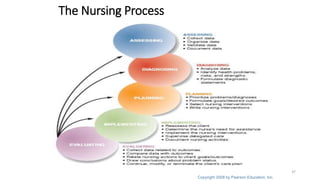
The document outlines the nursing process, which consists of assessment, planning, implementation, and evaluation. It describes the assessment phase in detail. Assessment involves collecting both subjective and objective data through various methods like observation, interview, and examination. The nurse organizes, validates, and documents the collected data to identify the patient's health status, problems, and needs in order to develop an appropriate care plan.