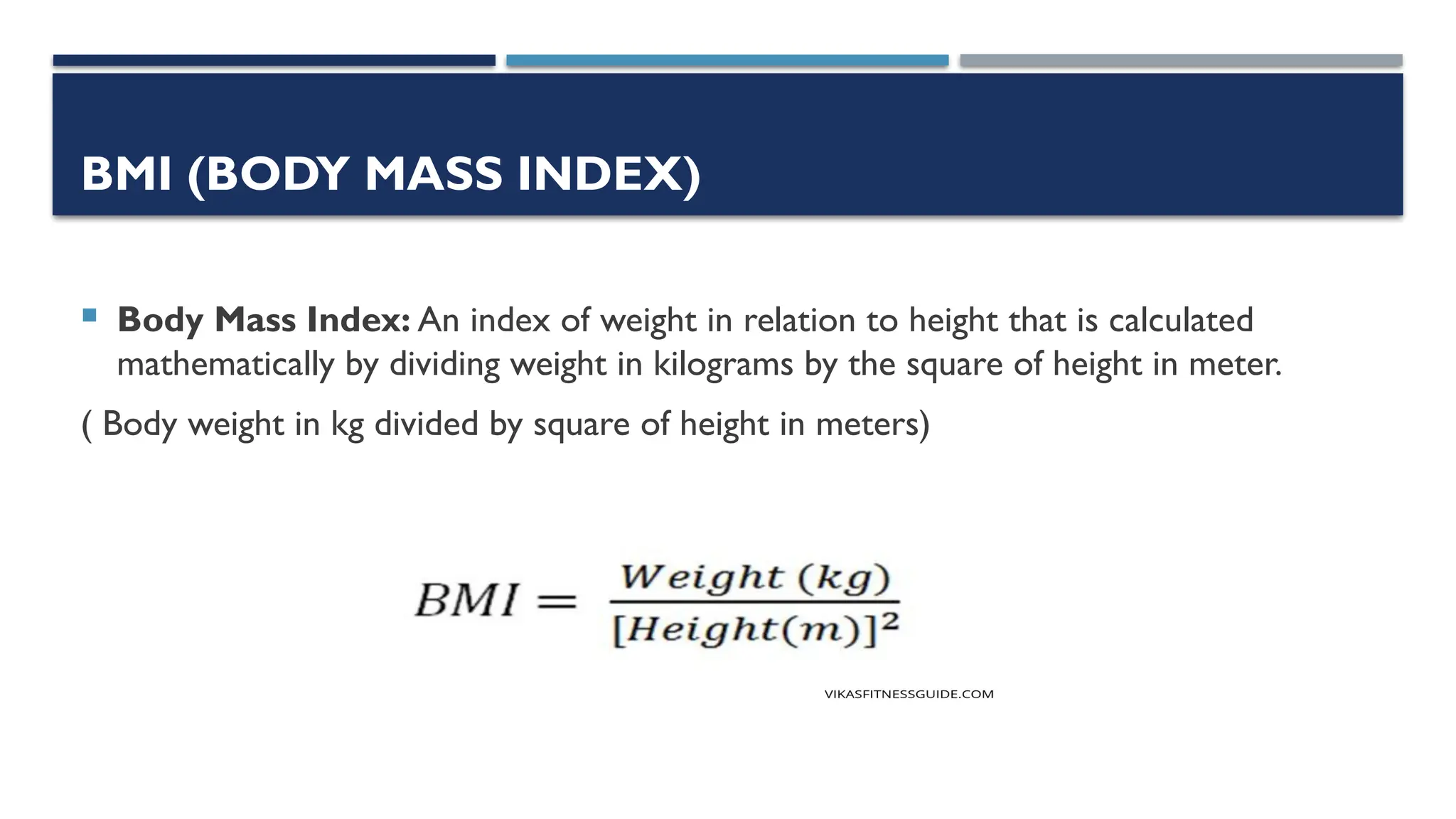
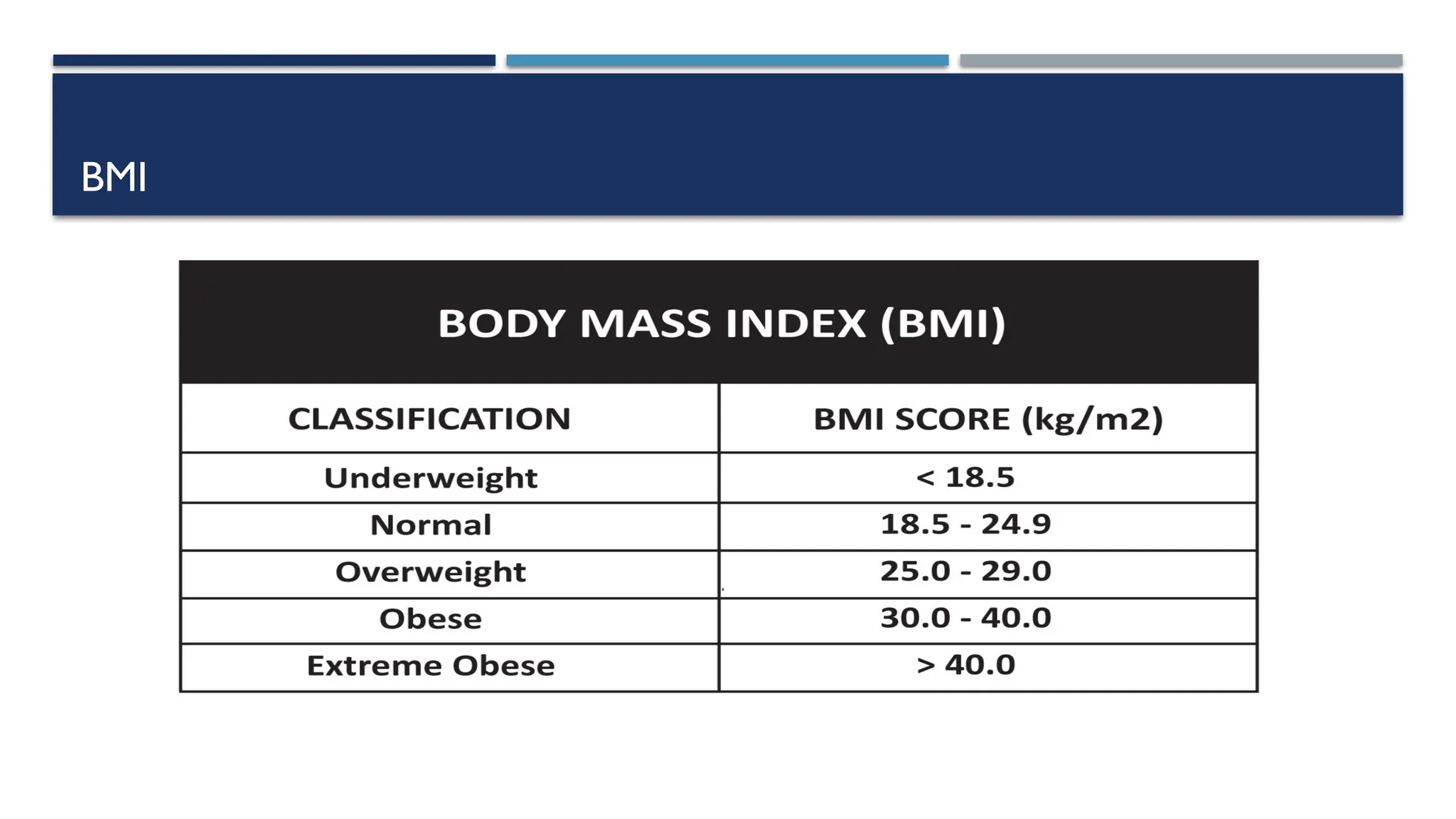
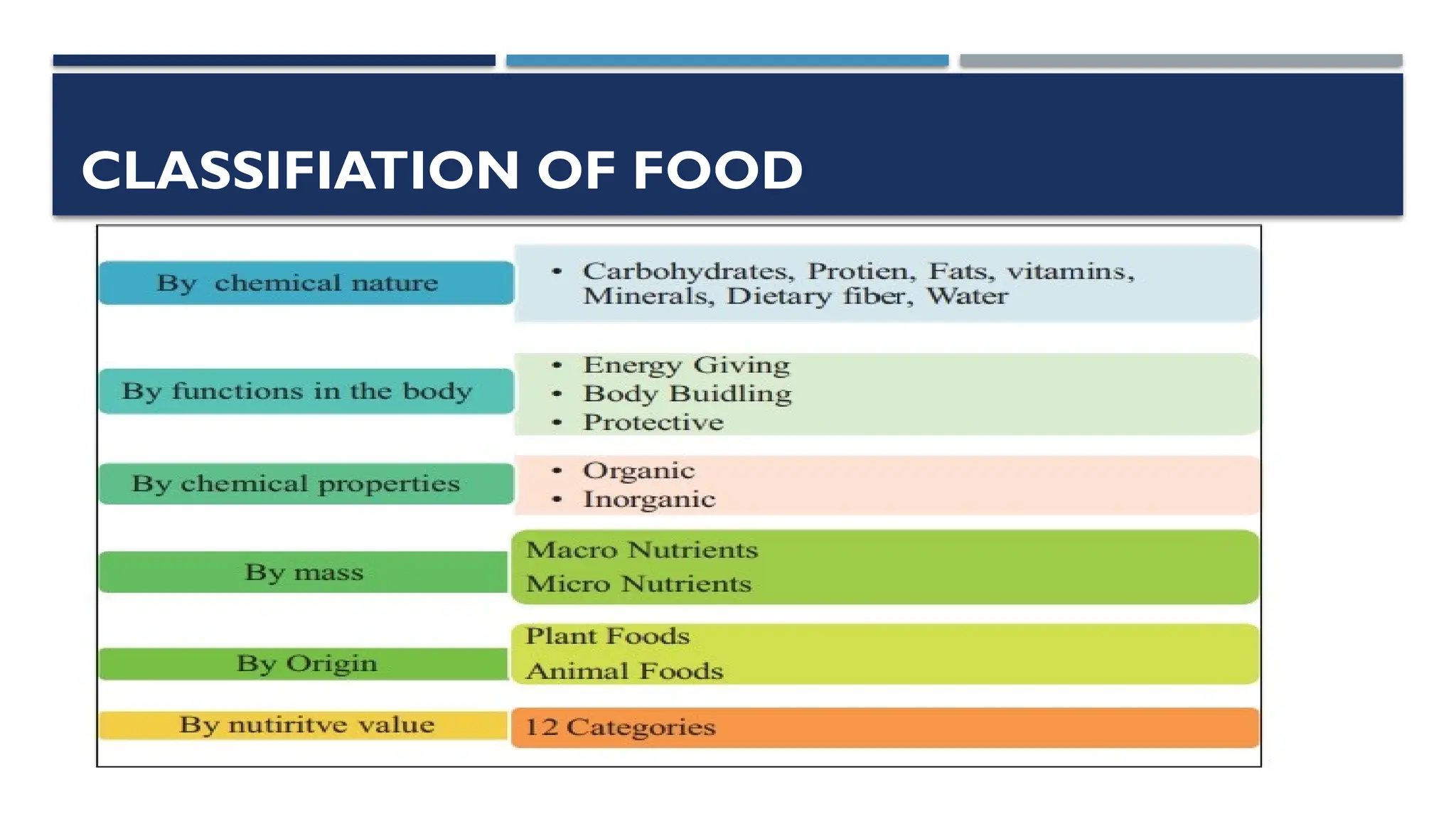
The document provides an overview of nutrition, defining it as the science of food and its relationship to health. It details various terms related to nutrition, the importance of balanced diets, and the classification of nutrients and foods. Additionally, it discusses the role of dietitians in addressing dietary issues and emphasizes the significance of adequate nutrition in preventing malnutrition and supporting health.