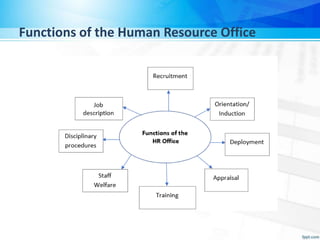
The human resource management office coordinates manpower supply to help the organization achieve its goals through both strategic and administrative functions. Key functions include recruitment, orientation, deployment, performance appraisal, training, staff welfare, disciplinary procedures, maintaining job descriptions, and liaising with other departments. The overall goal is to ensure a happy, motivated workforce by continuously monitoring employee feedback.