This document provides an overview of data warehousing. It defines a data warehouse as a subject-oriented, integrated, time-variant and non-volatile collection of data that helps analysts make informed decisions. Key points include:
- A data warehouse contains consolidated historical data from multiple sources to help executives analyze business trends and make strategic decisions.
- Features include being subject-oriented around topics like products or customers, integrating data from different systems, only including time-specific data, and not overwriting previous data when new info is added.
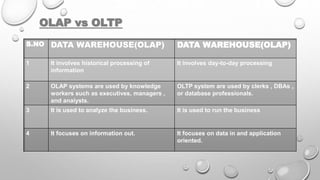
- Online analytical processing (OLAP) allows users to easily extract and analyze data from different perspectives across multiple database systems.
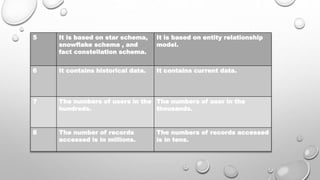
- Data warehouses differ from operational transaction systems which