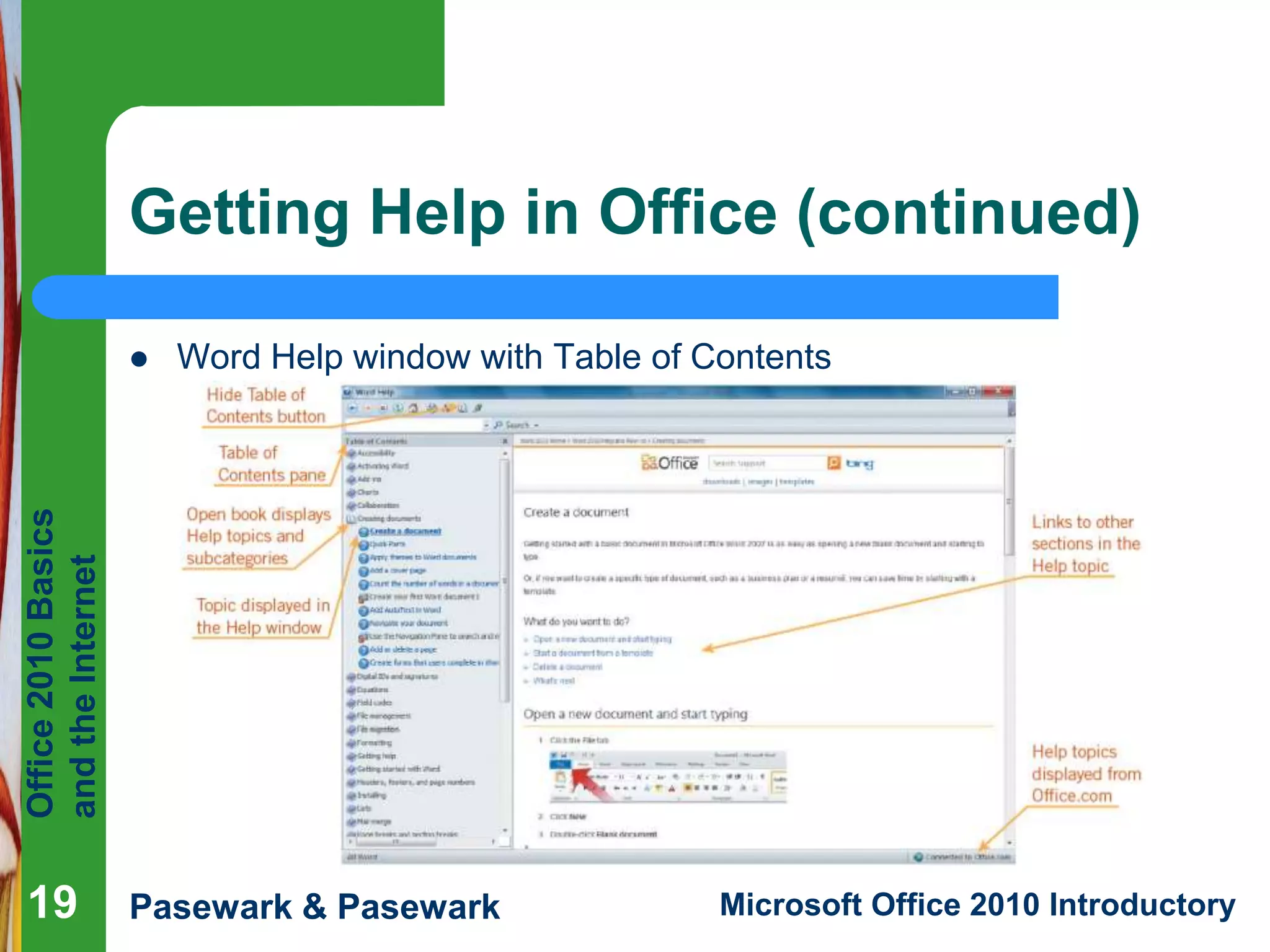
Microsoft Office 2010 is an integrated software suite containing programs like Word, Excel, PowerPoint. The document discusses the basic functions and features of Office 2010 programs, including how to open, save and close files using Backstage view. It also covers how to access help resources and use a web browser to view web pages on the Internet.