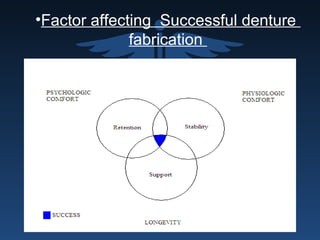
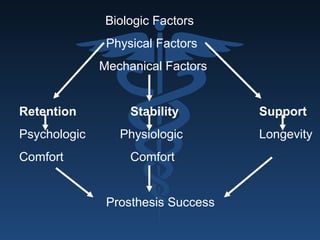
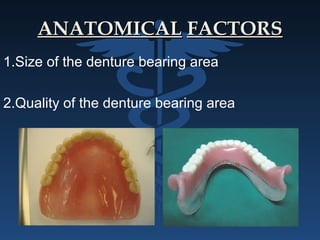
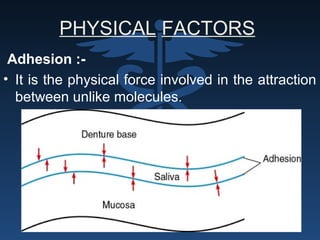
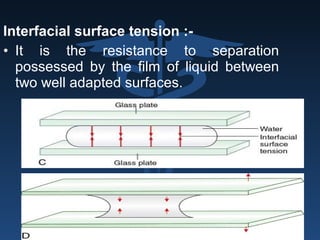
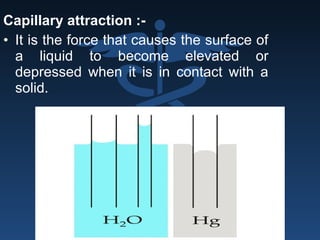
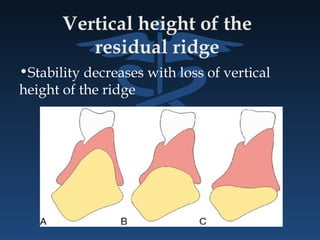
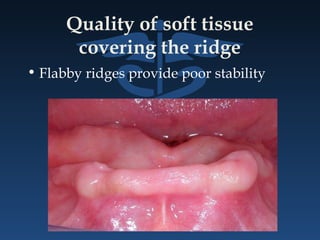
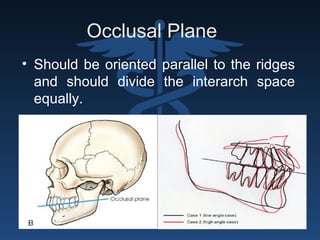
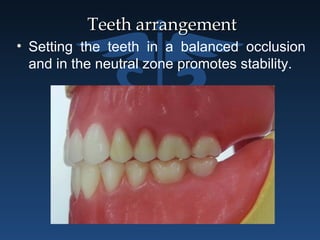
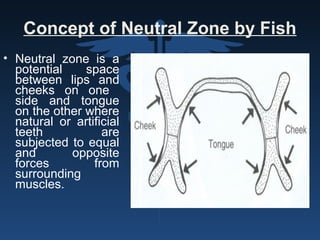
The document outlines the importance of retention, stability, and support in complete denture fabrication, detailing the factors influencing these characteristics. It explains the physical, biological, mechanical, and psychological factors that affect retention and stability, as well as the significance of educating patients on proper denture usage. The text emphasizes that effective denture function relies heavily on maximizing the contact area and adapting to the underlying tissues to achieve optimal comfort and longevity.