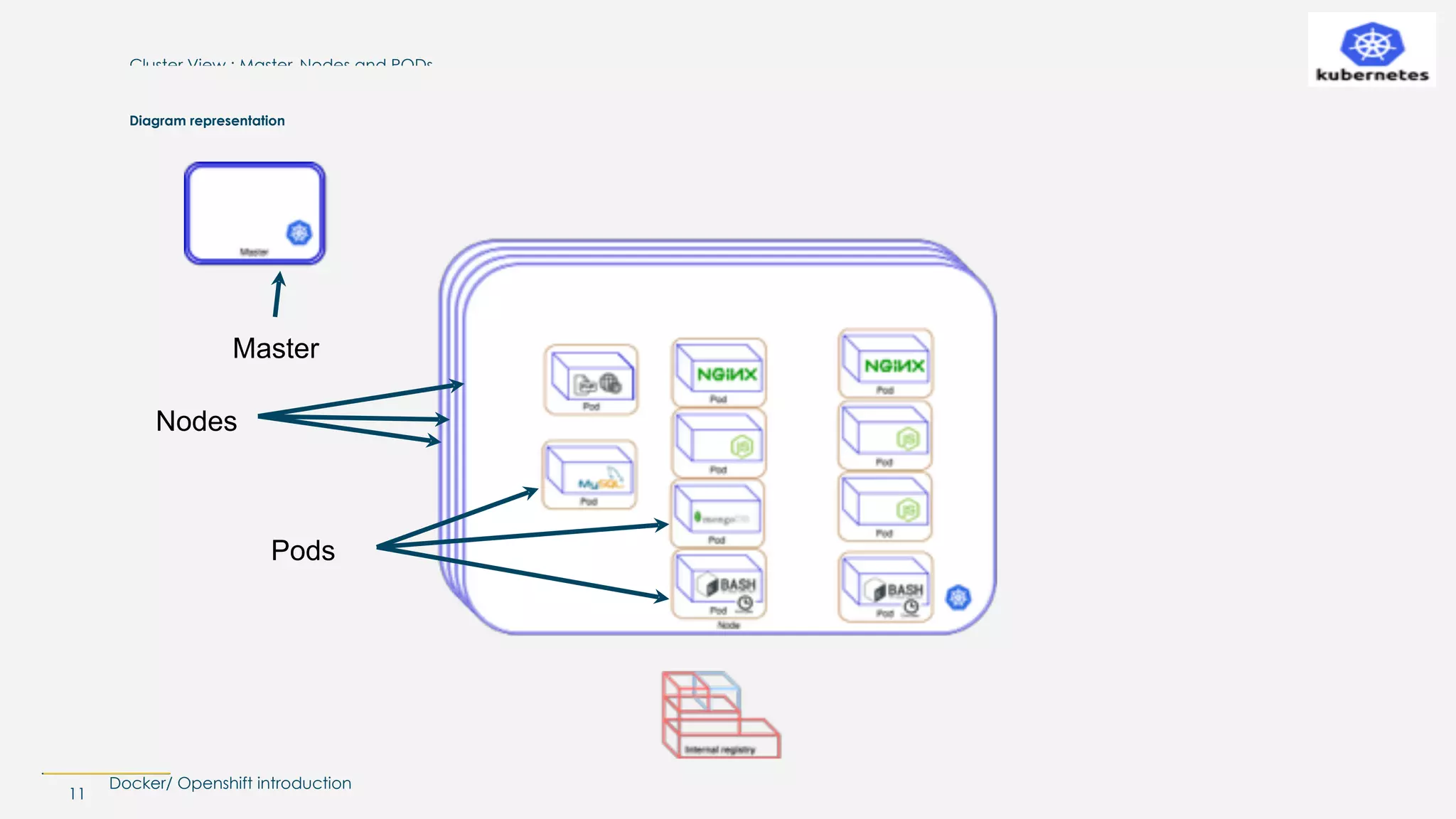
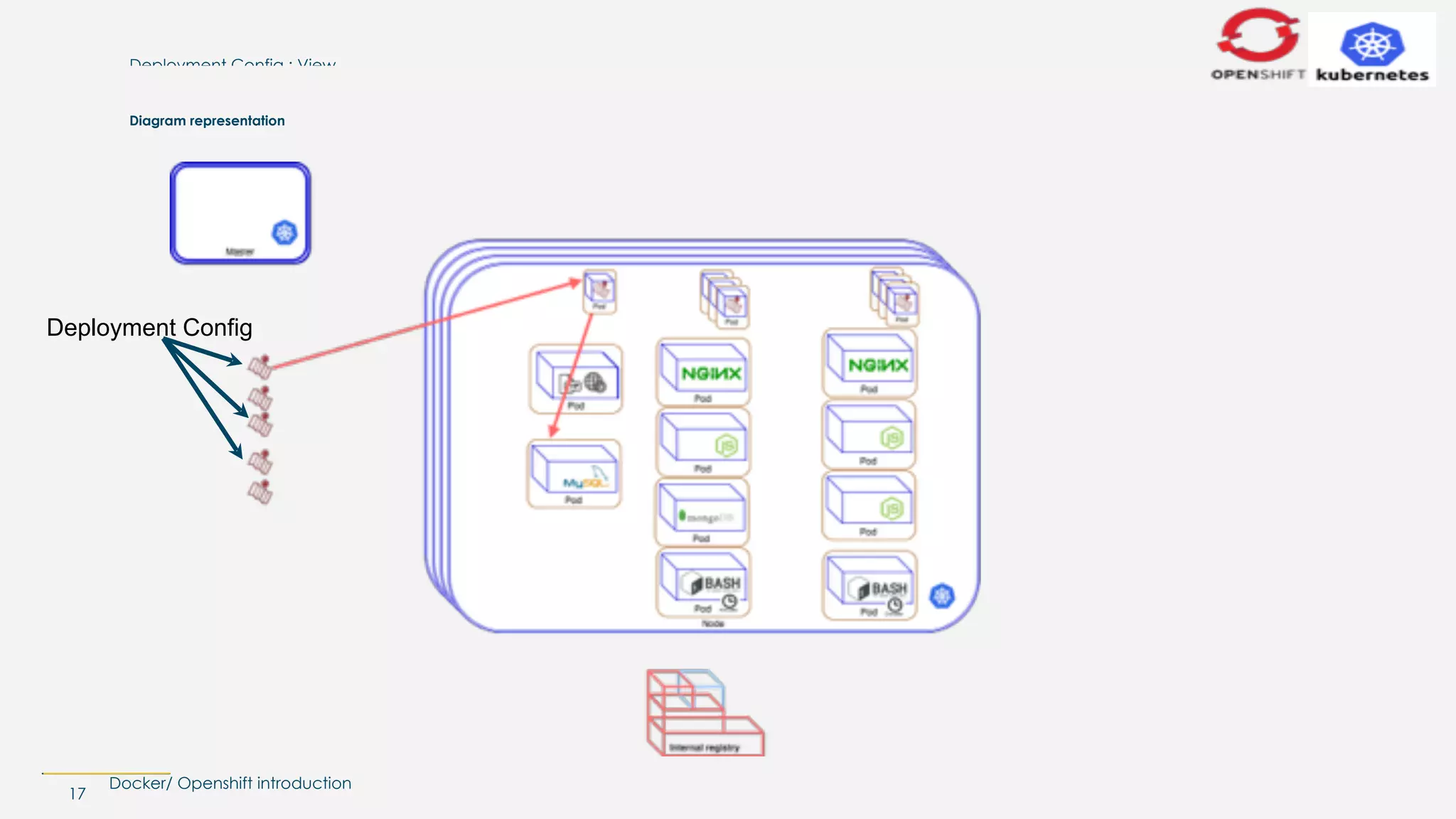
The document introduces Docker and OpenShift, explaining their functionalities in managing containers and deployment. It highlights how Docker encapsulates applications in images for easy deployment and how OpenShift serves as a platform as a service (PaaS) built on Kubernetes, streamlining the development and management of applications. Key concepts such as build configurations, deployment management, and resource allocation are also covered.