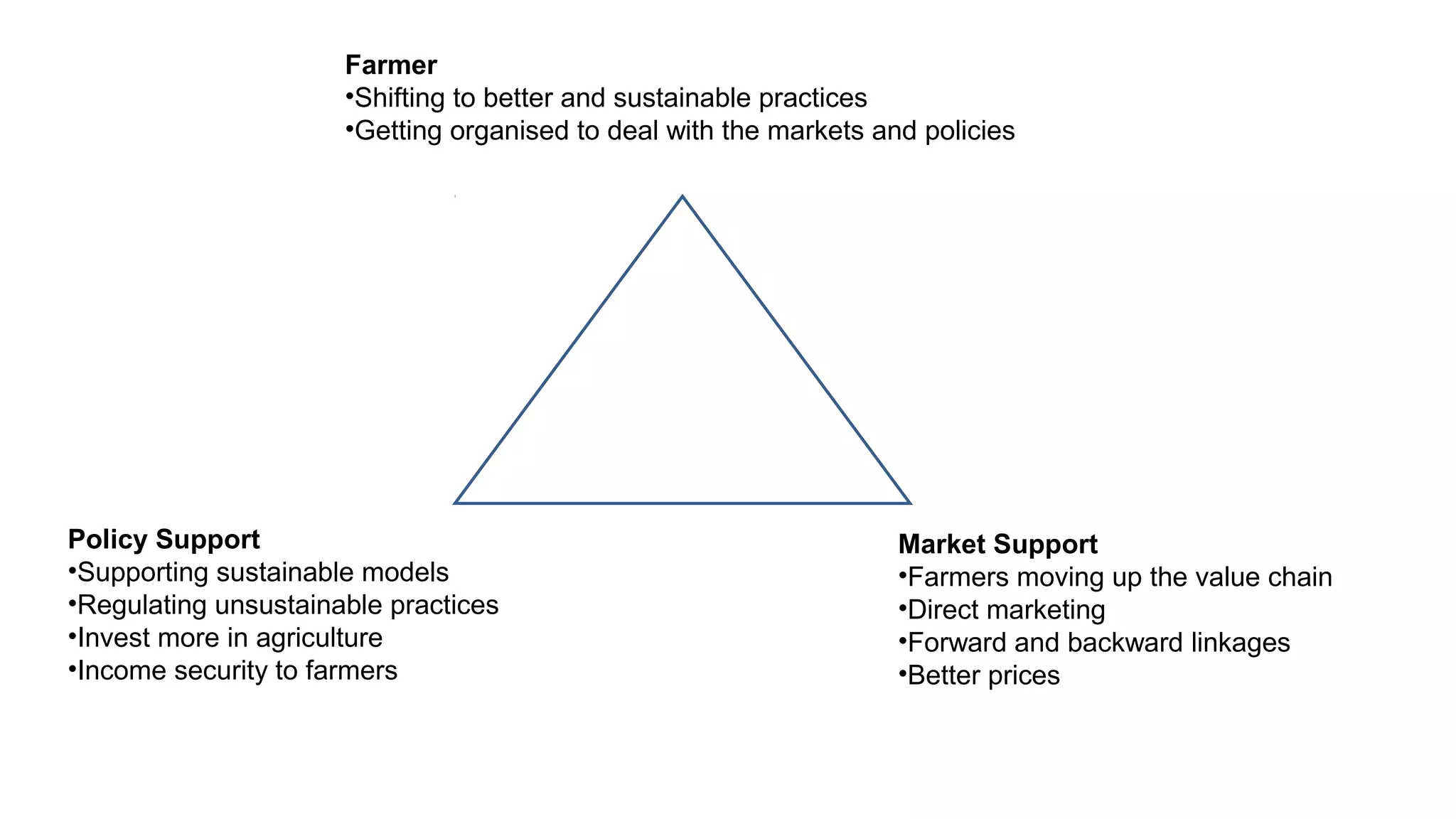
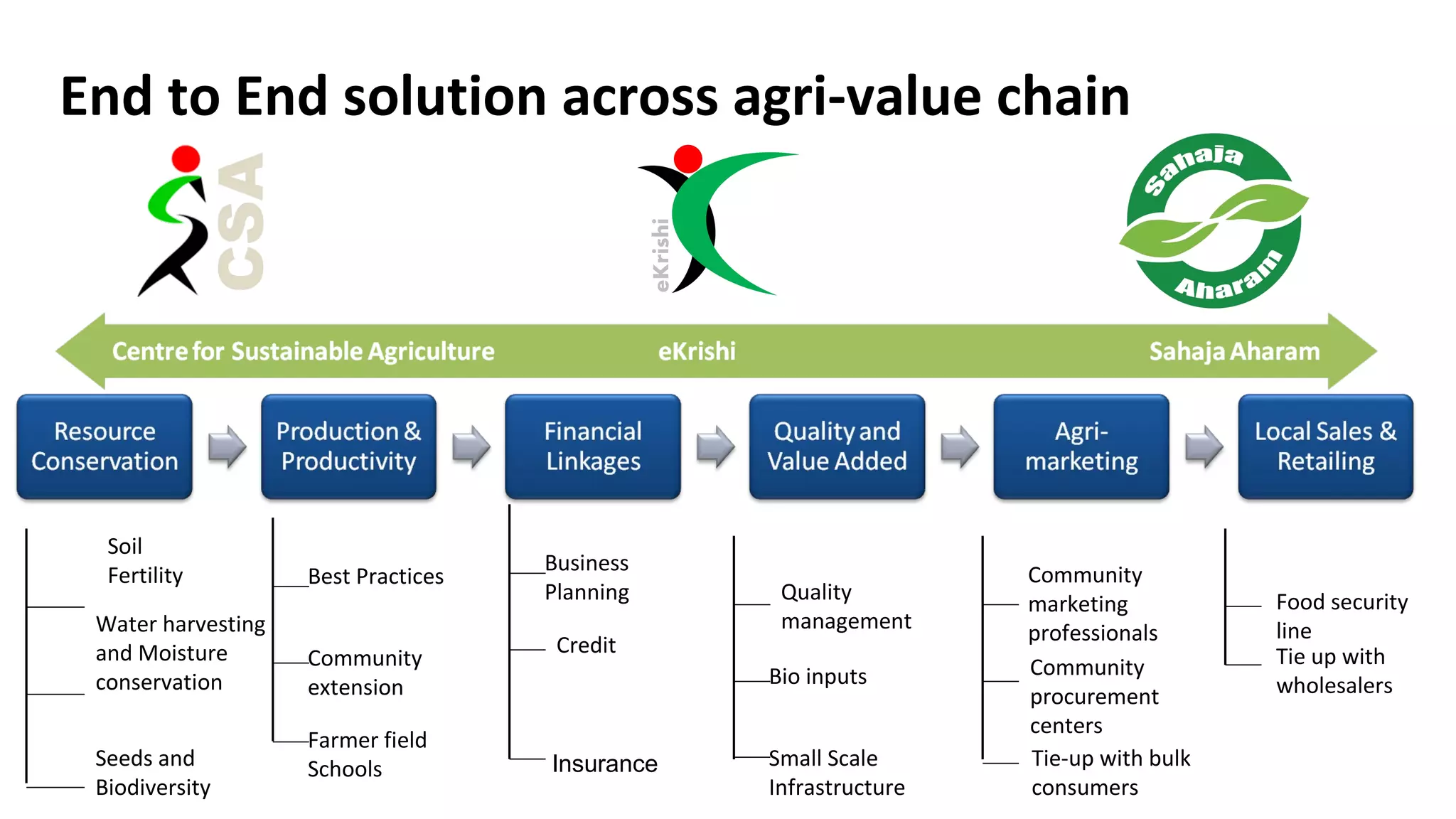
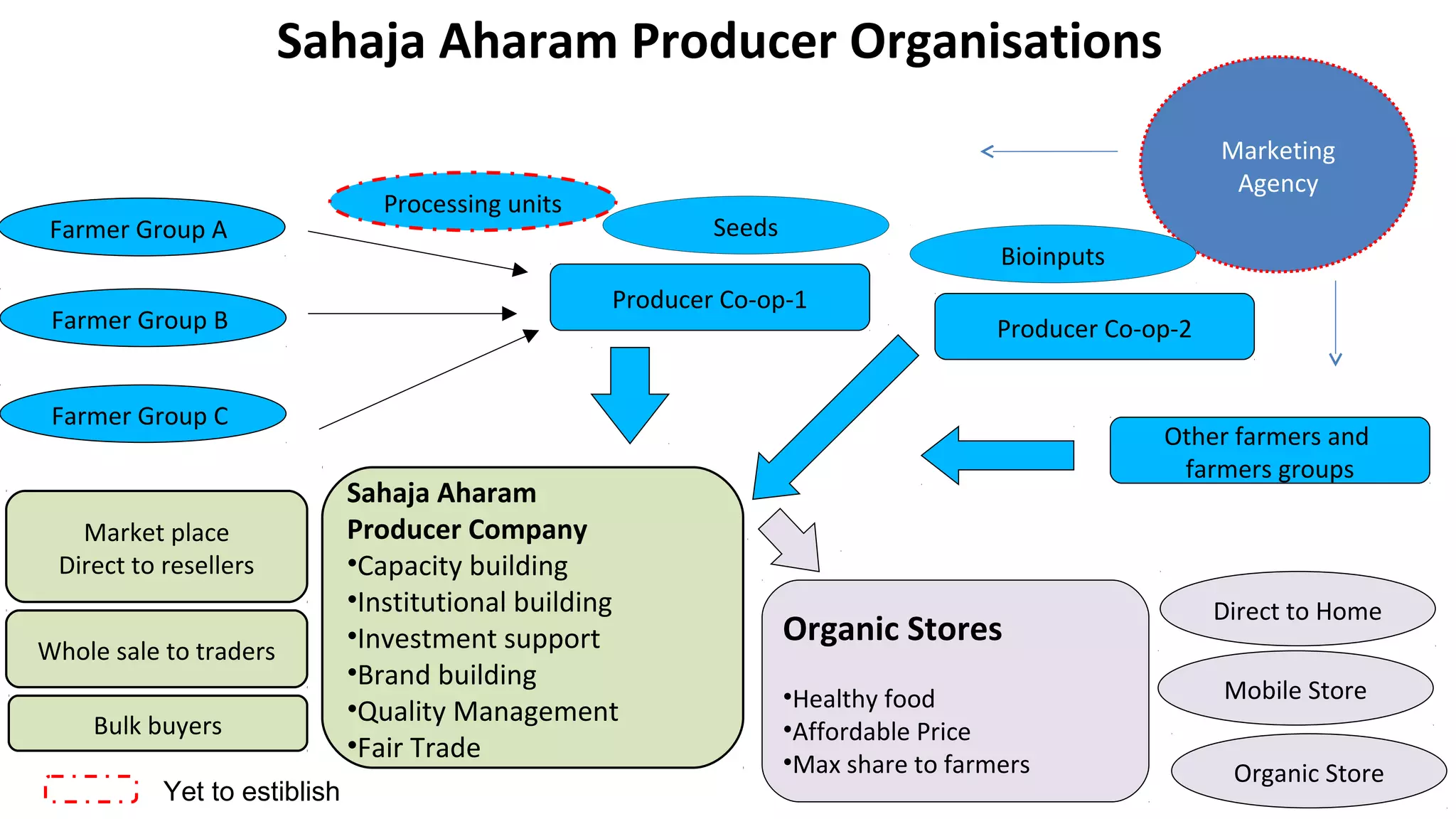
