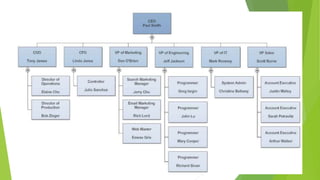
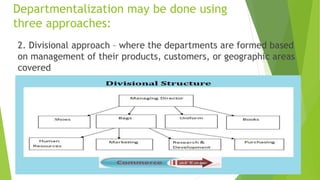
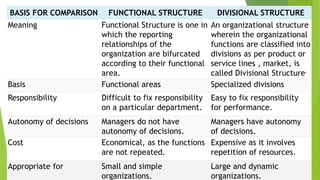
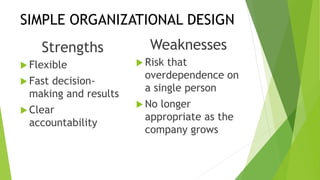
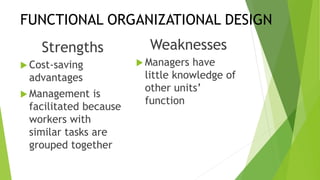
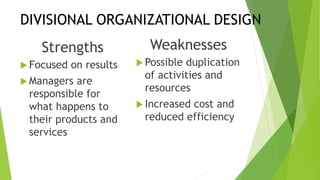
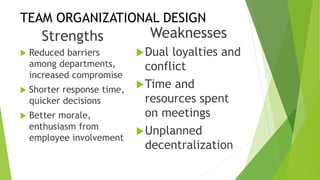
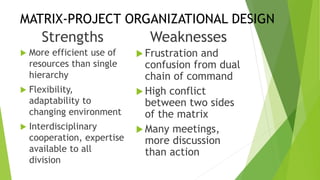
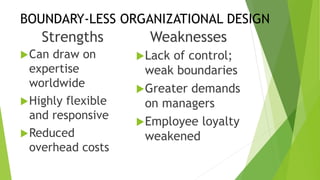
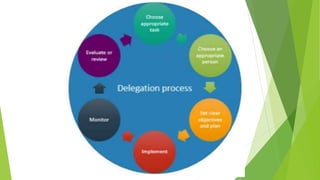
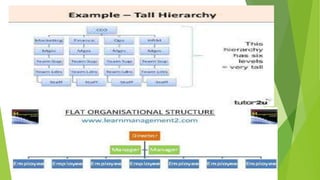
This document discusses key concepts related to organizing and organization structures. It begins by defining organizing as developing an organizational structure and allocating resources to achieve objectives. Common organization structures include functional, divisional, and matrix structures. The document then examines theories of organization design such as simple, functional, and divisional structures. Modern theories include team design, matrix design, and boundaryless design. Other topics covered include delegation, centralization vs decentralization, and the roles of formal and informal organizations.