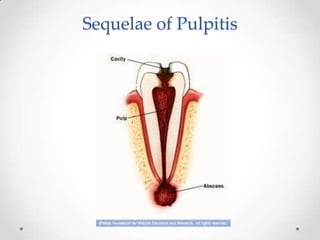
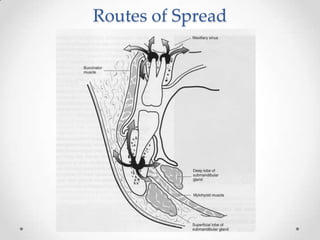
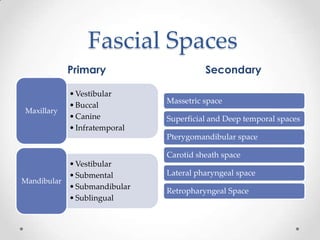
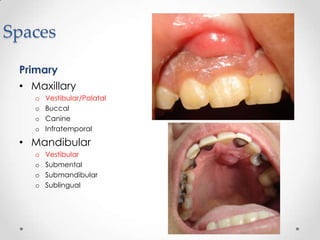
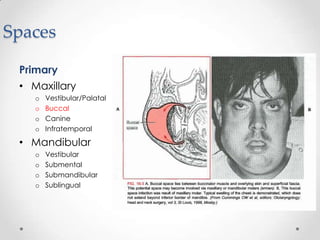
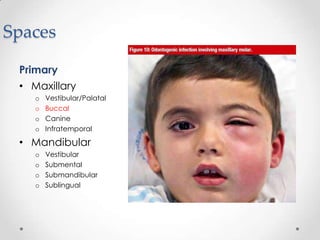
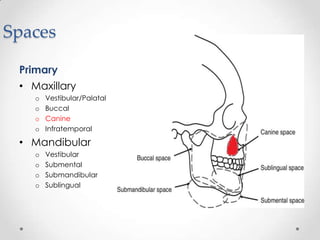
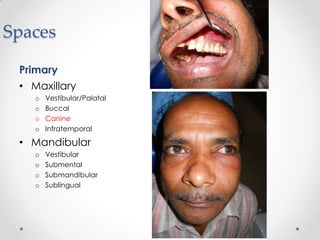
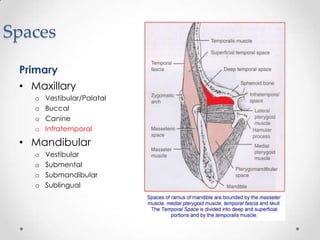
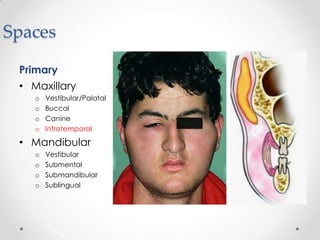
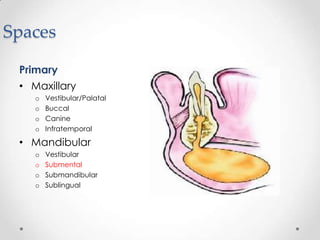
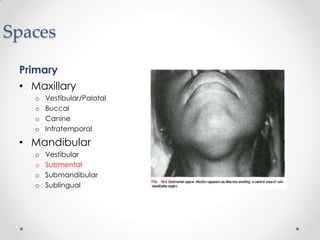
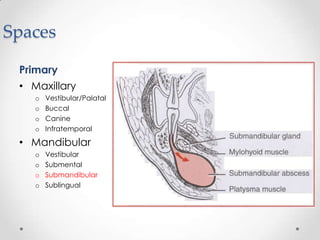
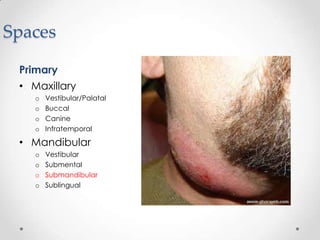
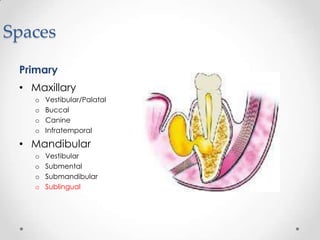
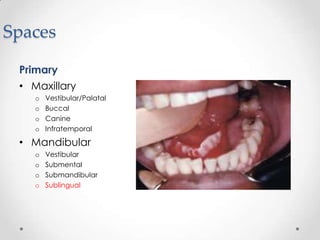
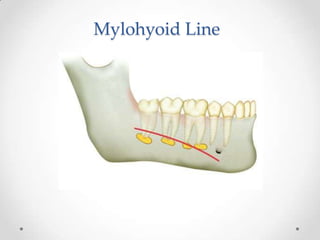
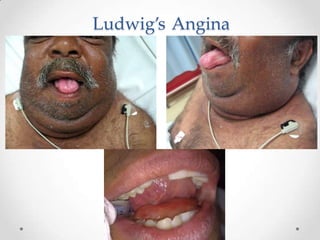
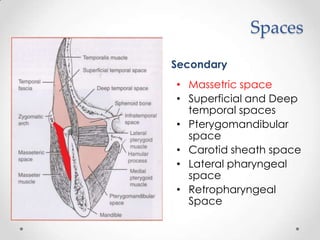
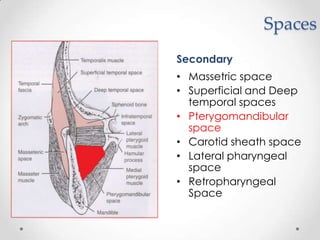
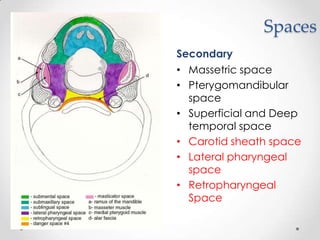
