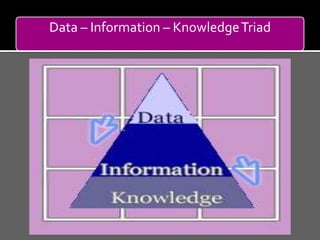
Nursing informatics is the use of computers and information technology to support nursing practice, education, administration, research, and clinical care. It involves managing nursing data, information, and knowledge through technologies like electronic health records. The goal is to improve patient health outcomes and support nurses' decision-making. While nursing informatics is still emerging, national nursing organizations recommend nurses become computer literate as healthcare increasingly relies on digital tools and data.