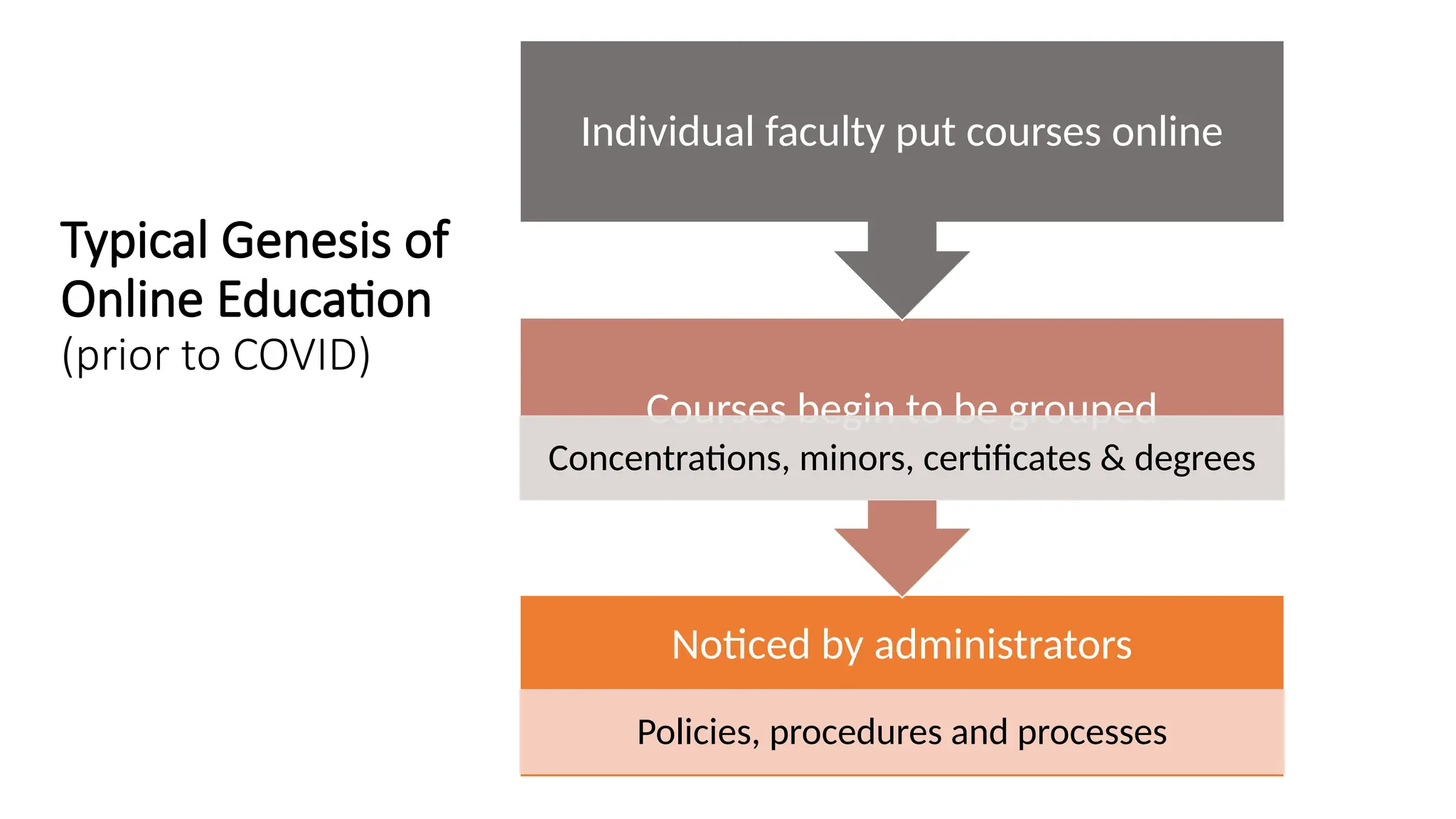
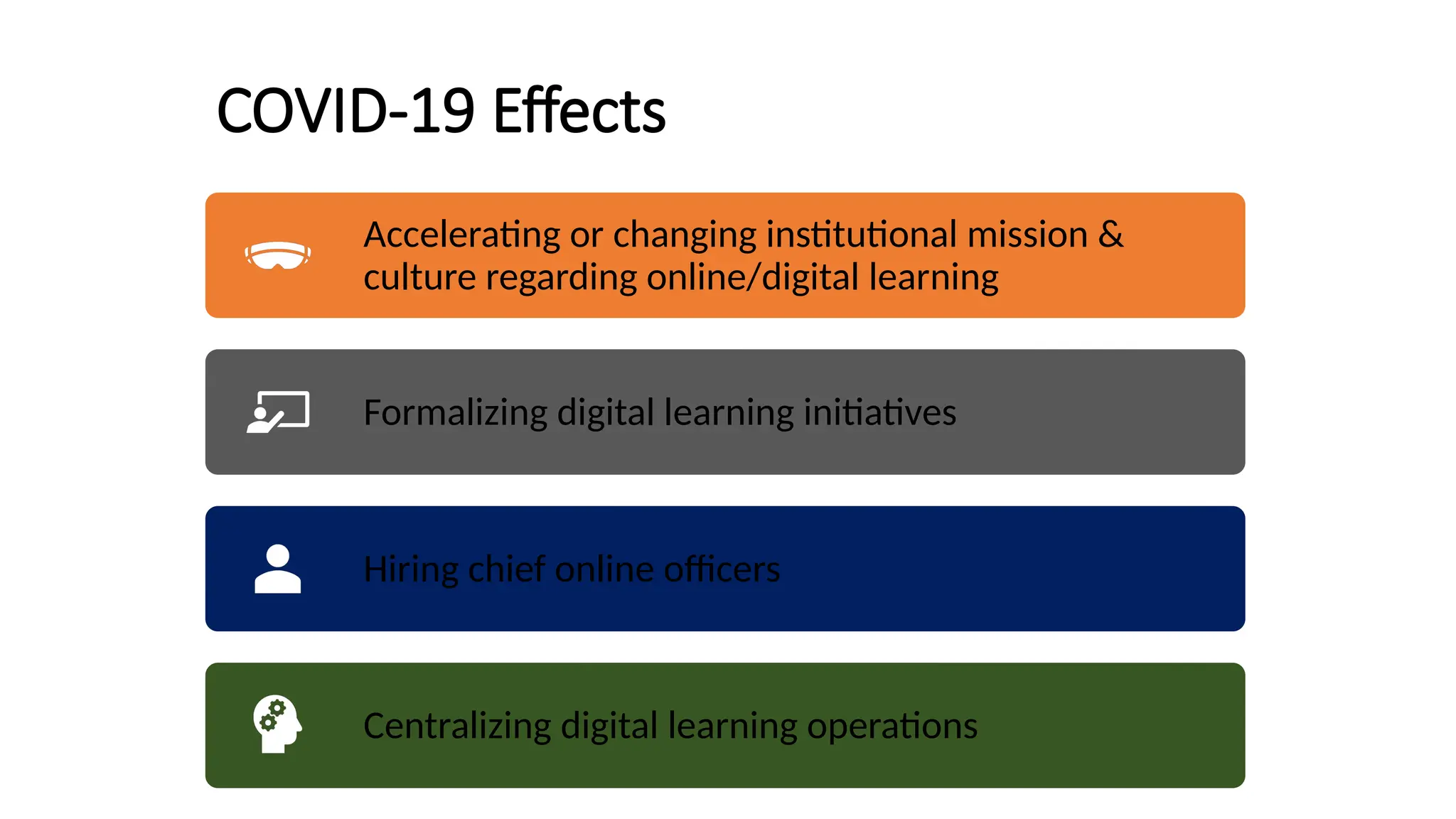
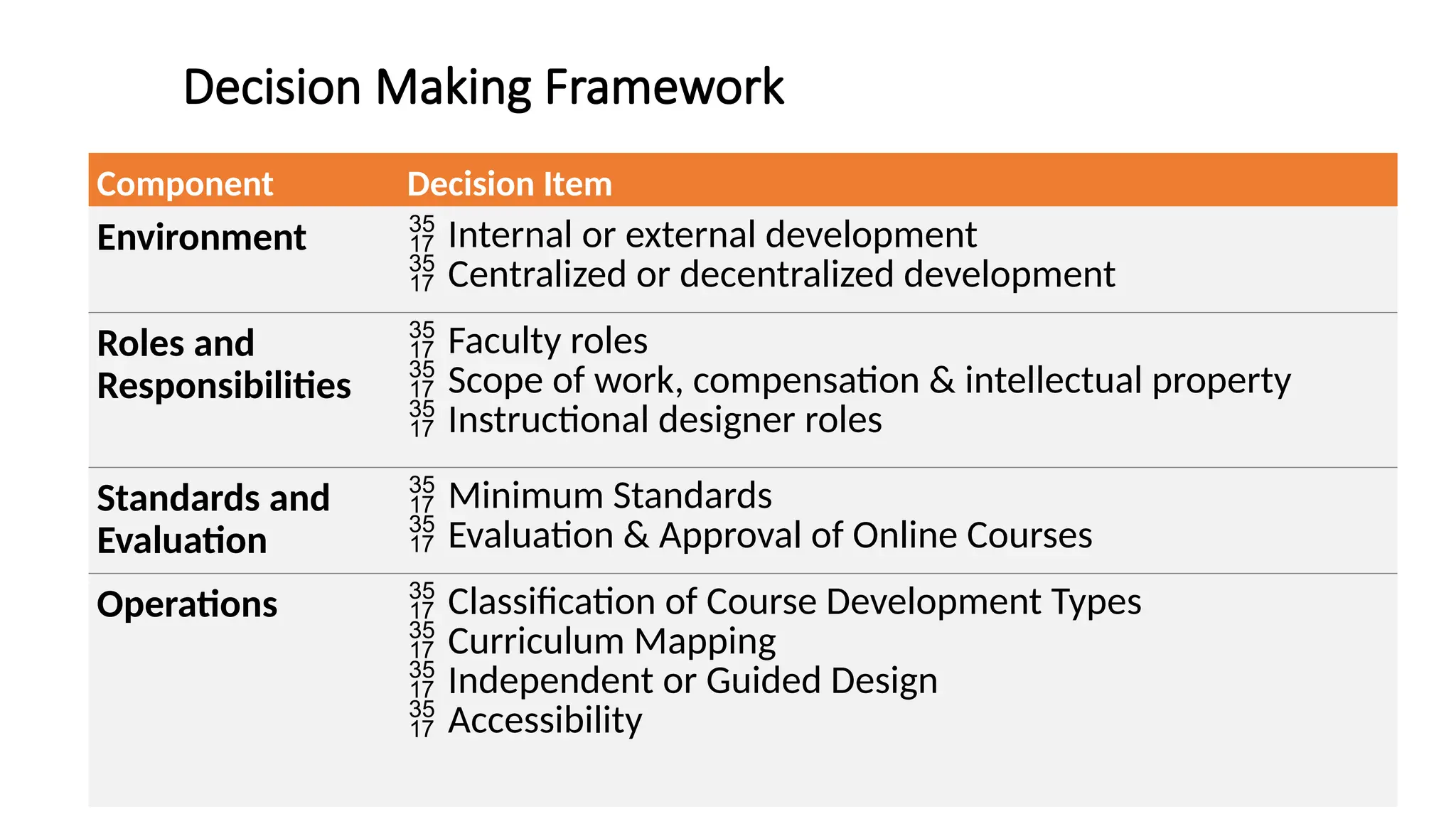