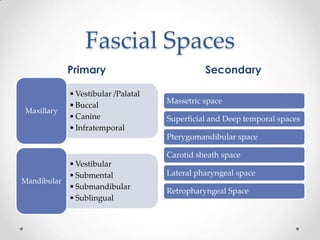
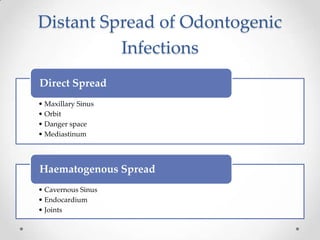
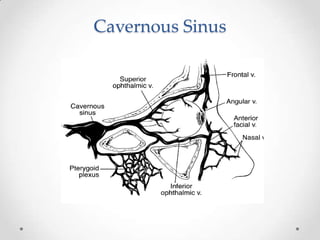
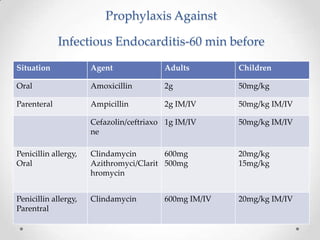
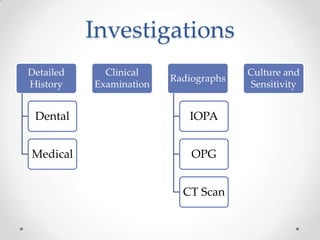
This document discusses odontogenic infections, which originate from tooth-related pathology. It describes how infections can spread from primary fascial spaces around the teeth to secondary spaces deeper in the head and neck region. Virulence of microorganisms and host immune response determine if an infection remains localized or becomes diffuse. Enzymes help degrade tissues, allowing spread through paths of least resistance. Clinical features may include swelling, pain, and fever. Diagnosis involves history, examination, radiographs, and culture/sensitivity testing. Treatment involves antibiotics, surgery to drain or remove the dental cause, and follow up.