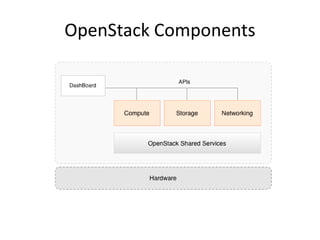
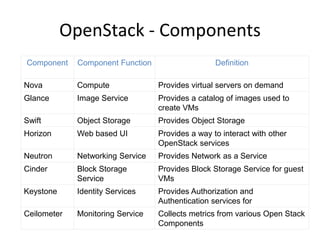
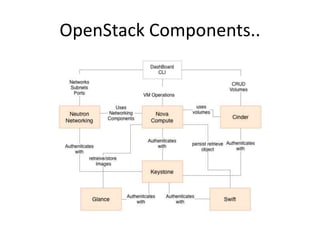
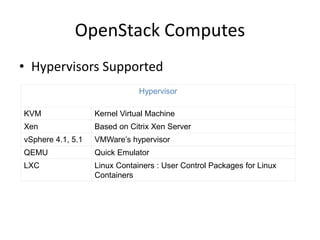
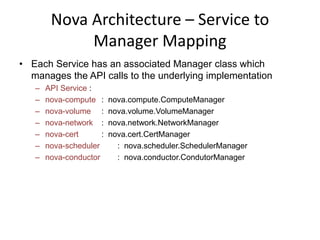
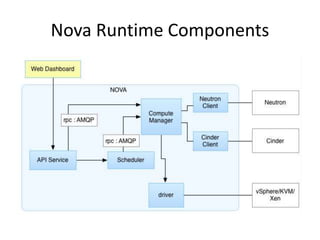
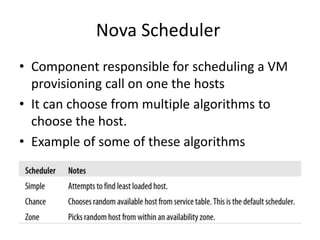
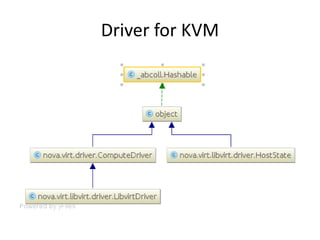
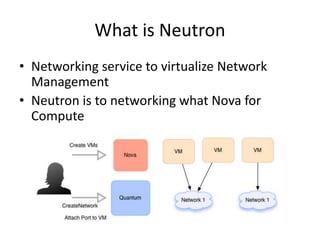
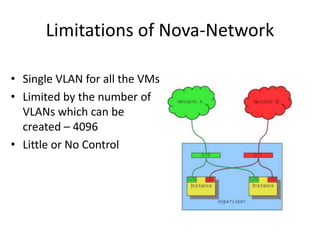
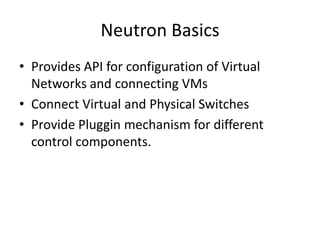
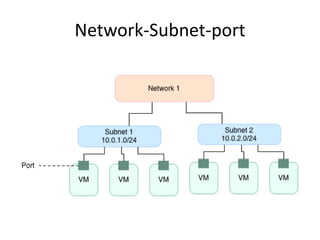
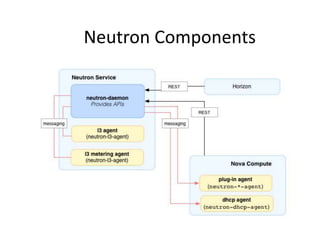
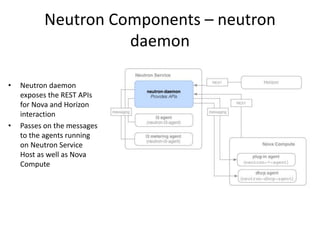
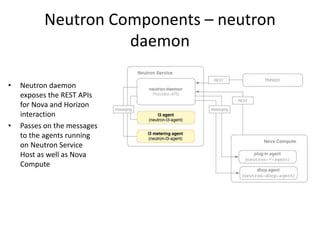
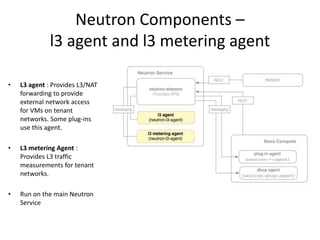
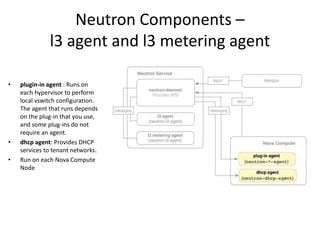
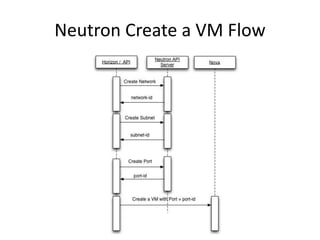
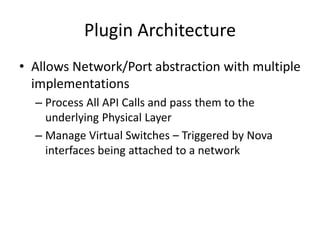
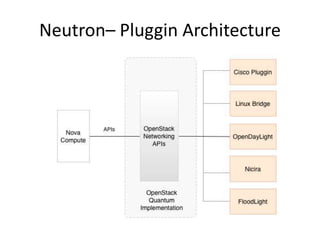
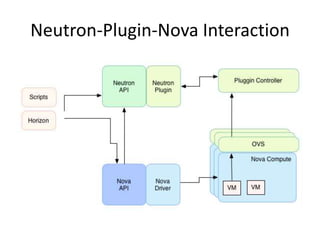
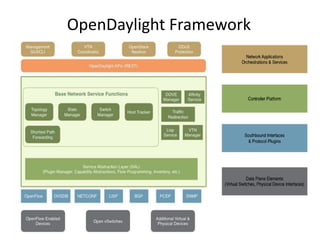
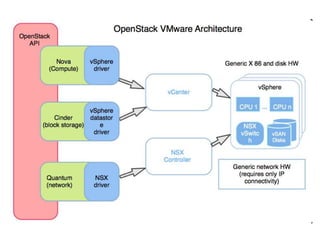
OpenStack is an open source cloud computing platform that provides infrastructure as a service. It abstracts compute, storage, and networking resources from physical hardware into a dashboard that manages these resources as virtual machines, object storage, and virtual networks. OpenStack uses a central dashboard and various components like Nova (compute), Glance (images), Swift (object storage), Neutron (networking), and Keystone (identity) that can work with different underlying hardware and be deployed both publicly or privately. Neutron provides network as a service and tools for building advanced virtual networks using plugins that support technologies like Open vSwitch, Linux bridges, NSX, and OpenDaylight.