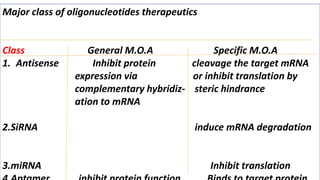
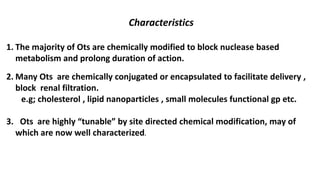
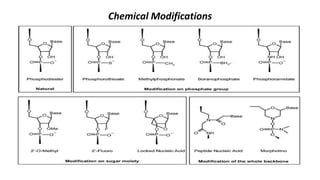
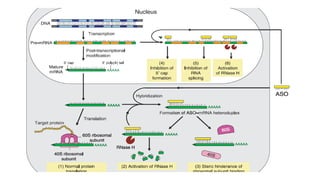
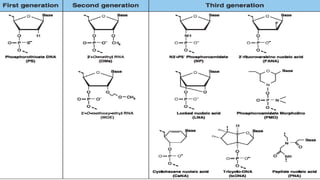
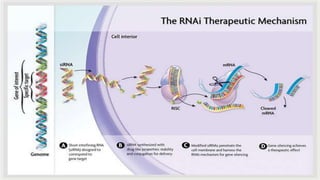
Oligonucleotides therapeutics work by altering gene expression through complementary binding to mRNA. There are three major classes: antisense oligonucleotides inhibit protein expression through hybridization to mRNA, siRNA induce mRNA degradation, and miRNA inhibit translation. Oligonucleotides are modified through conjugation or encapsulation to improve delivery and stability, and resist nuclease degradation. Antisense oligonucleotides specifically designed to hybridize with mRNA can function through RNase H degradation or steric blocking of translation.