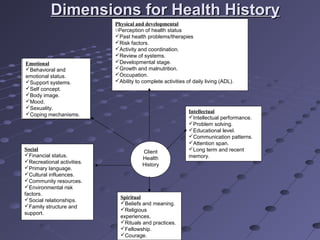
Nursing assessment involves the systematic collection of a patient's physiological, psychological, sociological, and spiritual data. It is the first phase of the nursing process. There are several types of nursing assessments, including initial, focused, emergency, and time-lapsed assessments. The goals of assessment are to gather baseline data, identify health problems, determine the patient's strengths and risks, and provide data to inform diagnosis. Key steps in assessment involve collecting, validating, organizing, and communicating patient information.