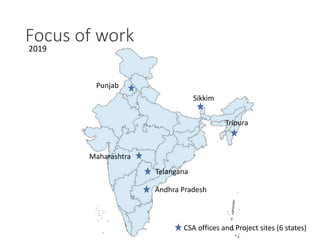
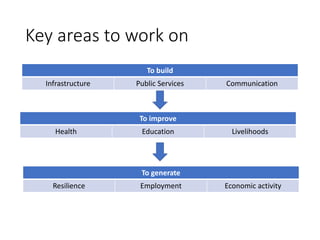
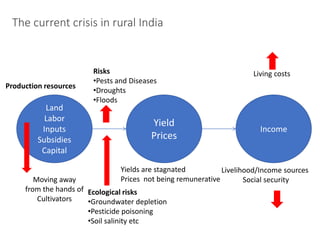
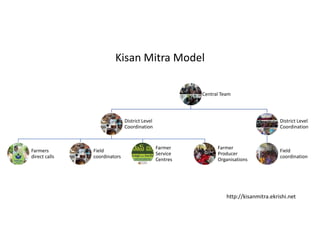
The document discusses efforts to improve rural development in India through information technology. It focuses on areas like organic farming, climate change adaptation, livelihood diversification, and building producer organizations. Key activities include farmer field schools, developing "bio villages", creating alternative livelihoods, and incubating farmers' cooperatives and companies. A helpline called KisanMitra aims to improve access to services, credit, and resolve farmers' issues. The organization works in 6 states and focuses on making public support services more accessible to farmers through various initiatives.