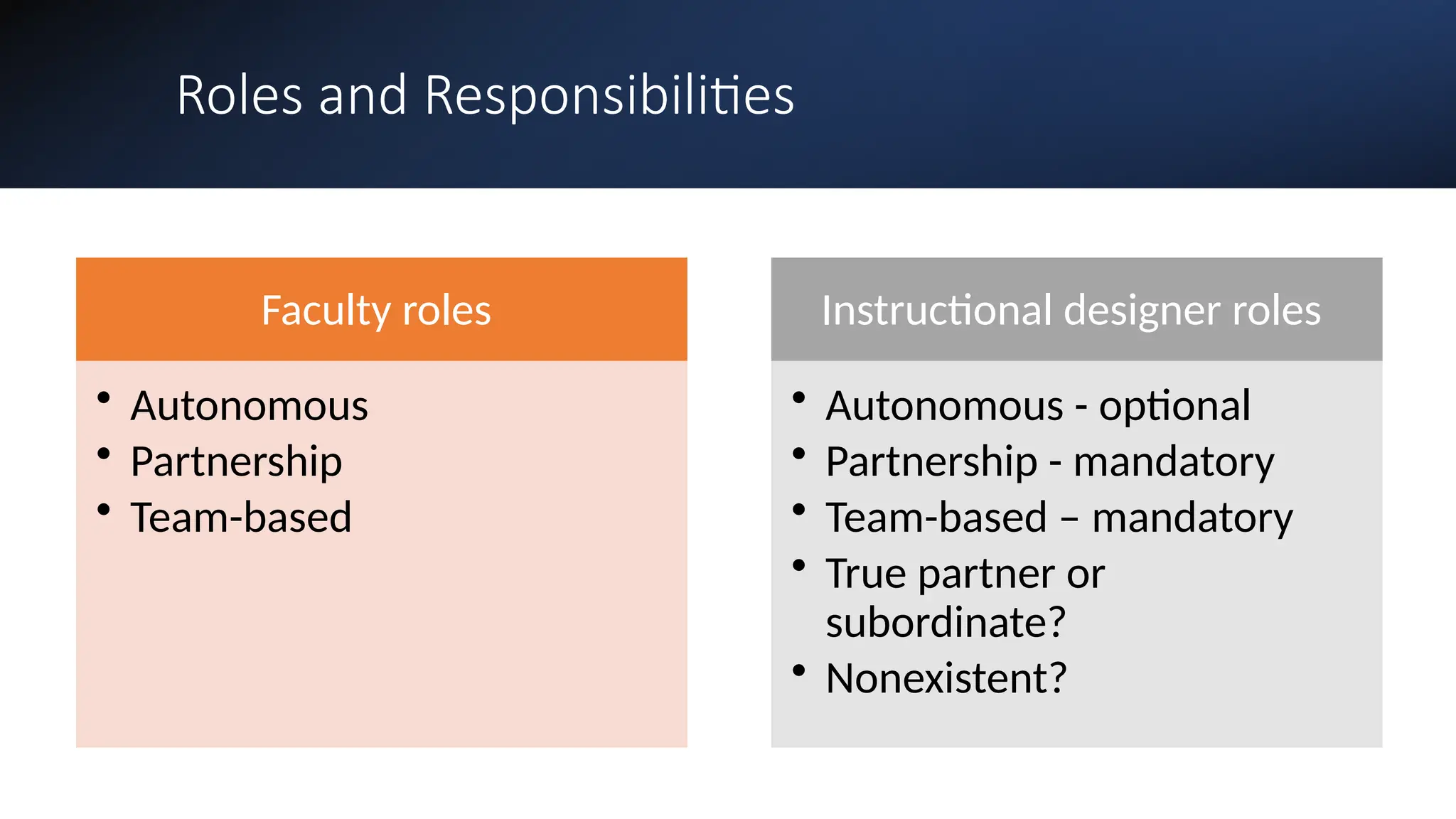
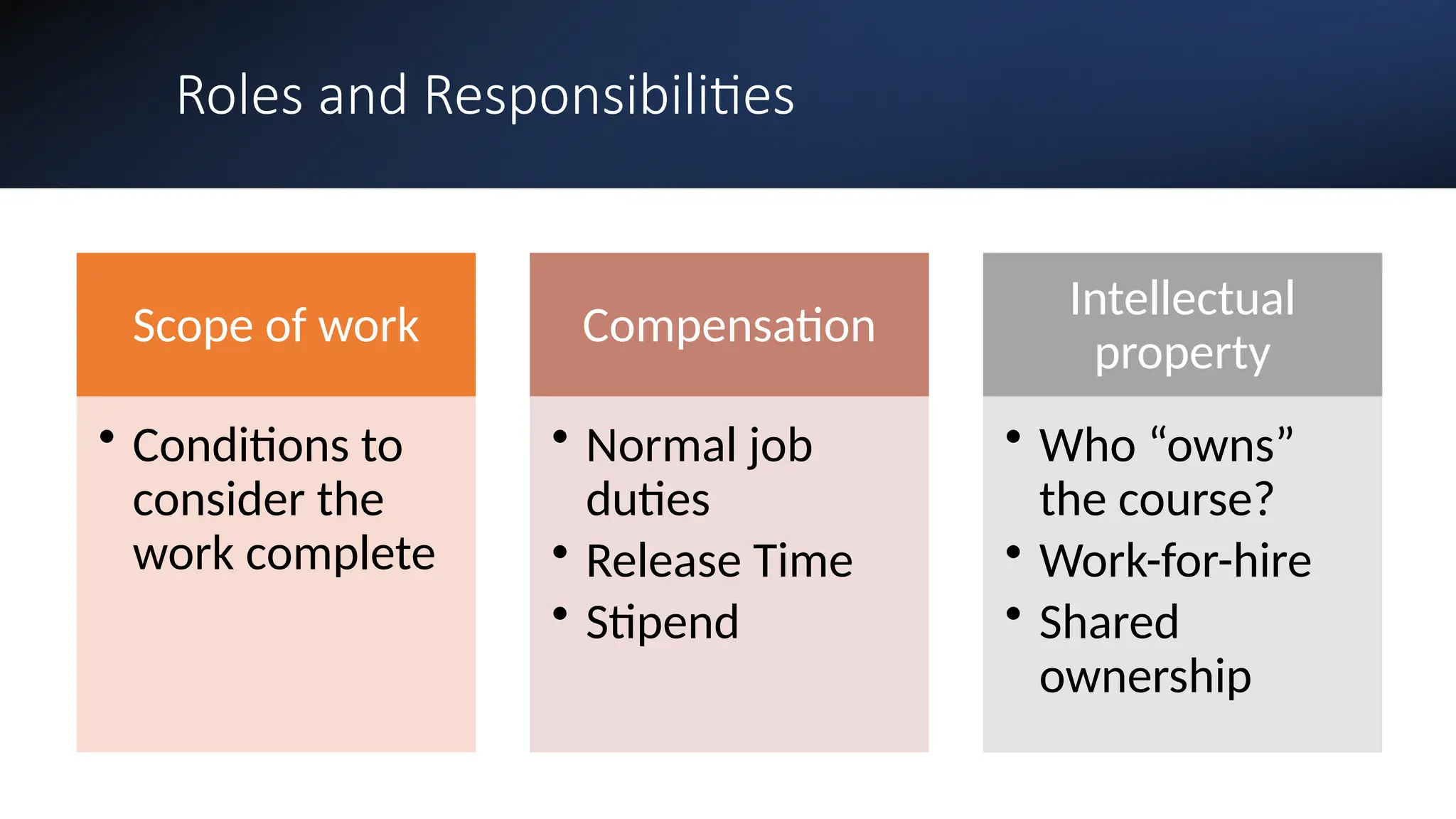
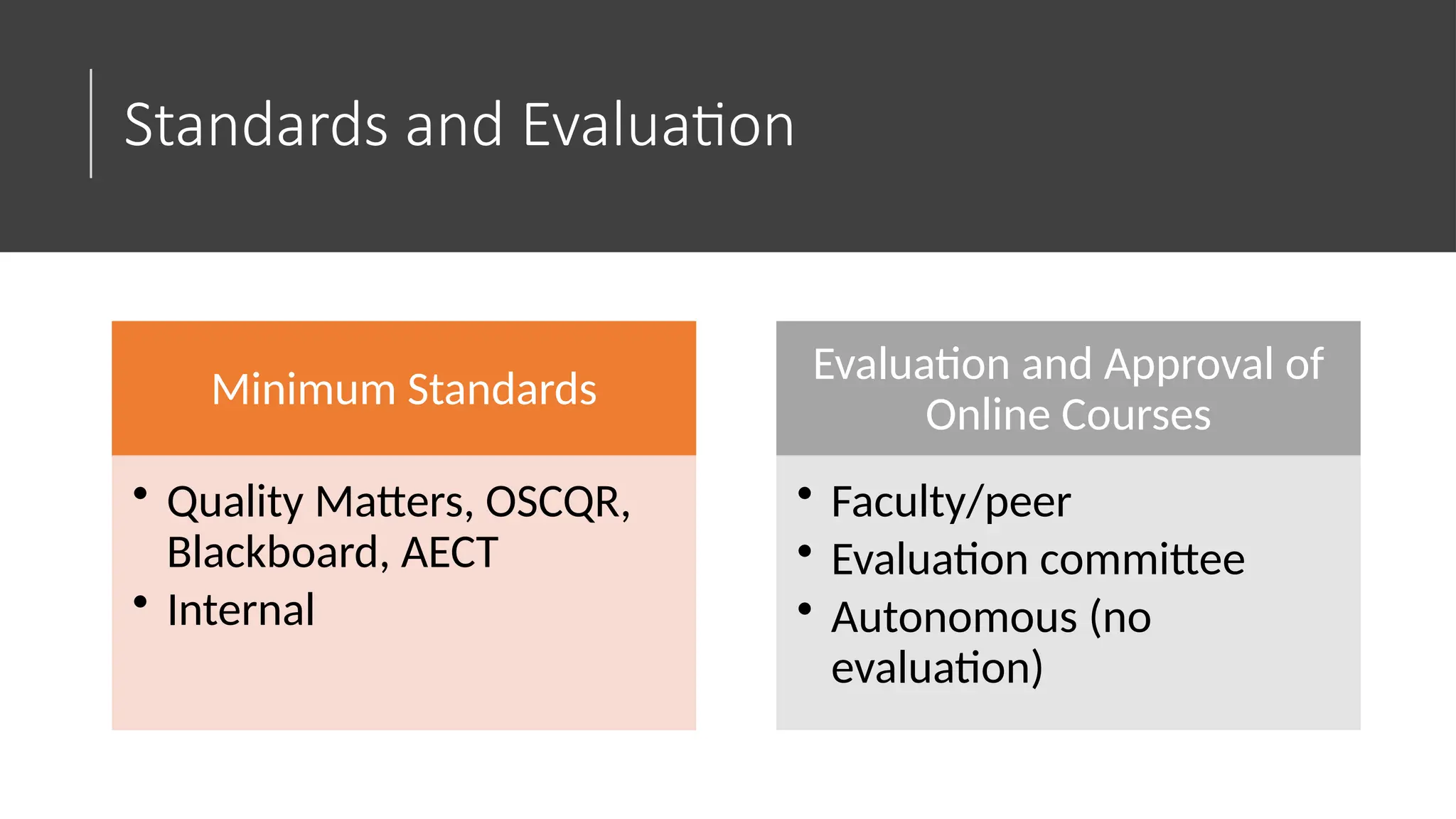
