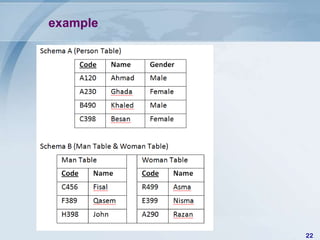
The document is a synthesis paper presented by Ali Ahmad Al Jadaa in a knowledge engineering course at Birzeit University, discussing ontology-based data integration. It highlights the challenges of data integration from diverse sources, including issues of heterogeneity in names, meanings, structures, and data types. The paper explores the significance of ontologies in facilitating data integration and presents various architectural solutions to address integration problems.








![Service Oriented Architecture
• Is a set of principles and methodologies for
designing and developing software in the
form of interoperable services[1]
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/knowledgeengineering12-ontology-baseddataintegration-alialjadaa-1125048-130116143444-phpapp02/85/ontology-based-data_integration-ali_aljadaa-1125048-16-320.jpg)
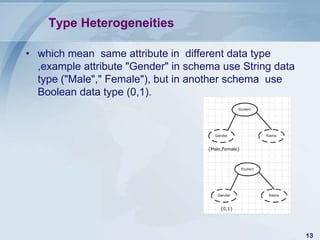
![Publish-Subscribe Architecture
• networking technologies and products
enable a high degree of connectivity across
a large number of computers, applications,
and users[5]
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/knowledgeengineering12-ontology-baseddataintegration-alialjadaa-1125048-130116143444-phpapp02/85/ontology-based-data_integration-ali_aljadaa-1125048-17-320.jpg)
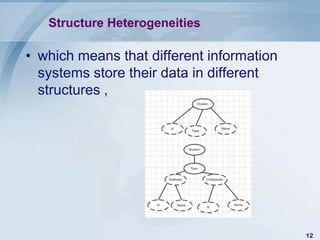
![Consolidation
• involves capturing of data from multiple
source systems and integrating into a single
persistent data store. The latency of the
information in the consolidated data store
depends upon whether batch or real time
data consolidation is being used and how
often the updates are being applied to the
data store.[2]
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/knowledgeengineering12-ontology-baseddataintegration-alialjadaa-1125048-130116143444-phpapp02/85/ontology-based-data_integration-ali_aljadaa-1125048-18-320.jpg)
![Multibase system
• A multibase (multiple database) system
allows the users to view the database
through a single global schema ,simulating
to users that a federated data base
exists.[3]
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/knowledgeengineering12-ontology-baseddataintegration-alialjadaa-1125048-130116143444-phpapp02/85/ontology-based-data_integration-ali_aljadaa-1125048-19-320.jpg)
![Data Warehouse
• Is a database used for reporting and data
analysis[4]
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/knowledgeengineering12-ontology-baseddataintegration-alialjadaa-1125048-130116143444-phpapp02/85/ontology-based-data_integration-ali_aljadaa-1125048-20-320.jpg)
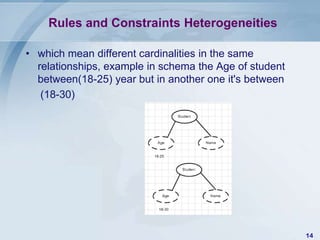
![Federated systems (Virtual Data Integration)
• It is characterized by the existence of a
federated schema which establishes the
interface to this integrated system.[4]
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/knowledgeengineering12-ontology-baseddataintegration-alialjadaa-1125048-130116143444-phpapp02/85/ontology-based-data_integration-ali_aljadaa-1125048-21-320.jpg)