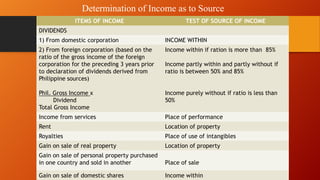
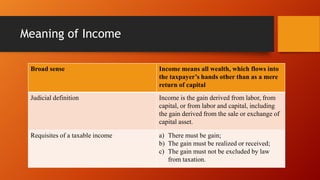
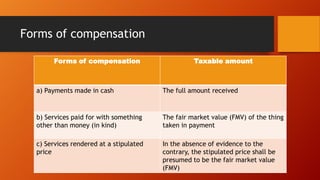
This document discusses sources of income and classification of income for tax purposes. It defines income as coming from sources within the Philippines, without, or partly within and partly without. It provides examples of how different types of income like dividends, income from services, rent, royalties, and gains from property sales are treated. The document also discusses what constitutes gross income, how income is distinguished from capital, receipts, and revenue, and provides examples of different types of compensation that are considered taxable income.