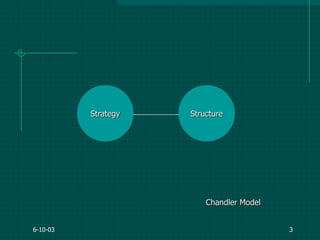
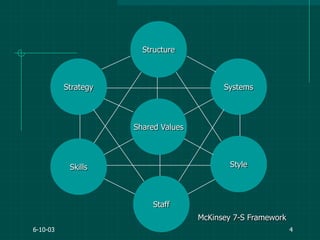
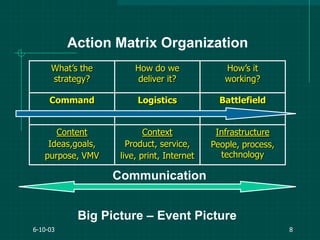
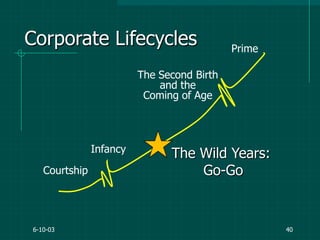
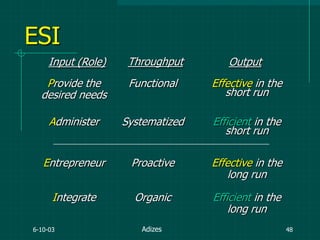
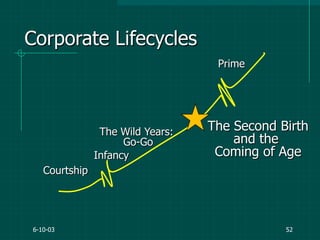
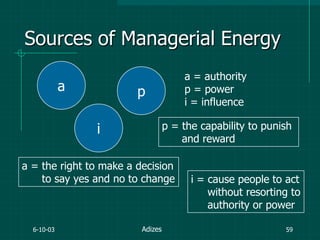
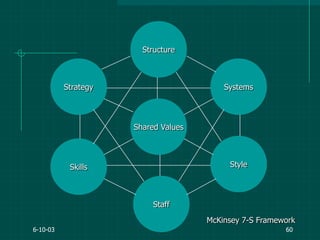
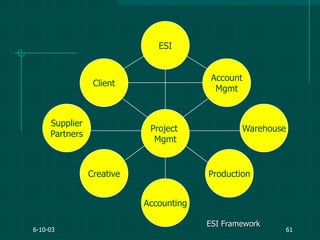
The document covers various aspects of event management and organizational development, outlining key principles and lessons from noted leadership figures like Colin Powell. It emphasizes the importance of effective infrastructure involving people, processes, and technology in achieving successful outcomes. Additionally, it discusses the corporate lifecycle, providing insights into the challenges organizations face during different phases and the significance of leadership in navigating these challenges.