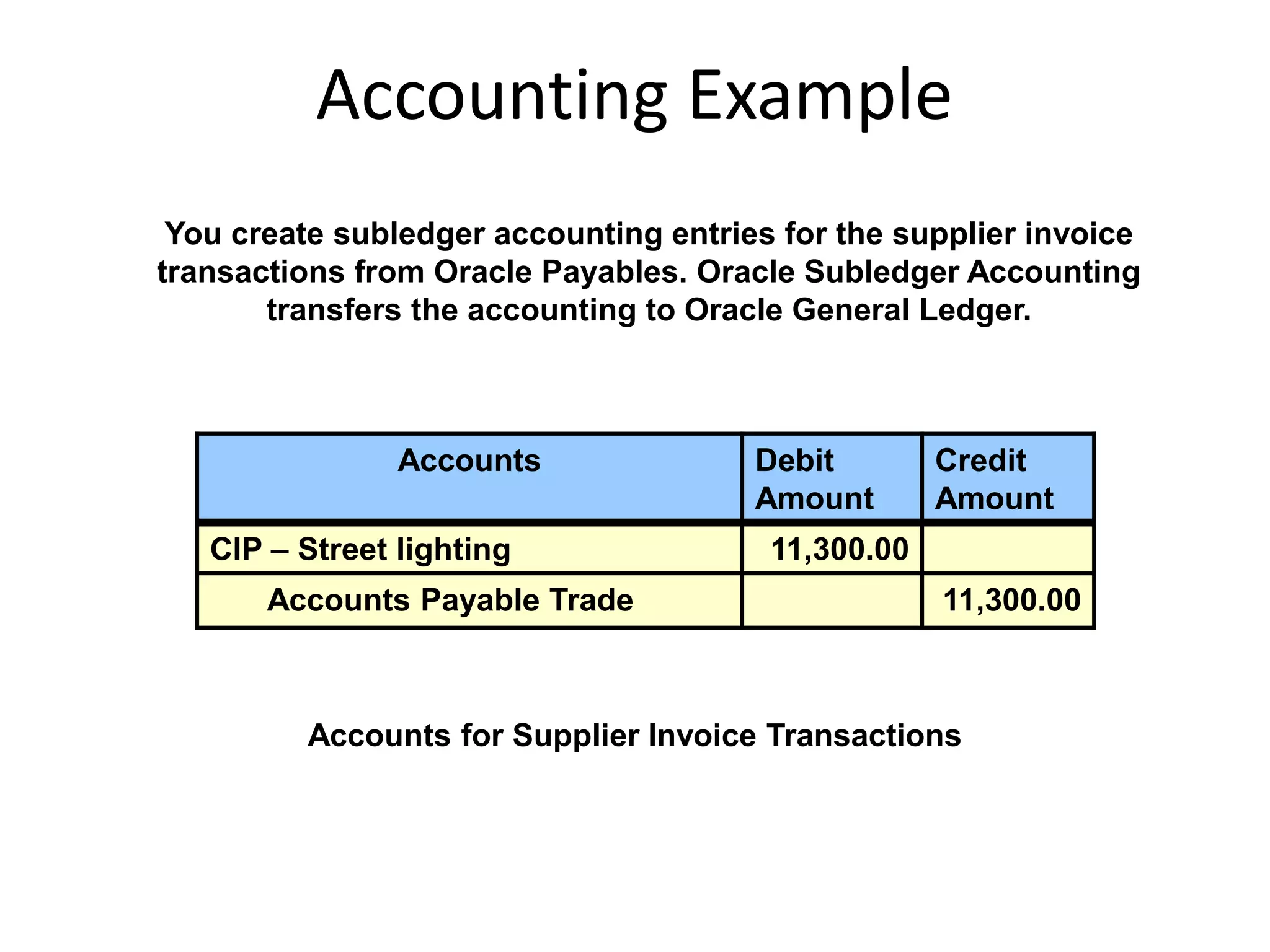
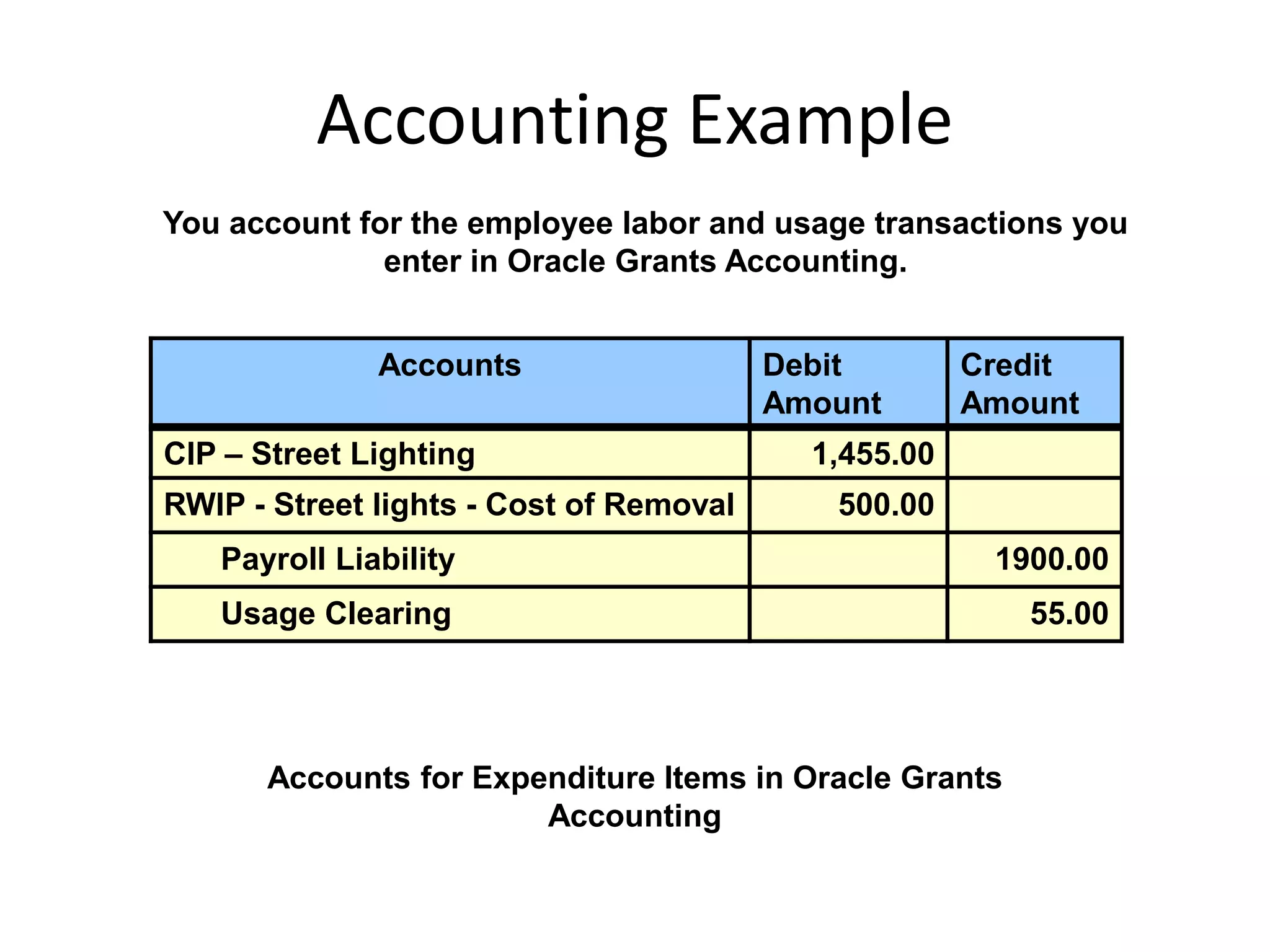
