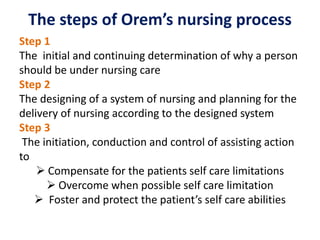
Dorothea Orem developed the Self-Care Deficit Nursing Theory, which has three related parts: self-care, self-care deficit, and nursing systems. The theory proposes that individuals require nursing care when they are unable to independently meet their self-care needs. Orem identified universal, developmental, and health-deviation self-care requisites. Her theory provides a framework for the nursing process to assess self-care deficits, design and implement nursing systems to meet needs, and evaluate outcomes. The document outlines Orem's theory and provides an example of its application in planning care for a client.