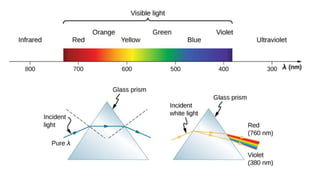
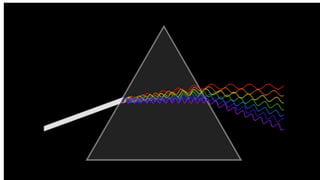
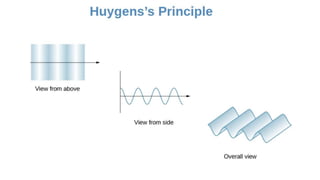
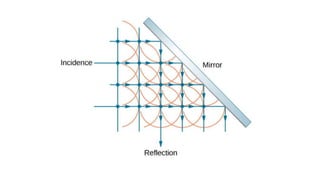
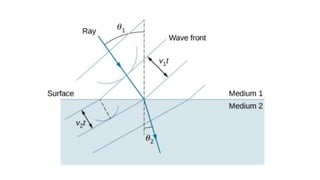
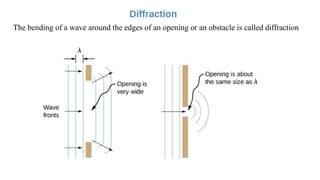
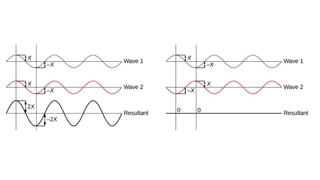
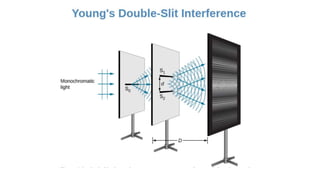
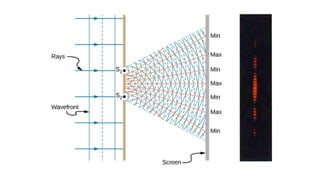
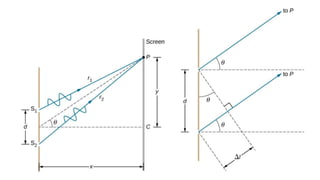
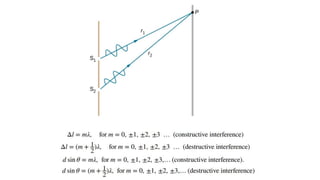
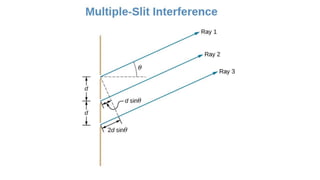
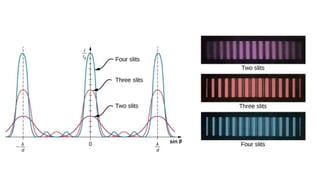
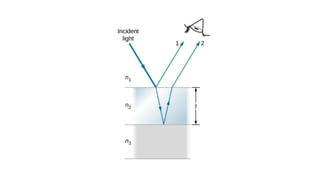
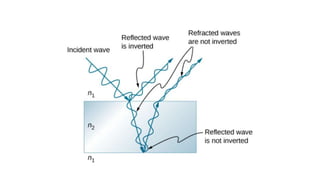
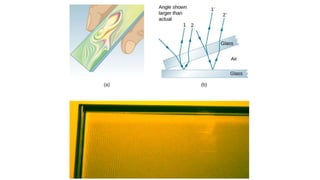
Dispersion is the spreading of white light into a spectrum of wavelengths when light propagates through a medium. It occurs when the speed of light depends on its wavelength. We see colors like red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet associated with different light wavelengths. The sequence of colors in a rainbow is the same as the visible light spectrum. Huygens' principle describes how each point on a wavefront acts as a secondary source, with the new wavefront determined by the tangent to the secondary wavelets. Interference patterns form when waves interact constructively or destructively, such as with double slits. Thin film interference produces the bright colors seen in oil slicks and soap bubbles.