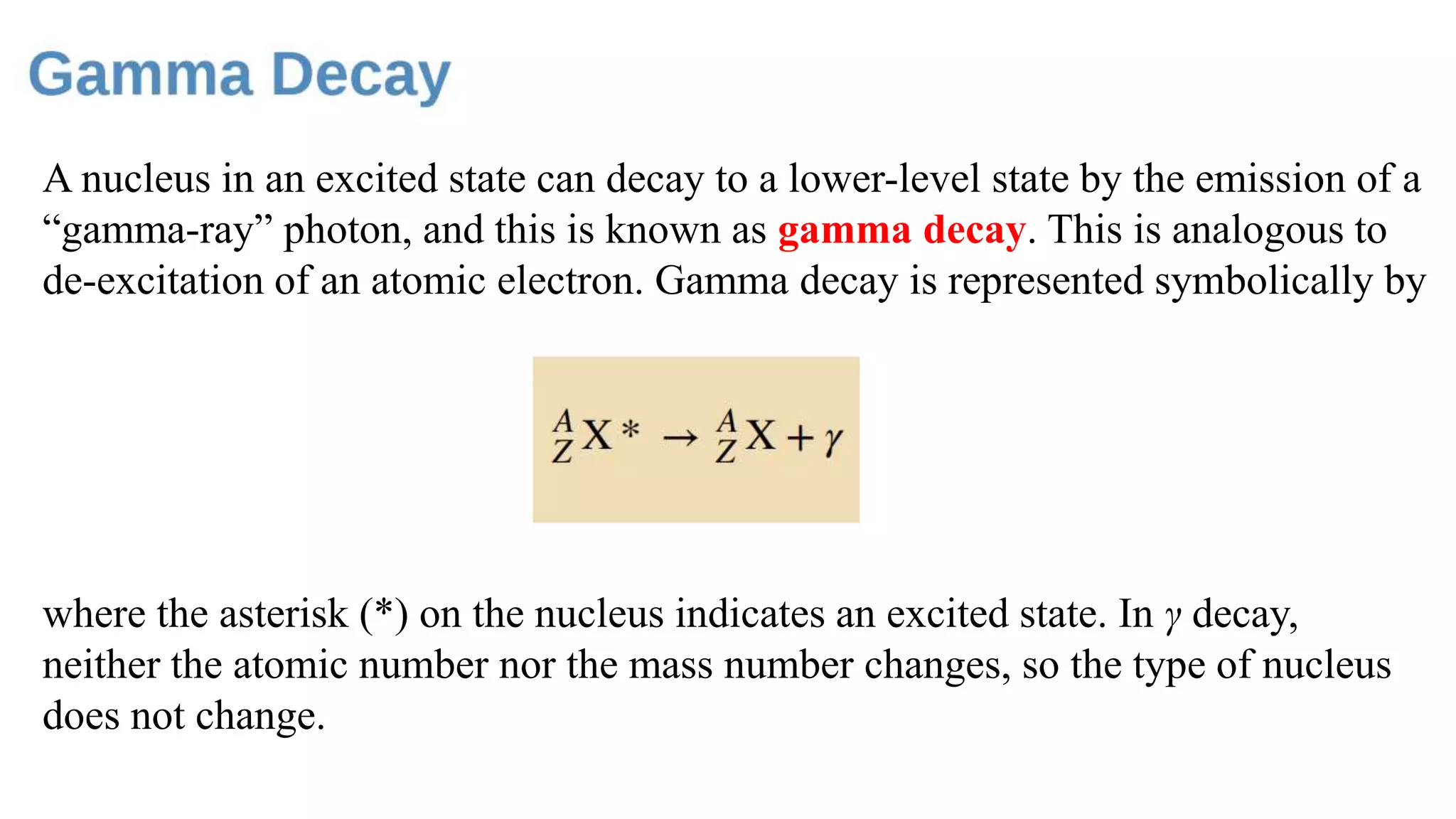
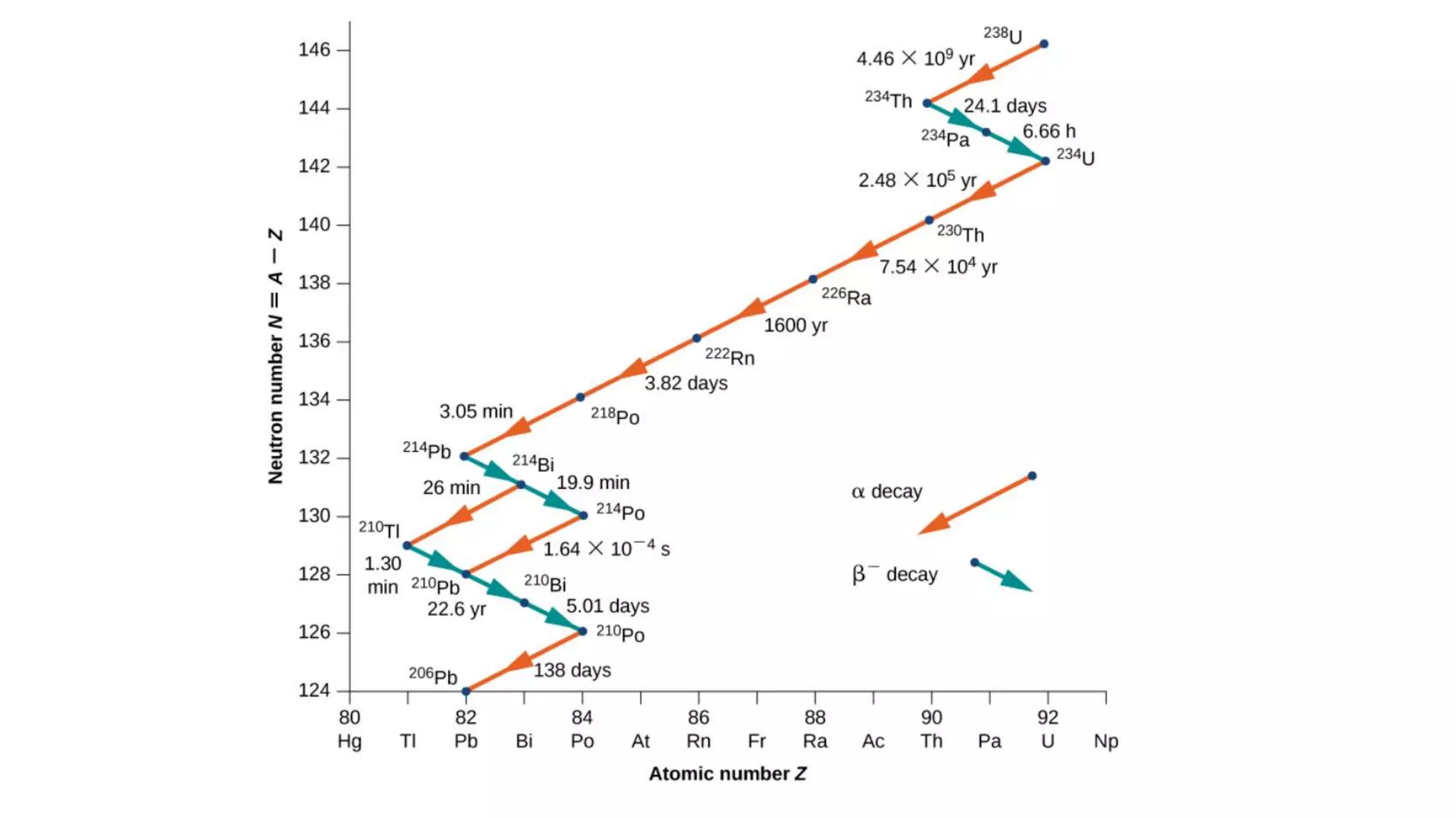
Nuclear physics involves different types of radioactive decays such as alpha decay where a nucleus loses two protons and two neutrons decreasing its atomic number by two and mass number by four, gamma decay where a nucleus in an excited state decays to a lower energy state by emitting a gamma ray photon without changing atomic or mass numbers, and decay series where a parent nucleus decays into one or more daughter nuclei through successive decays. Radioactive decay rates depend on factors like the strong and electromagnetic forces, and radioactive decay inside Earth from elements like uranium and thorium produces heat through high-energy particles, providing an internal heat source that has kept Earth's interior hotter than