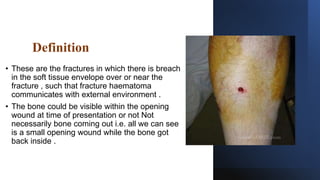
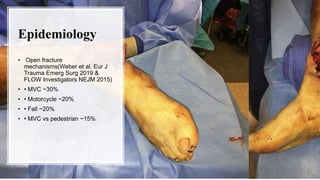
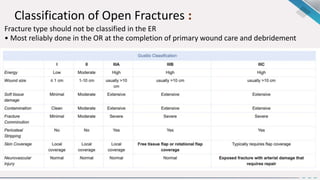
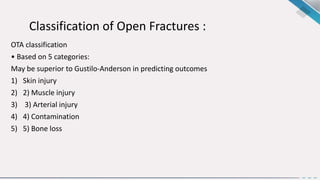
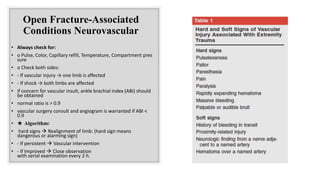
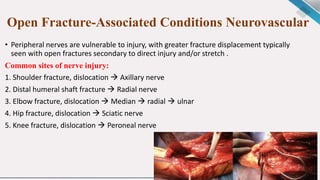
1. Open fractures occur when a broken bone pierces the overlying soft tissue, exposing the bone. The most common causes are motor vehicle accidents, motorcycle accidents, falls, and pedestrian injuries.
2. Treatment goals are to preserve life, limb, and function. This involves assessing for other injuries, stabilizing the patient, cleaning and debriding the wound, administering antibiotics and tetanus prophylaxis, and stabilizing the fracture—often initially with external fixation.
3. Further debridement and irrigation is done in the operating room, followed by temporary stabilization. Definitive reconstruction and internal or intramedullary fixation is done later, once the risk of infection decreases. Close monitoring is