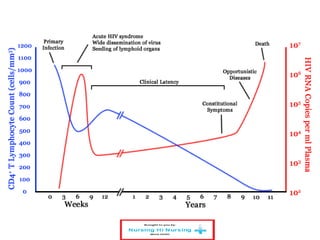
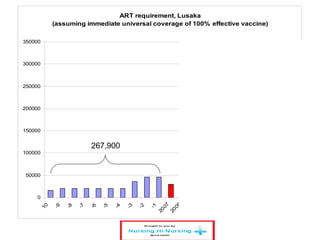
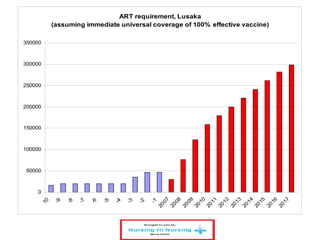
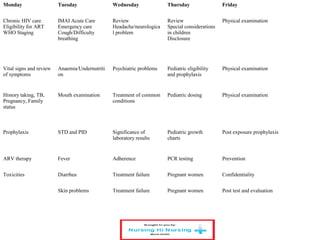
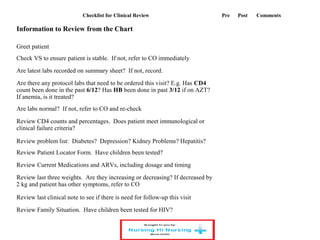
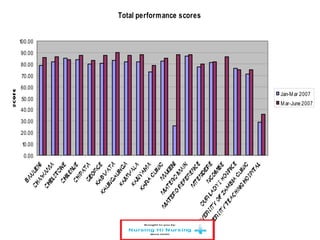
This document discusses how nurses are being trained in Zambia to take on expanded roles in supporting rapid scale up of antiretroviral therapy (ART) for HIV patients. It outlines a training program where nurses receive 5 days of classroom instruction followed by clinical mentoring to learn how to triage and manage stable HIV patients on ART. Over 670 nurses and clinical officers have been trained, and 74 nurses have completed the triage training program allowing them to independently manage patients and help address staffing shortages. Ongoing monitoring shows the quality of nurse-managed care has improved over time as their clinical skills and data management abilities progress.