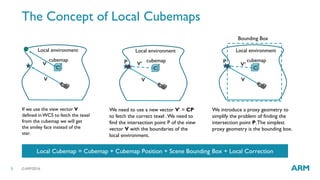
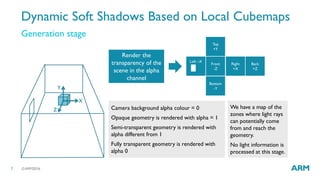
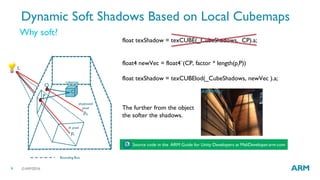
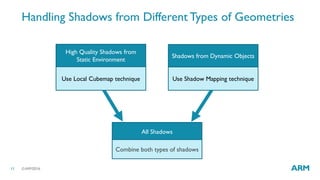
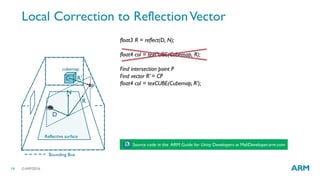
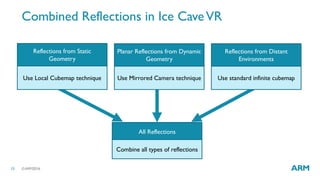
The document describes optimized rendering techniques for mobile VR, including local cubemap techniques for dynamic soft shadows and stereo reflections. Local cubemaps allow high quality shadows and reflections from static geometry to be efficiently combined with other techniques for dynamic objects. Stereo reflections improve the user experience in VR by using separate textures for the left and right eyes.