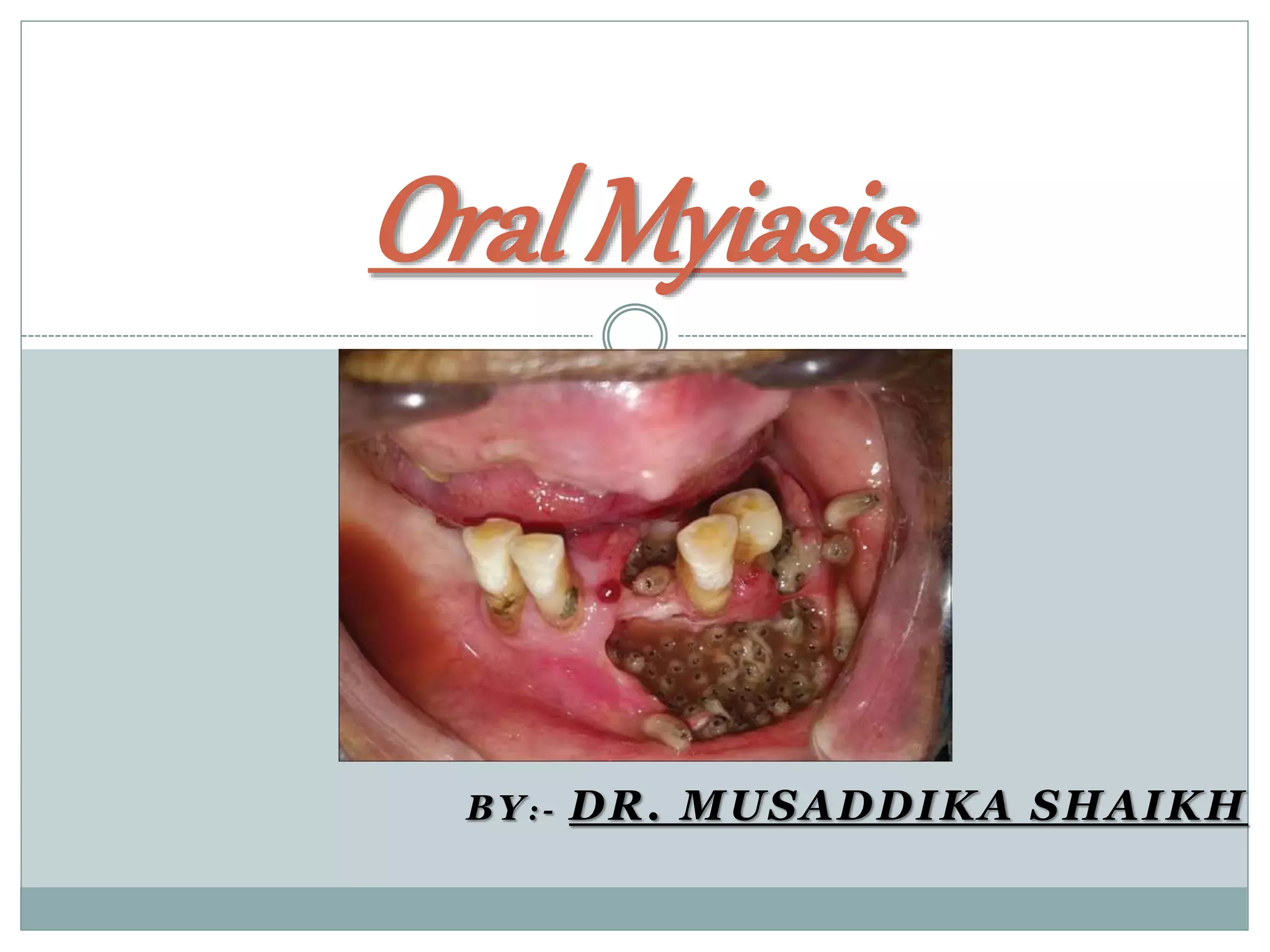
Oral myiasis is a rare condition caused by fly larvae invading oral tissues. It occurs most often in patients with poor oral hygiene, alcoholism, or medical conditions. The document discusses the classification, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of oral myiasis. Maggots are usually removed using turpentine oil and tweezers under anesthesia. Necrotic tissue is also debrided and antibiotics are prescribed to prevent infection while the tissues heal. Maintaining good oral hygiene is important for prevention.