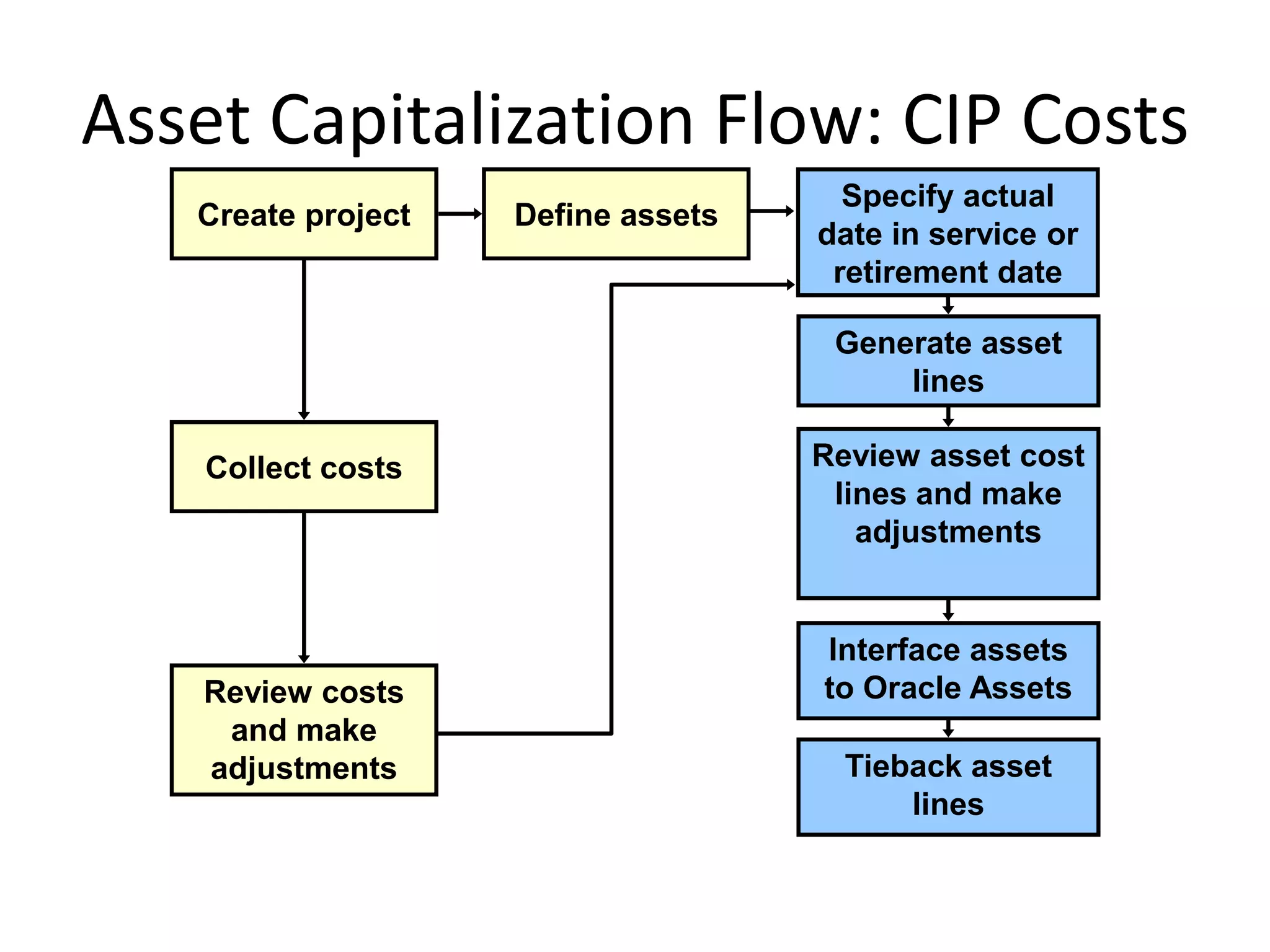
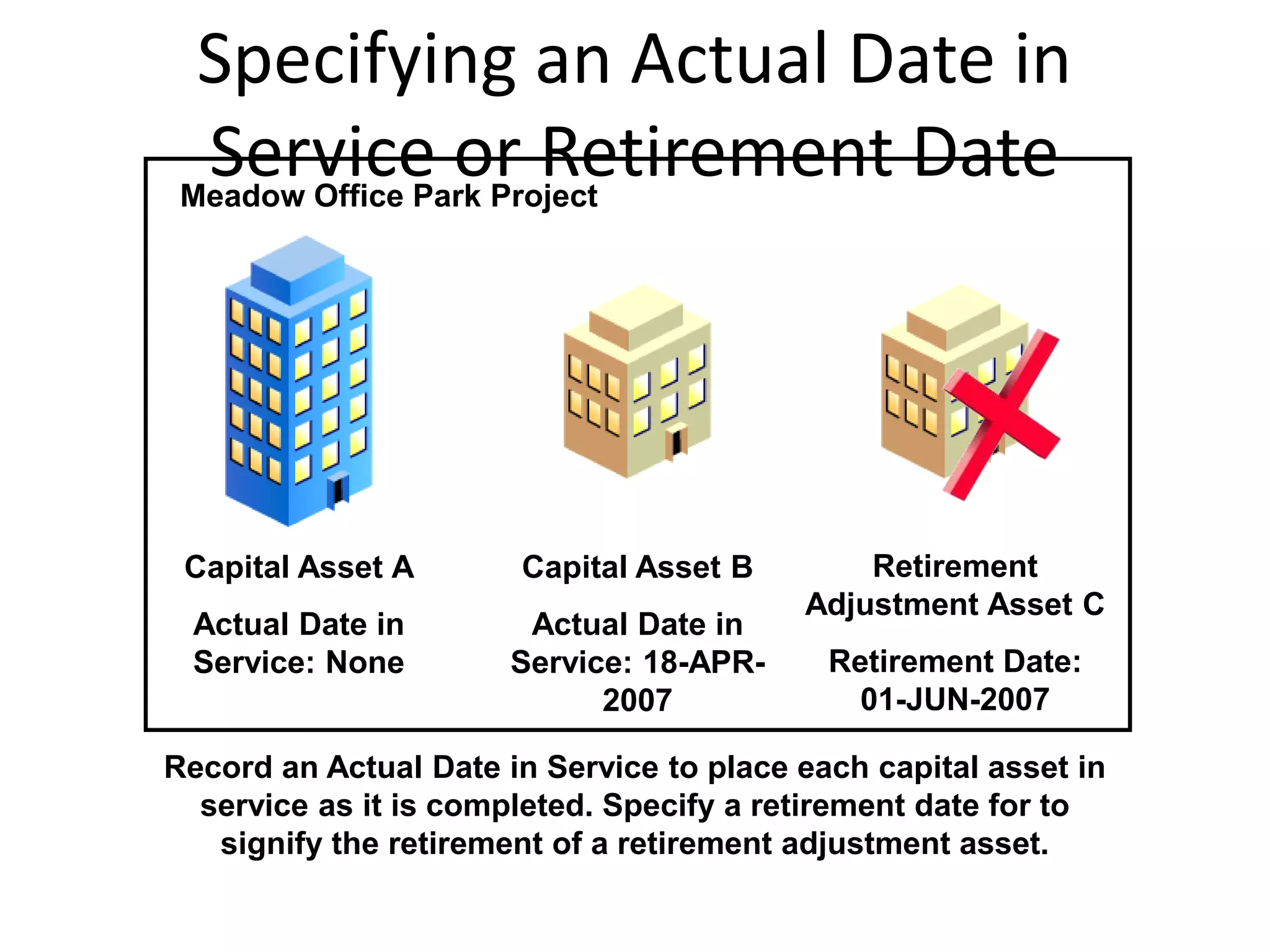
