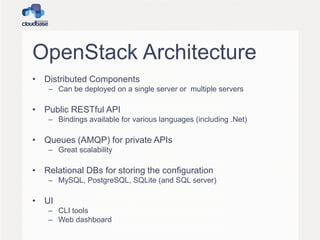
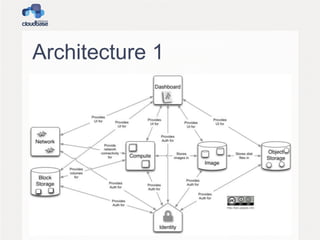
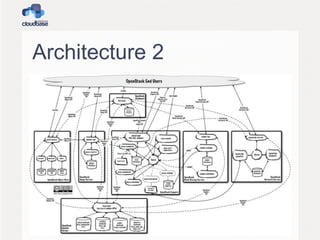
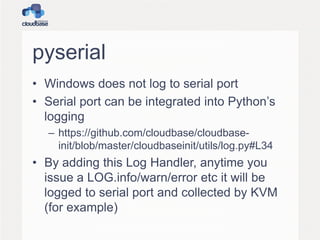
This document summarizes OpenStack, an open source IaaS project managed by the OpenStack Foundation. It discusses OpenStack's architecture, components, releases, and guest provisioning challenges. OpenStack has a distributed architecture with RESTful APIs and AMQP queues. Its components include Compute, Object Storage, Block Storage, Image Service, Networking, Dashboard, Identity, and Metering. Guest provisioning is tricky as OpenStack components don't handle what happens after a VM boots. Cloudbase-Init was created to standardize guest initialization across operating systems like Linux, Windows, and FreeBSD. It uses various Python libraries and APIs to integrate with different OSes.