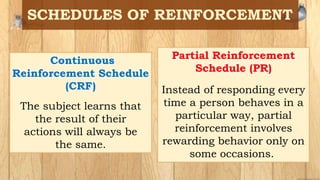
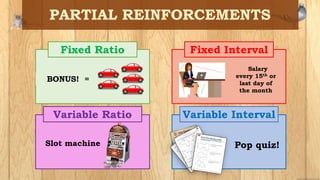
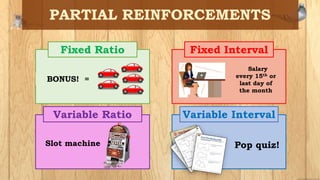
The document discusses operant conditioning, which is a method of learning developed by psychologists Edward Thorndike and B.F. Skinner. Operant conditioning operates on the principle that behaviors followed by pleasant consequences are more likely to be repeated, while behaviors followed by unpleasant consequences are less likely to be repeated. Skinner developed various techniques for operant conditioning through his experiments using pigeon and rats, including his invention of the Skinner Box. The document also defines key concepts in operant conditioning like reinforcement, punishment, positive and negative reinforcement, primary and secondary reinforcement, and different reinforcement schedules.