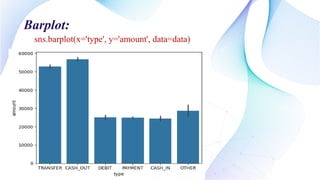
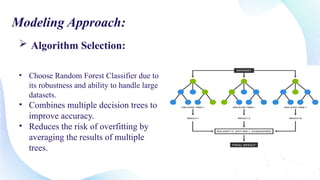
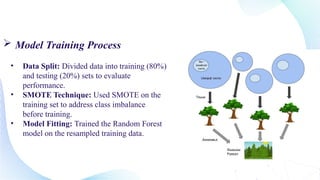
This document outlines the development of a machine learning model using Python to detect online payment fraud through a random forest classifier. The model addresses issues of imbalanced data and aims to accurately identify fraudulent transactions while minimizing false positives. Key components include data preprocessing, feature selection, and model evaluation metrics showing an accuracy of 86.91%.









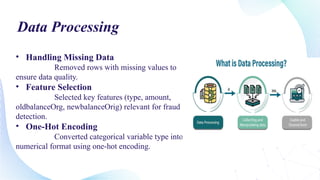
![data.dropna(inplace=True)
data.isnull().sum()
x = data[['type', 'amount', 'oldbalanceOrg',
'newbalanceOrig']]
y = data['isFraud']
Feature Selection
Handling Missing Data
CODE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onlinefraudprojectfianlptx-240828052429-0bb1b3e0/85/Online-Payment-fraud-Detection-Final-Project-12-320.jpg)
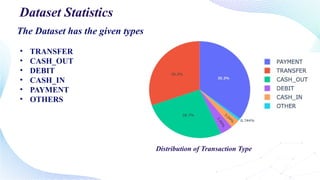
![type=data['type'].value_counts()
transactions=type.index
quantity=type.values
figure=px.pie(data,
values=quantity,
names=transactions,
title='Distribution of Transaction Type')
figure.show()
CODE:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onlinefraudprojectfianlptx-240828052429-0bb1b3e0/85/Online-Payment-fraud-Detection-Final-Project-14-320.jpg)