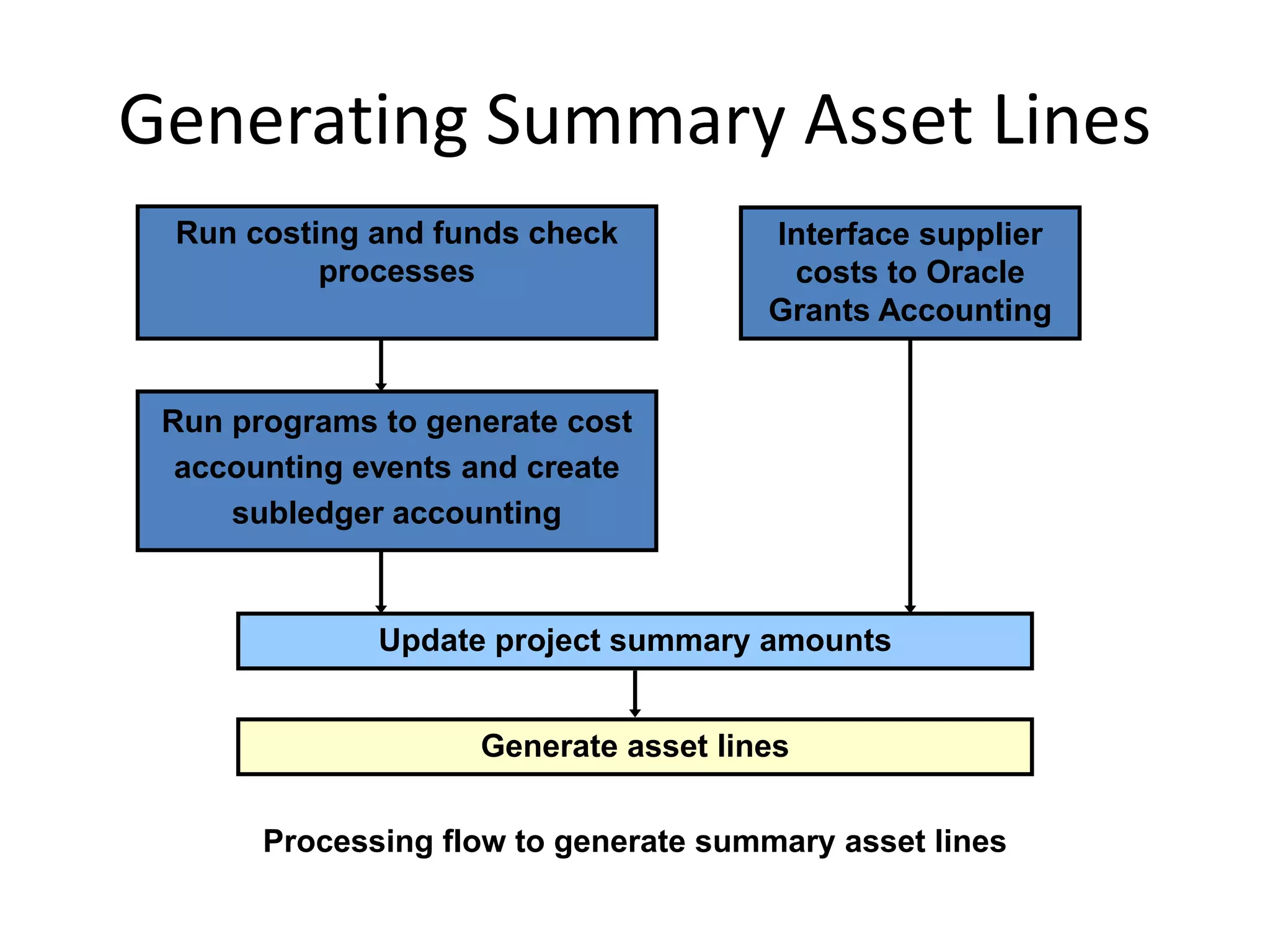
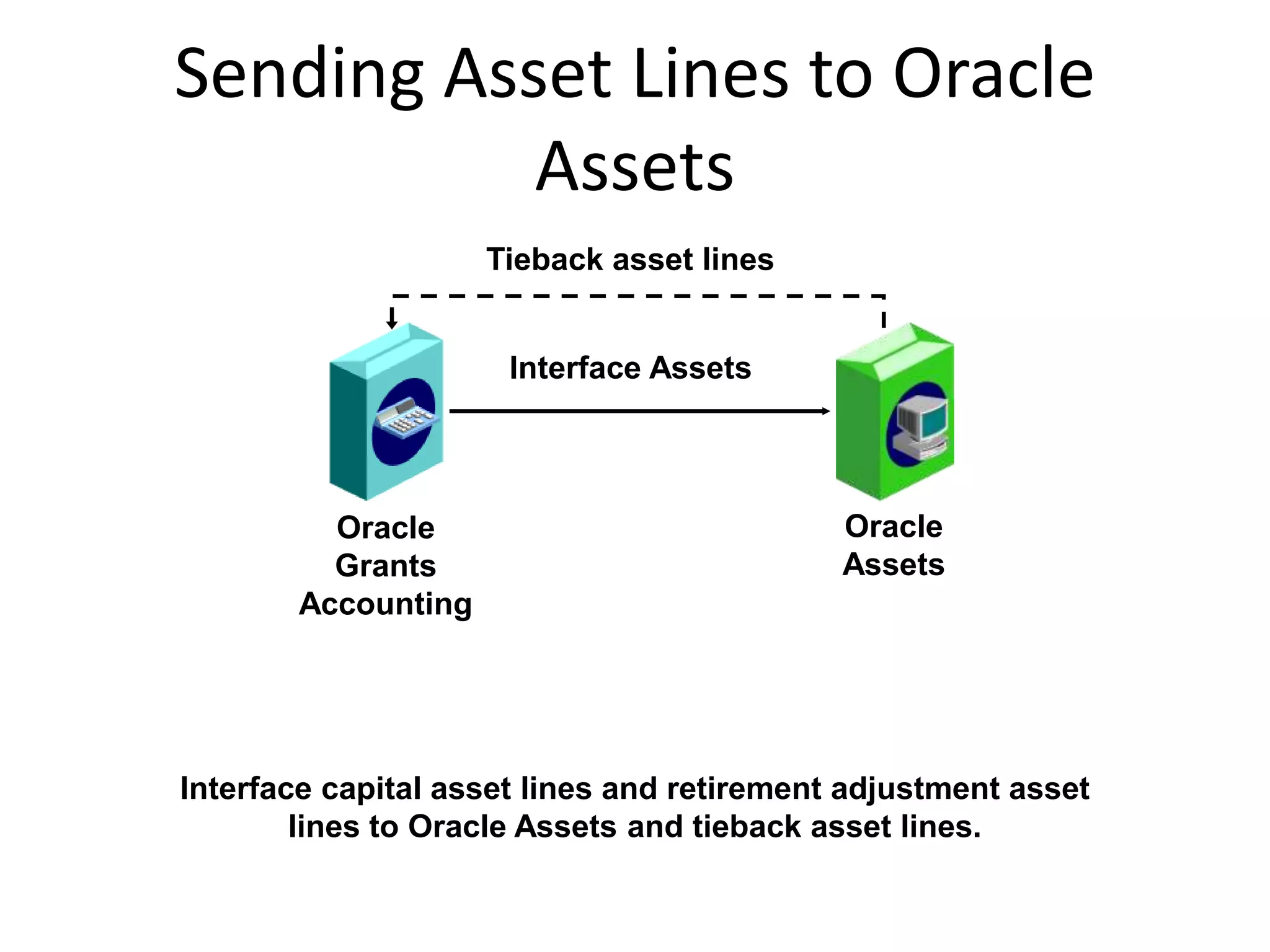
