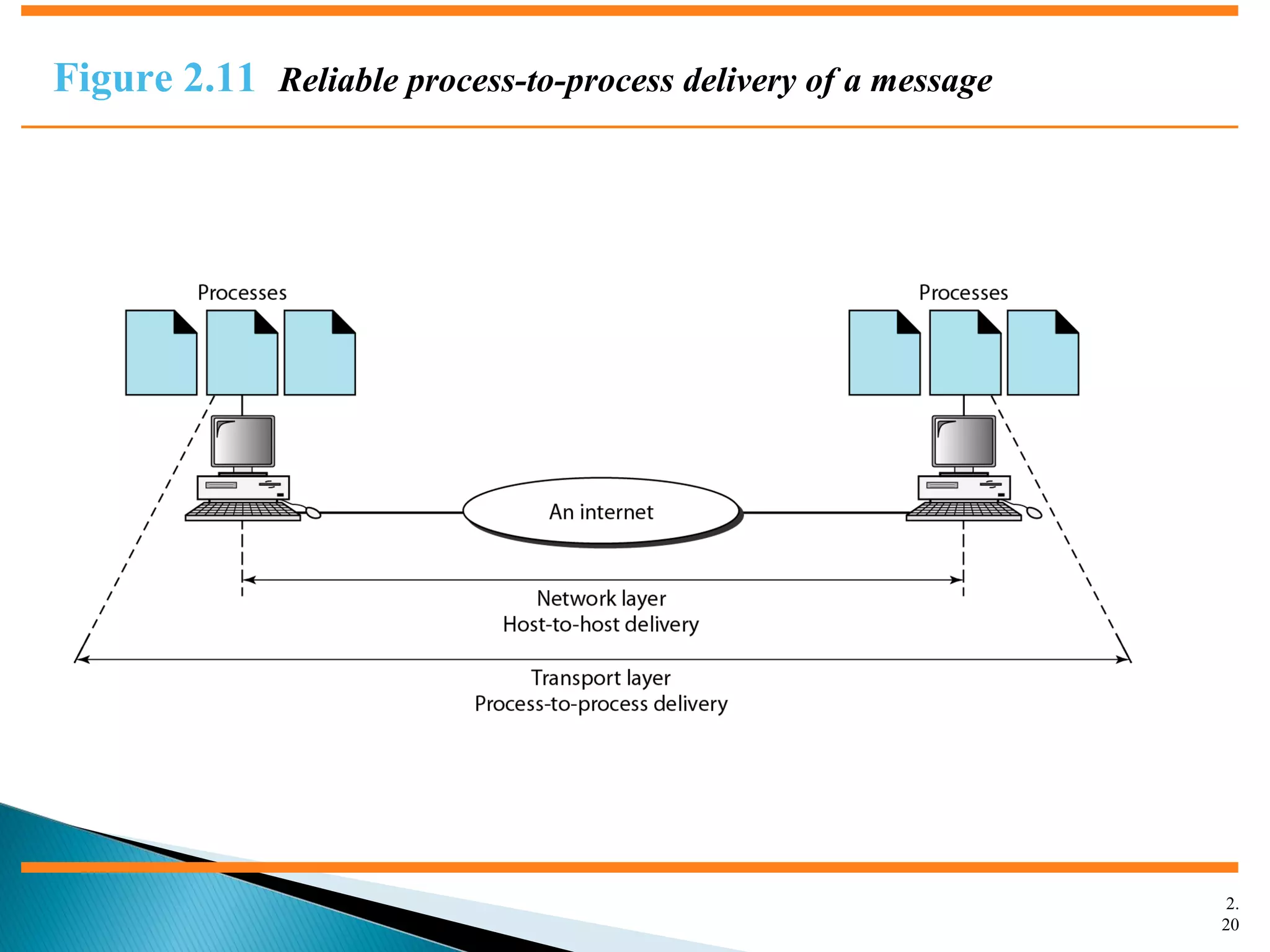
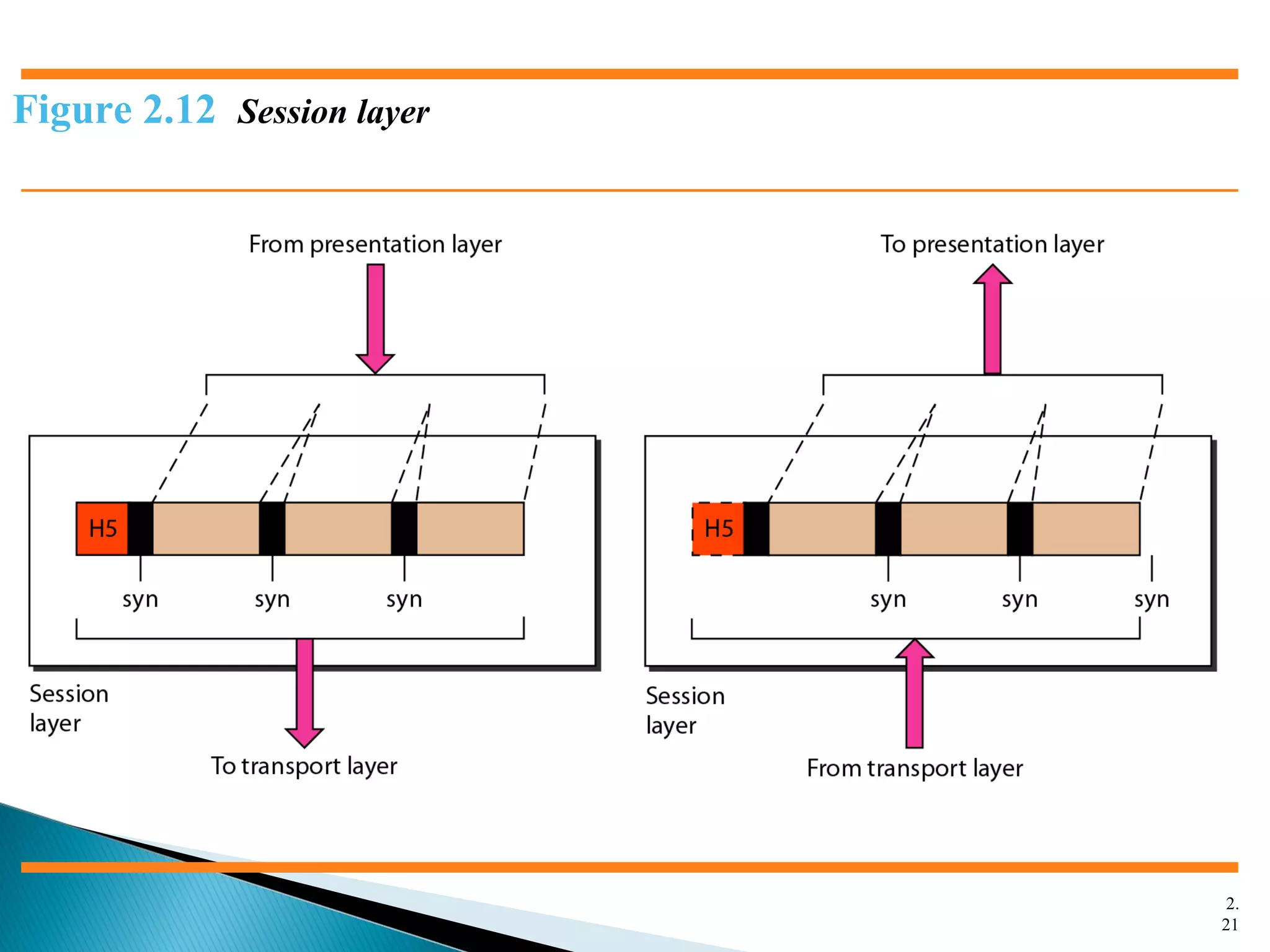
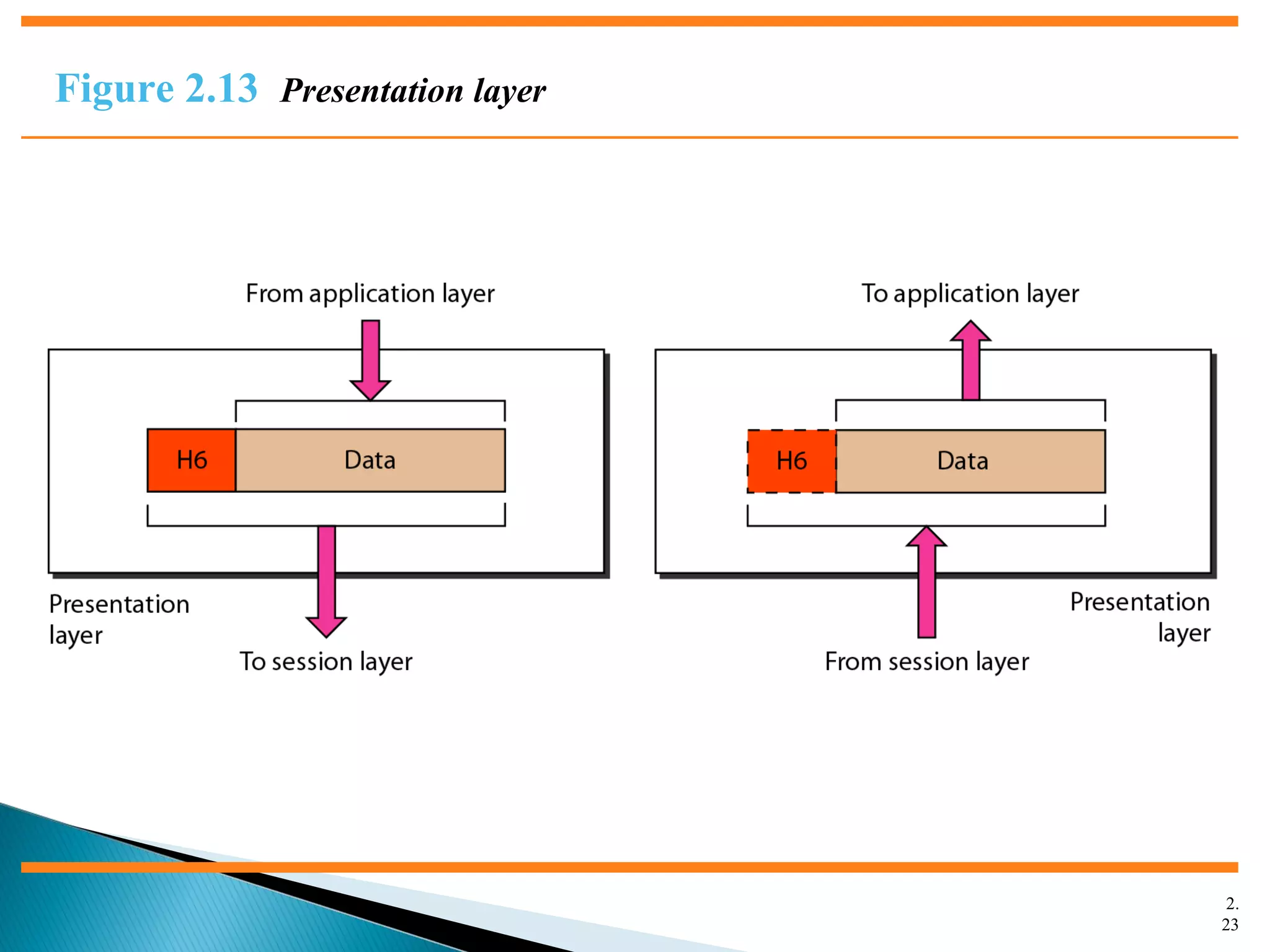
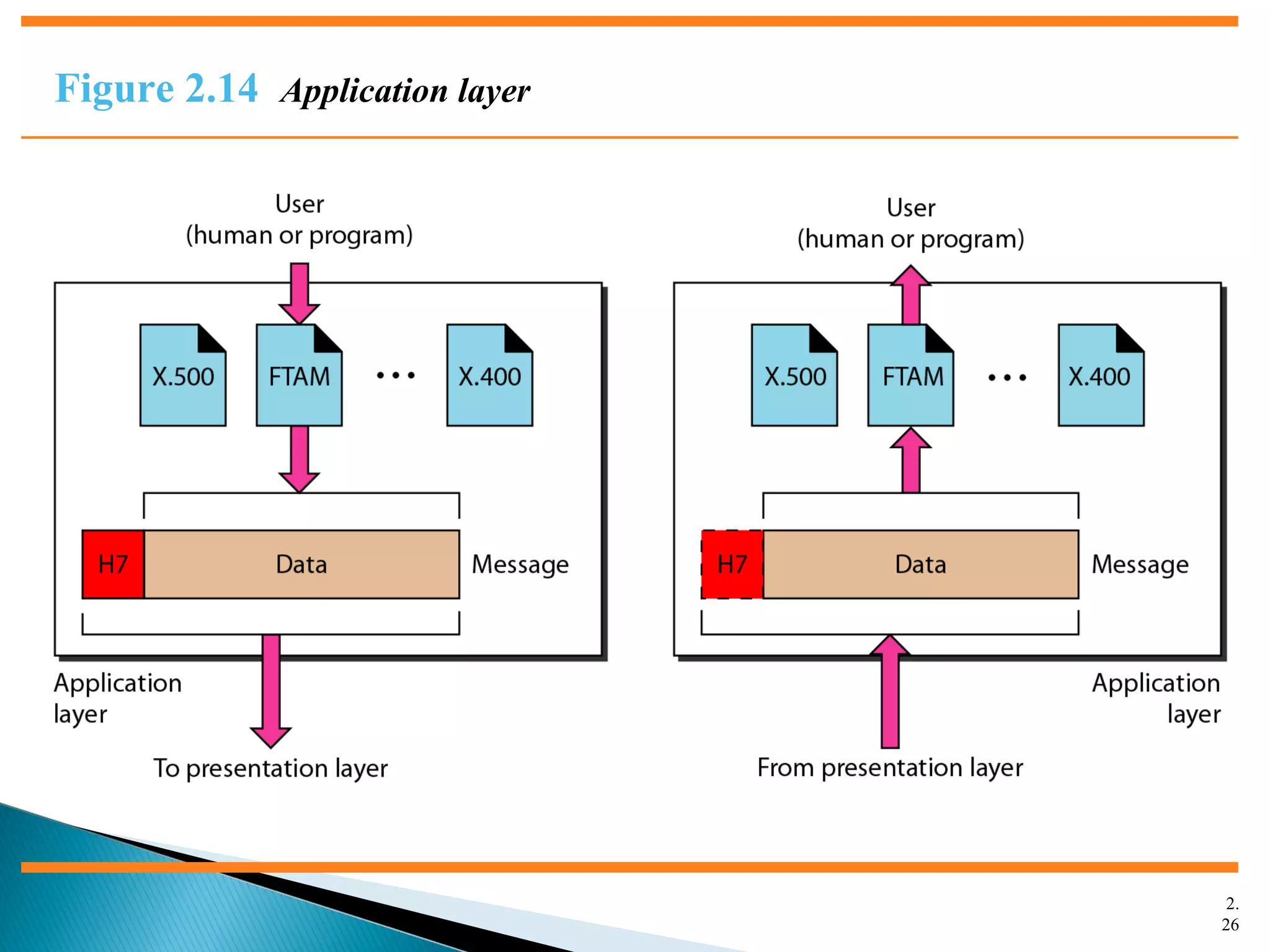
