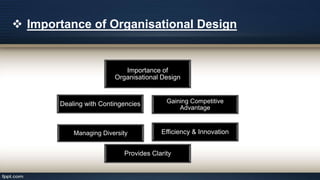
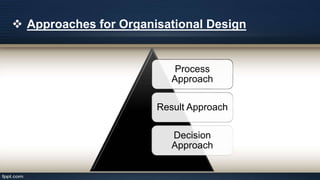
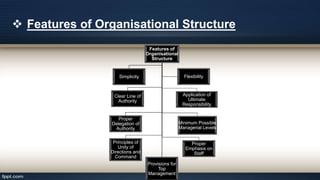
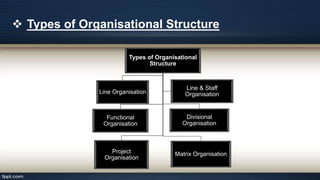
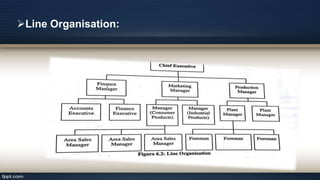
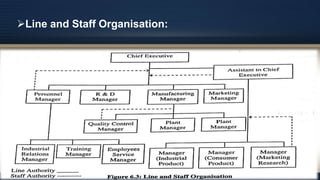
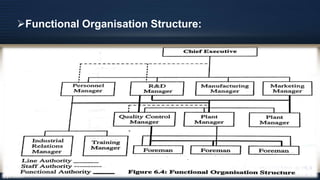
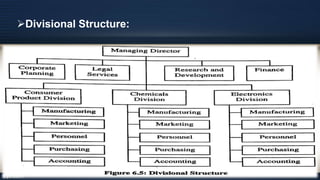
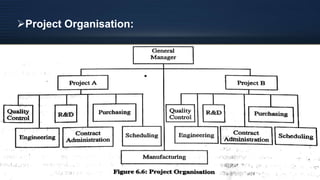
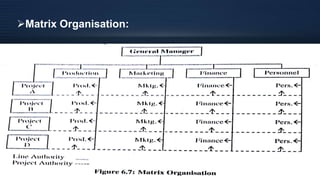
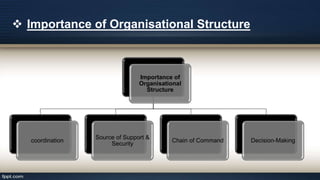
Organizational design involves assessing and reshaping an organization's structure and positions to better meet its goals. Key aspects of organizational design include determining structure, allocating resources, and matching strategic actions to accomplish work and goals. Organizational structure establishes authority relationships and provides for coordination. Common structures include functional, divisional, line, project, matrix and line-and-staff configurations. Structure impacts organizational behavior by influencing motivation, response to change, decision-making, and conflict levels. Larger organizations tend to have more complex, specialized and formalized structures to facilitate coordination at increased scale. Technology choices also influence appropriate organizational design and structure.