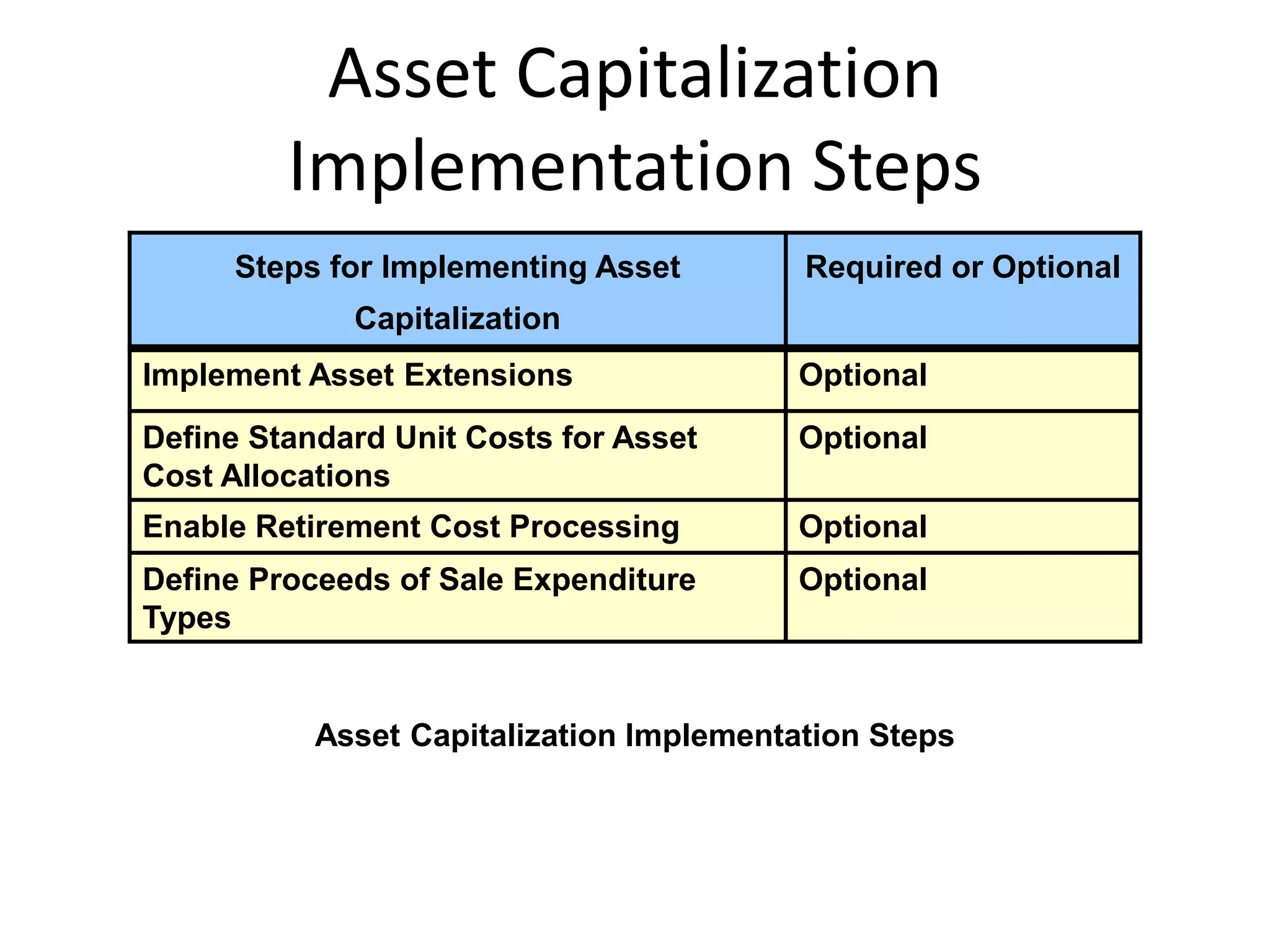
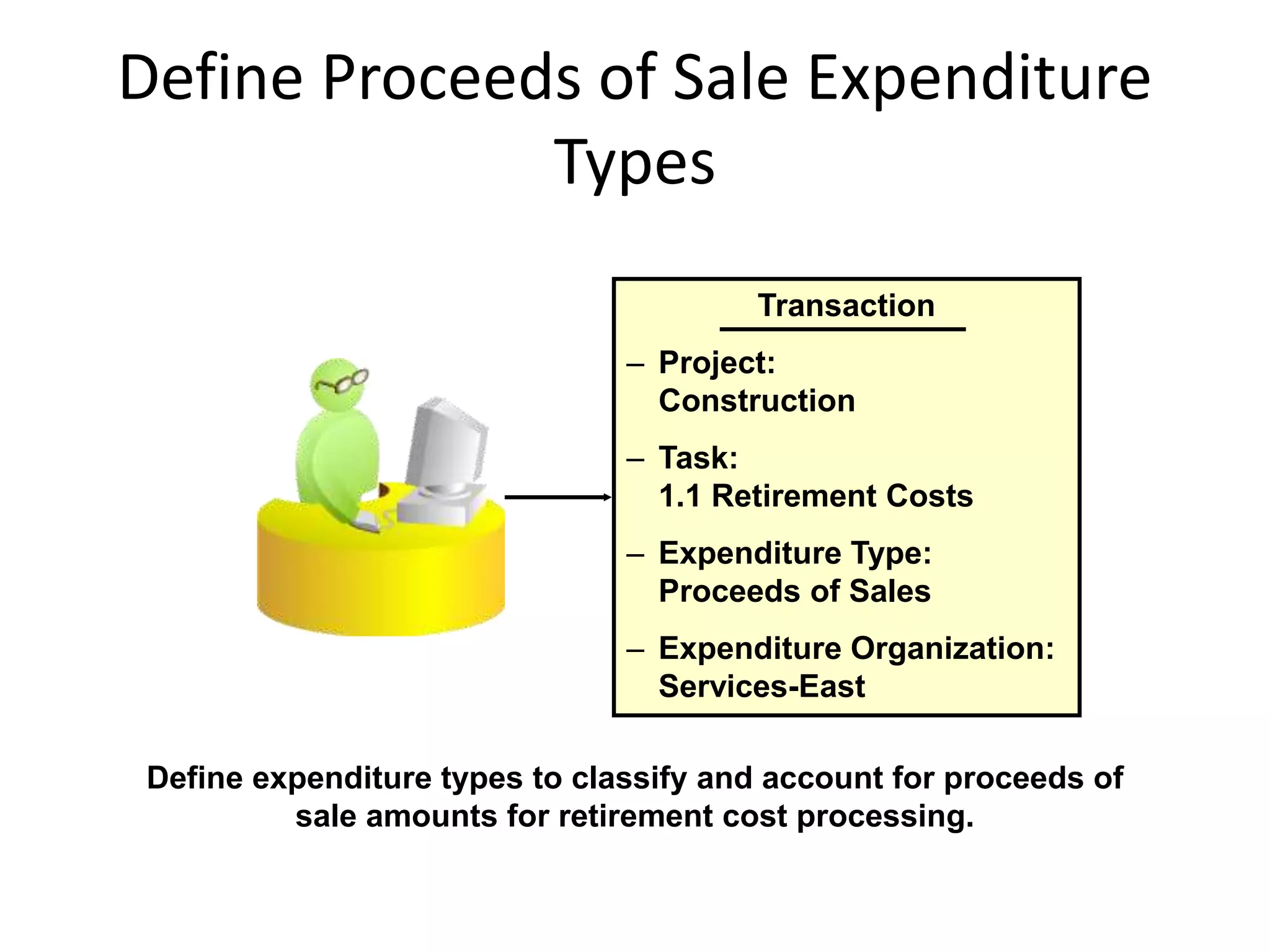
This document discusses asset capitalization in Oracle Grants Accounting. It provides an overview of asset capitalization, describes project types for capitalizing assets, explains the process for capitalizing asset costs, and outlines steps for implementing asset capitalization such as defining standard unit costs and enabling retirement cost processing.