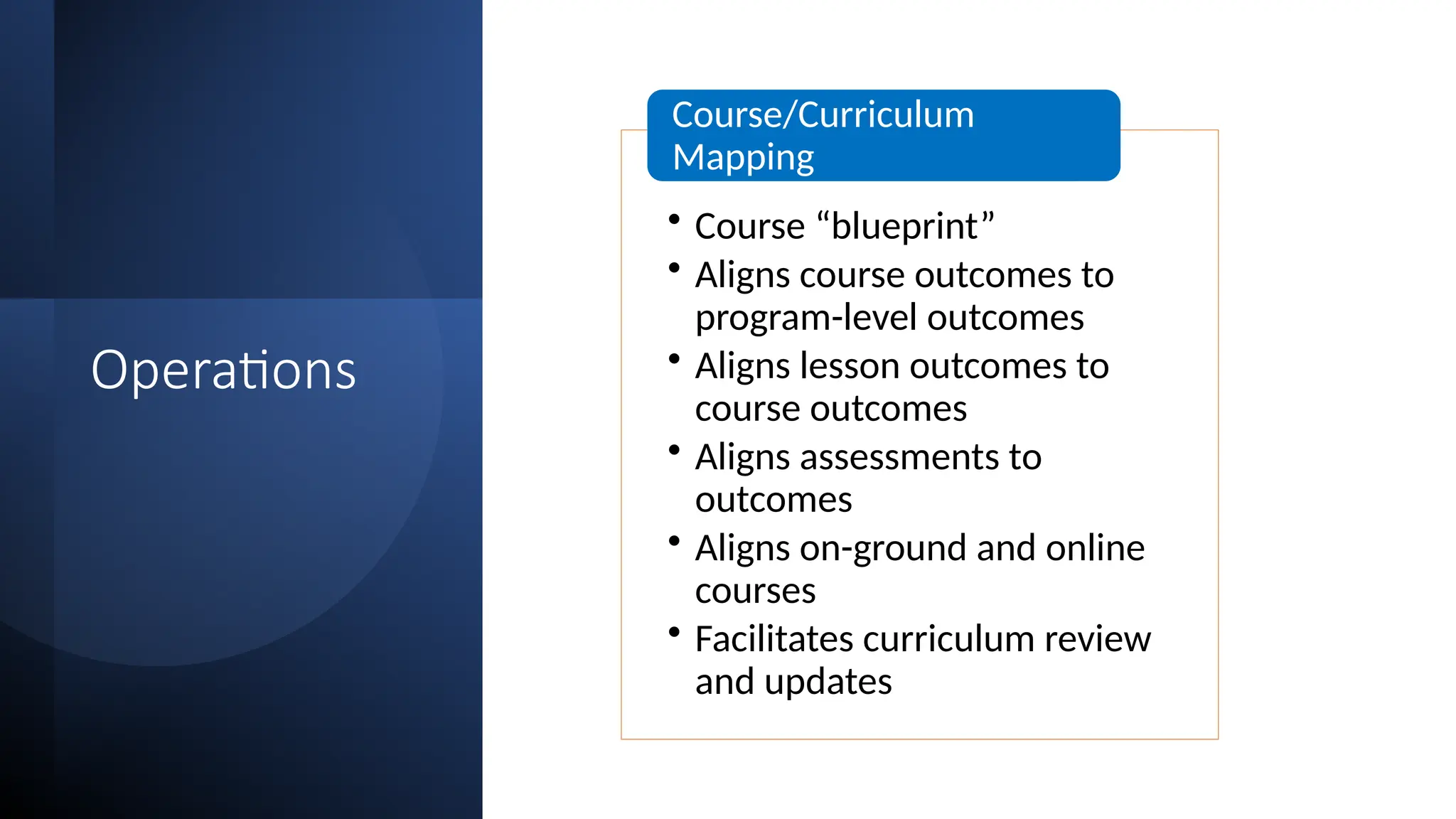
The document discusses the evolution and management of online course development in higher education, particularly in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. It emphasizes the importance of formalizing digital learning initiatives, centralizing operations, and establishing clear roles and responsibilities to enhance course quality and consistency. Key considerations include faculty roles, compensation, intellectual property, and adherence to standards for online course evaluation and accessibility.