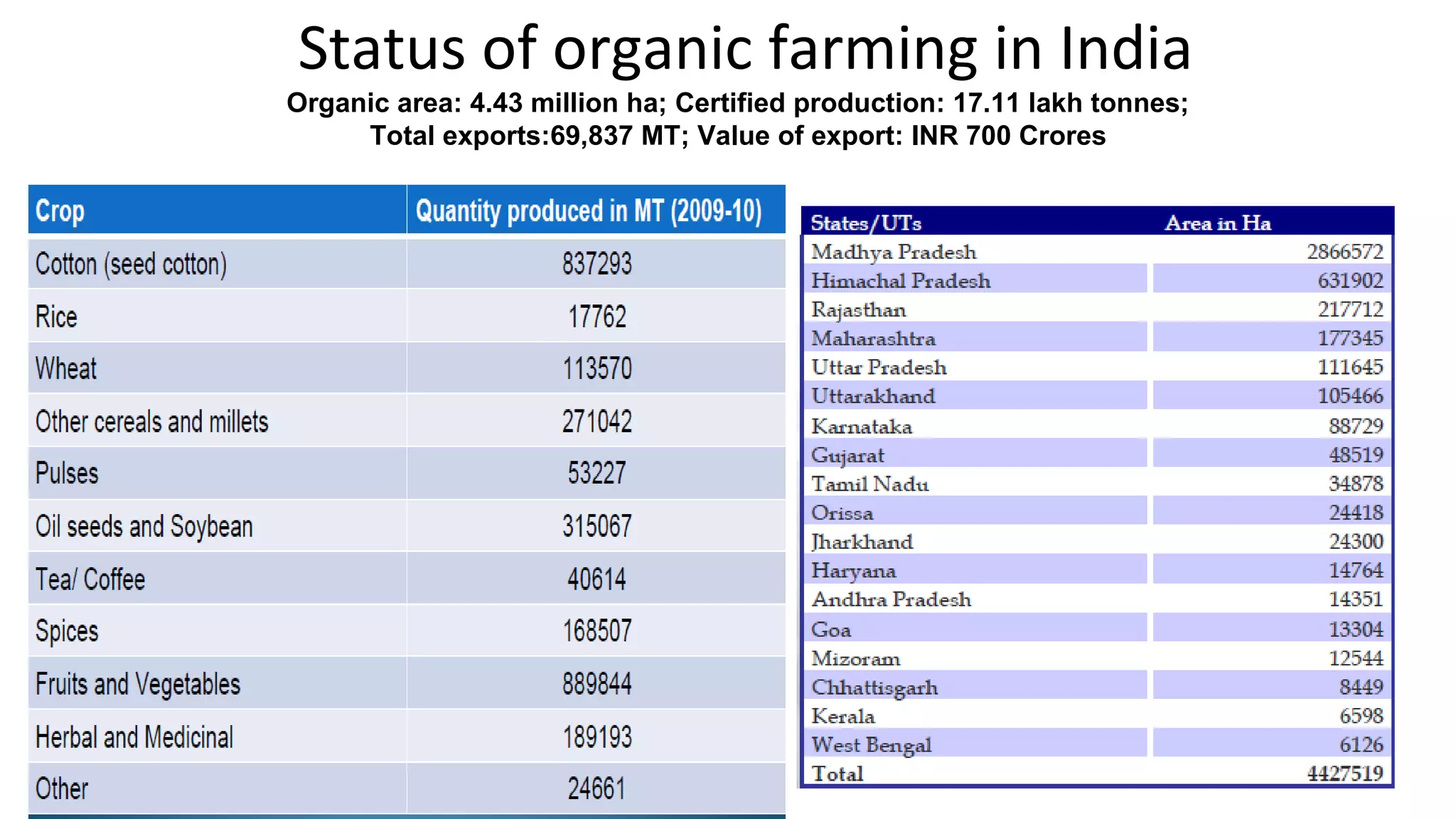
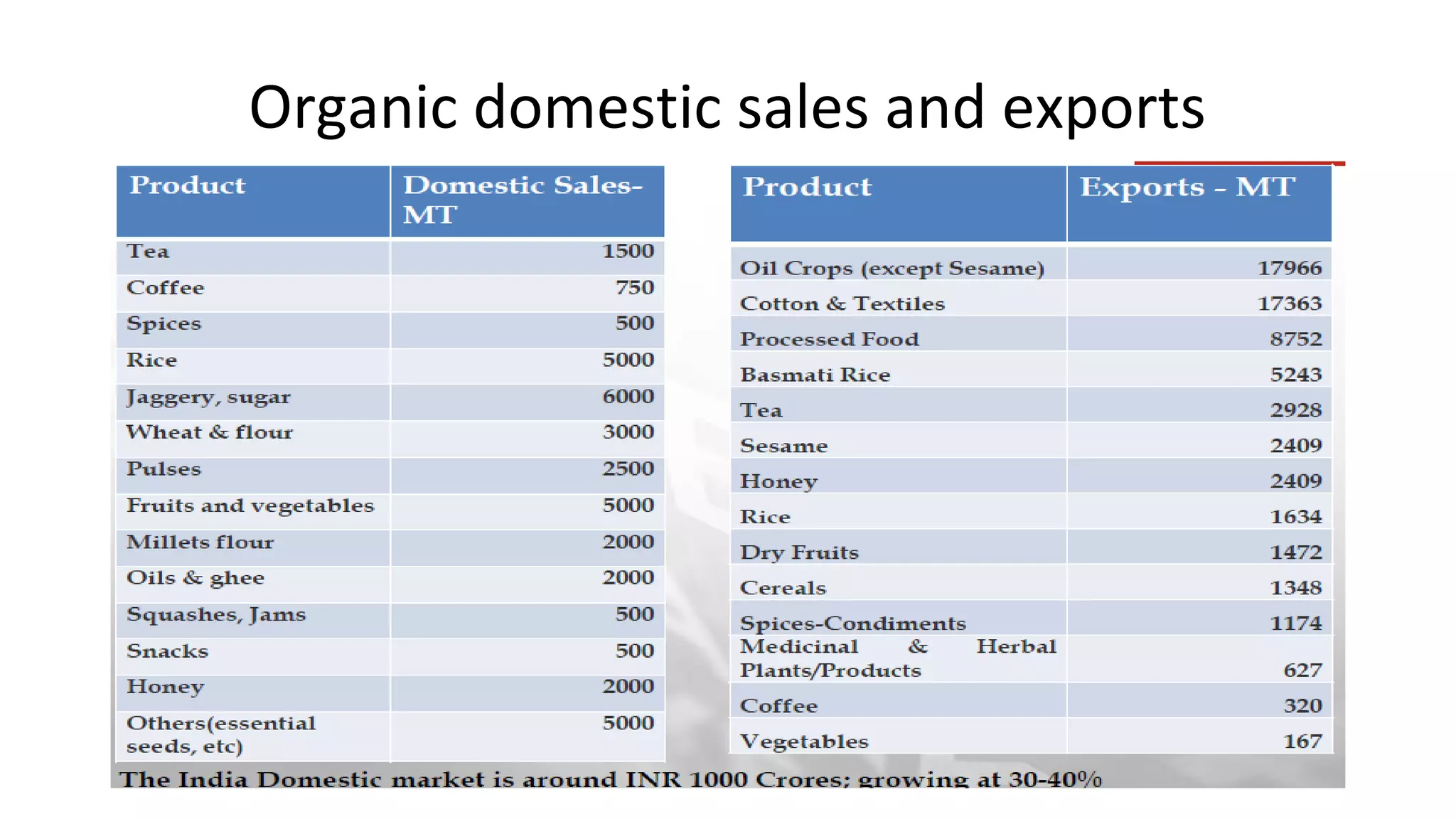
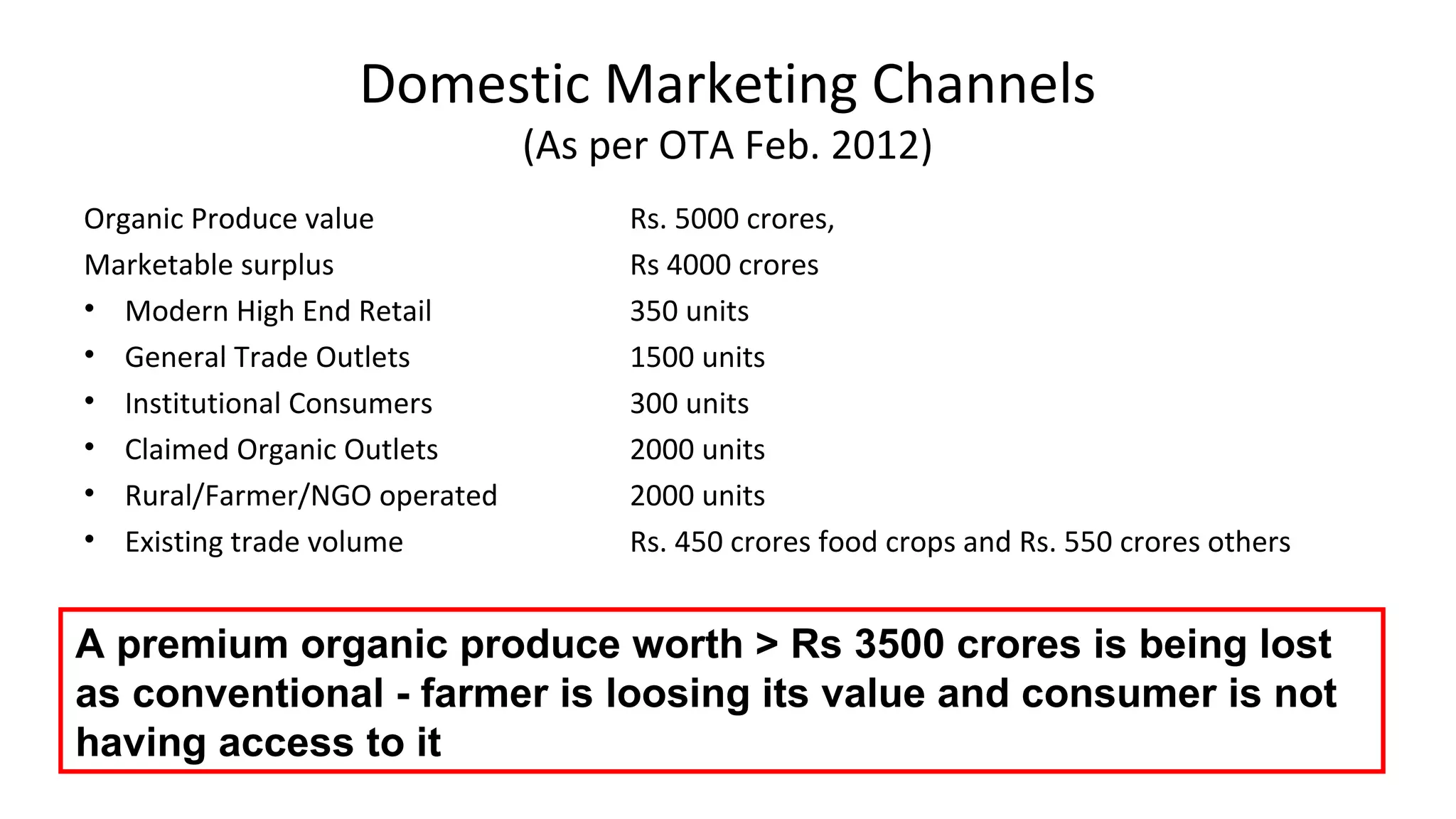