![Classification of Myiasis
A] Clinical classification:-
i) Primary Myiasis – when larvae feed on living tissue
ii) Secondary Myiasis – when larvae feed on dead tissue
B] Depending on condition of invoved tissue:-
i)Accidental Myiasis – when larve get ingested along with food
ii)Semi-specific Myiasis – when larvae are laid on necrotic tissue of wound
iii)Obligatory – required living tissue for larvae development
iv)Facultative – required necrotic tissue for flies to lay eggs and incubate them
C]Based on Anatomic sites:-
i)Cutaneous Myiasis
ii)Myaisis of External Orifies
iii)Myaisis of Iternal Organs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oralmyiasis-200705224305/85/Oral-Myiasis-5-320.jpg)

![Diagnosis
A] Clinical Examination :-
1. Poor oral hygiene
2. Redness
3. Swelling
4. Tissue destruction
5. Maggots in affected area
6. Trauma
7. Open lips
8. Difficulty in breathing
9. Tender to palpate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oralmyiasis-200705224305/85/Oral-Myiasis-9-320.jpg)
![B]Radiographic Investigation :-
1. Orthopantamogram (OPG)
2. Tomography scan
3. Water’s Veiw
4. Intraoral Periapical](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oralmyiasis-200705224305/85/Oral-Myiasis-10-320.jpg)
![C] Haematological Investigation :-
1. Total White Blood Cells(WBC) Count
2. Total Red Blood Cells(RBC) Count
3. Platelet Count
4. Haemoglobin Concentration(HB)
D] Entomological Investigation :-
It is process of collecting evidence based on insect
It is done after removal of Maggots from oral cavity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oralmyiasis-200705224305/85/Oral-Myiasis-11-320.jpg)

![Treatment
A] Procedure for removing Maggots :-
B] Removal of necrotic tissue
C] Repair of tissues or any fracture
D] Medications
E] Instructions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oralmyiasis-200705224305/85/Oral-Myiasis-13-320.jpg)
![A] Procedure of Removal of Maggots :-
Patient is given General Anesthesia
Cotton bud is dipped in Turpentine Oil and is
applied to Lacerated mucosa for 10-12 min
Maggots are removed with help of blunt tweezer
and curved forceps
Entomological Investigation is done](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oralmyiasis-200705224305/85/Oral-Myiasis-14-320.jpg)
![B] Removal of dead tissues :-
Surgical Removal of Necrotic Tissues is done
Then area is irrigated with saline,Hydrgen
peroxide, and betadine with metronidazole
After debridement repair can be done](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oralmyiasis-200705224305/85/Oral-Myiasis-15-320.jpg)
![C] Repair of Tissues or any Fracture :-
First Patient is planned for open reduction
Then internal Fixation is done
Repair is done
Patient is on medication for 5 days](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oralmyiasis-200705224305/85/Oral-Myiasis-16-320.jpg)
![D] Medications :-
Patient is put on the following tablets
1. Ivermectin 6mg OD for 5 days
2. Doxycycline(Antibiotic) 100mg BD for
5 days
3. Metronidazole 100 ml 8h given for 5
days](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oralmyiasis-200705224305/85/Oral-Myiasis-17-320.jpg)
![E] Instructions :-
Patient is advised to maintain proper oral hygiene
Rinse wound with 0.2% Chlorhexidine mouthwash 3-5
times a day
Patients is also advised to do oral prophalaxis
Patientgetdischargedon4th day
Followupappointmentis given
Extrasuturesareremoved
Patientis recalledperiodically
On14th daywoundgetscompletelycleaned](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oralmyiasis-200705224305/85/Oral-Myiasis-18-320.jpg)
