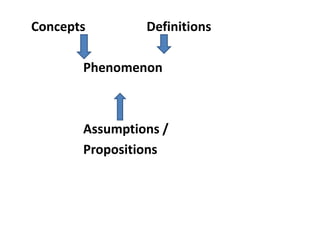
Nursing theories provide a framework for nursing practice, education, research, and management. They describe concepts like person, health, environment, and nursing that are important to the nursing profession. A theory consists of concepts, definitions, assumptions, and propositions that explain relationships between concepts. Developing nursing theories helps nursing establish a unique body of knowledge and distinguishes its practice from other professions. Theories guide the assessment, intervention, and evaluation of nursing care.