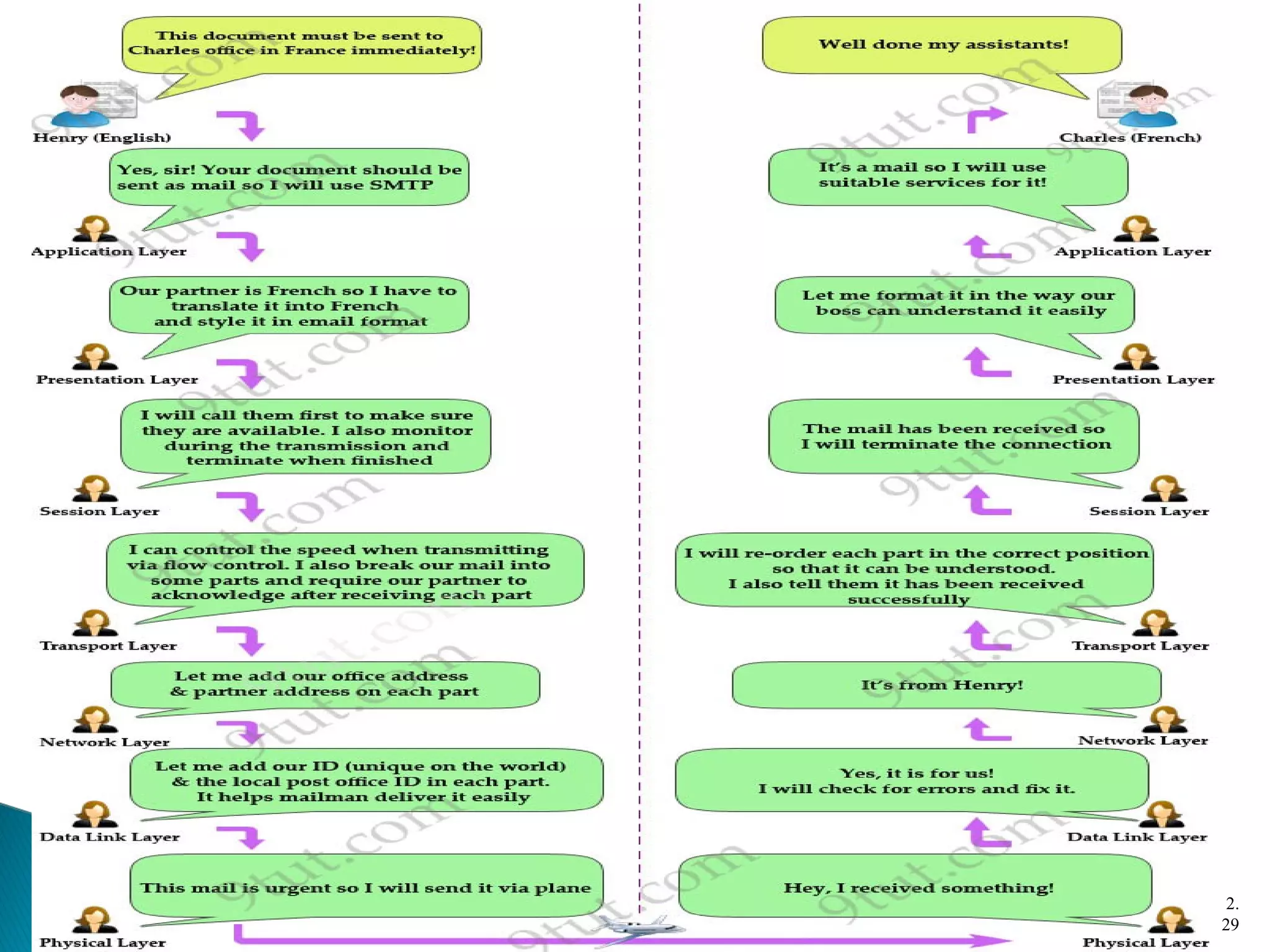
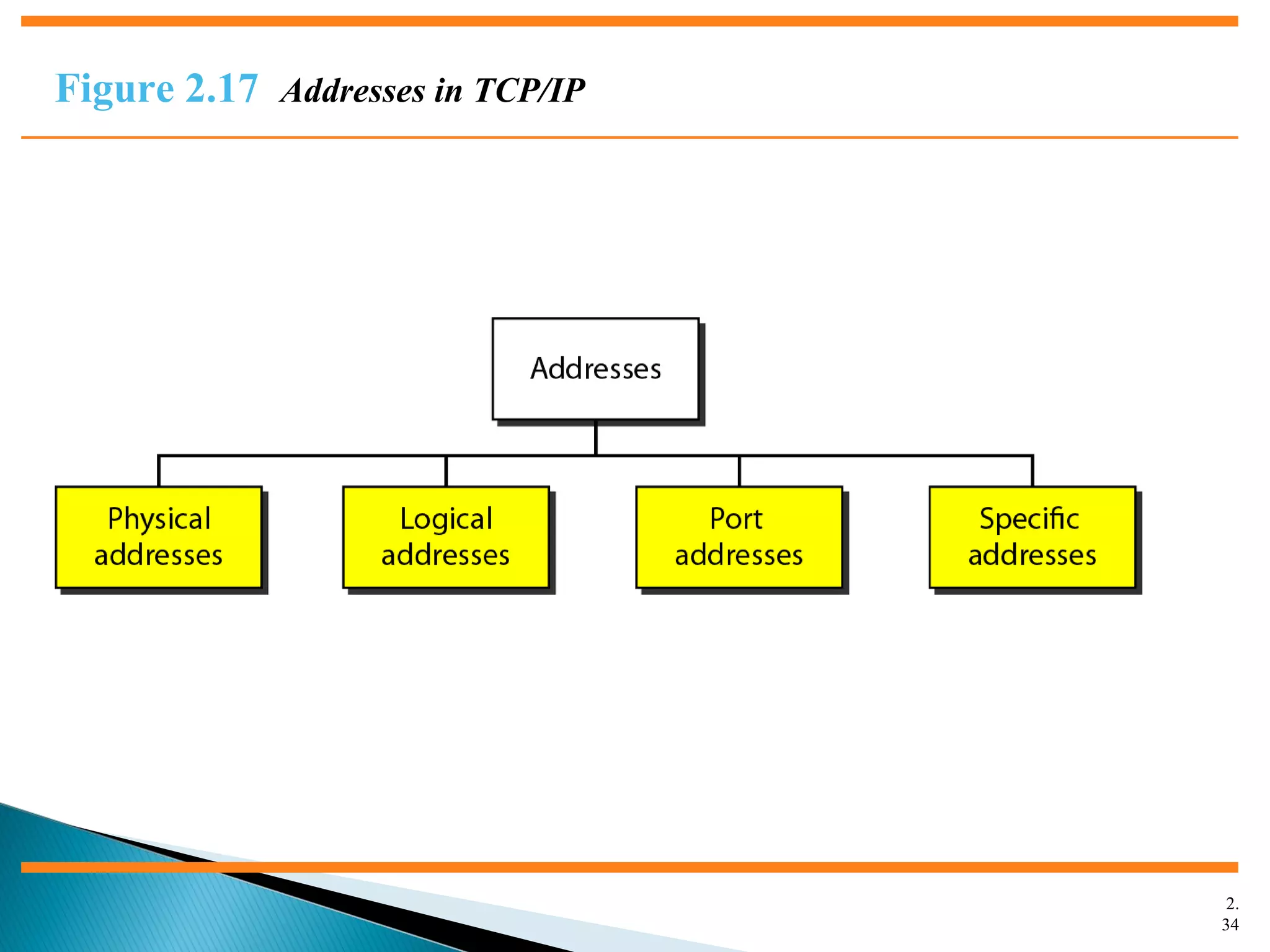
The document discusses network models and the OSI model. It describes the seven layers of the OSI model which are physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation, and application. Each layer has a specific function like the physical layer is responsible for bit transmission between nodes, the data link layer handles frame transmission between nodes, and the transport layer provides reliable transmission of messages between processes. The document also discusses the TCP/IP protocol suite and how it maps to the OSI layers. It describes the different address types used in TCP/IP like physical, logical, port, and specific addresses.