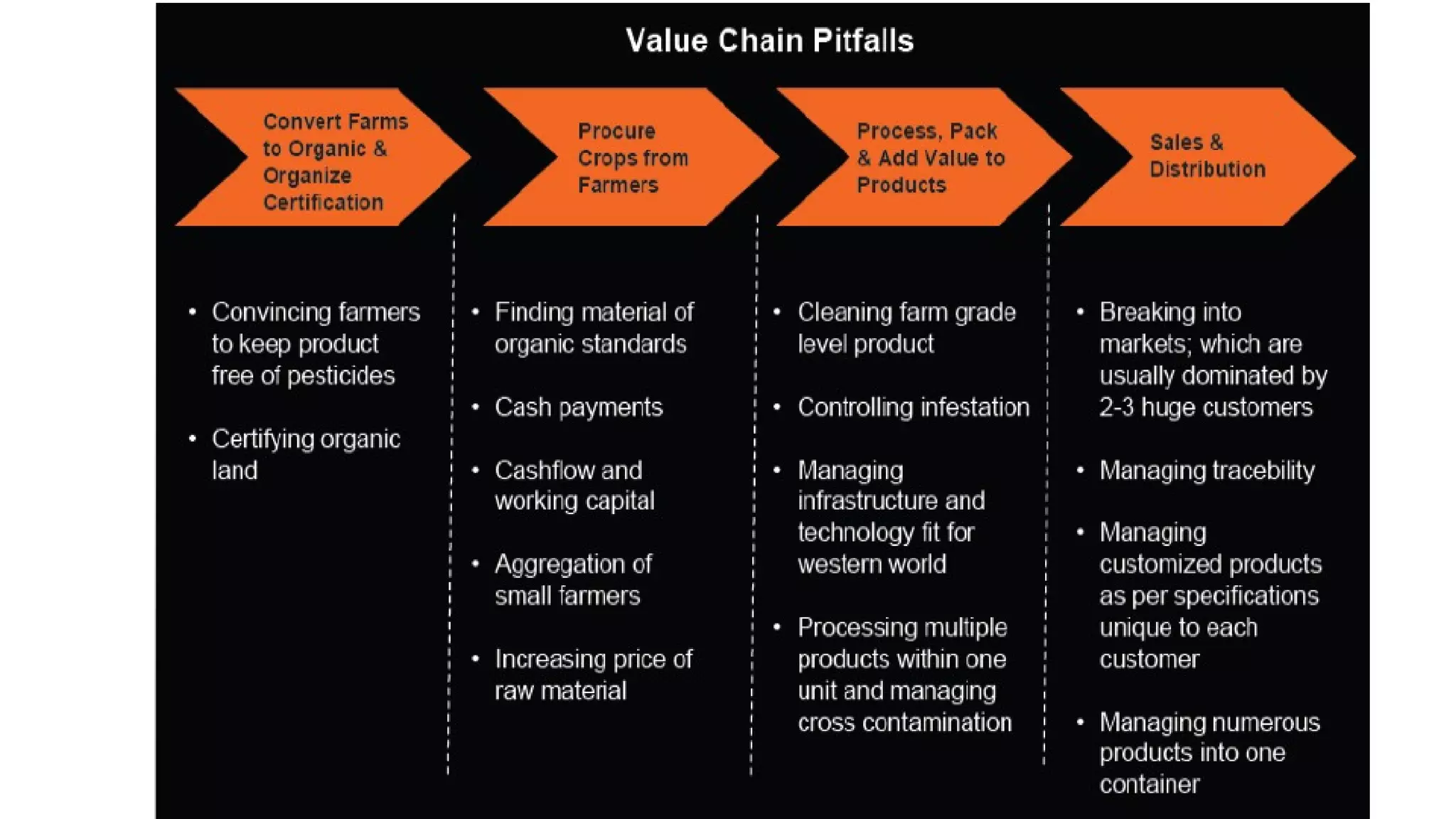
The Centre for Sustainable Agriculture (CSA) is a non-profit organization based in Telangana, India that works to promote organic and sustainable farming practices. Over the past 10 years, CSA has worked with farmers and state governments in Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Maharashtra, and Chhattisgarh to establish community-managed sustainable agriculture programs covering over 200,000 hectares. CSA has also helped form 14 agricultural cooperatives with over 1,500 member farmers. The organization provides training, resources and market support to help farmers transition to organic practices and improve their incomes.