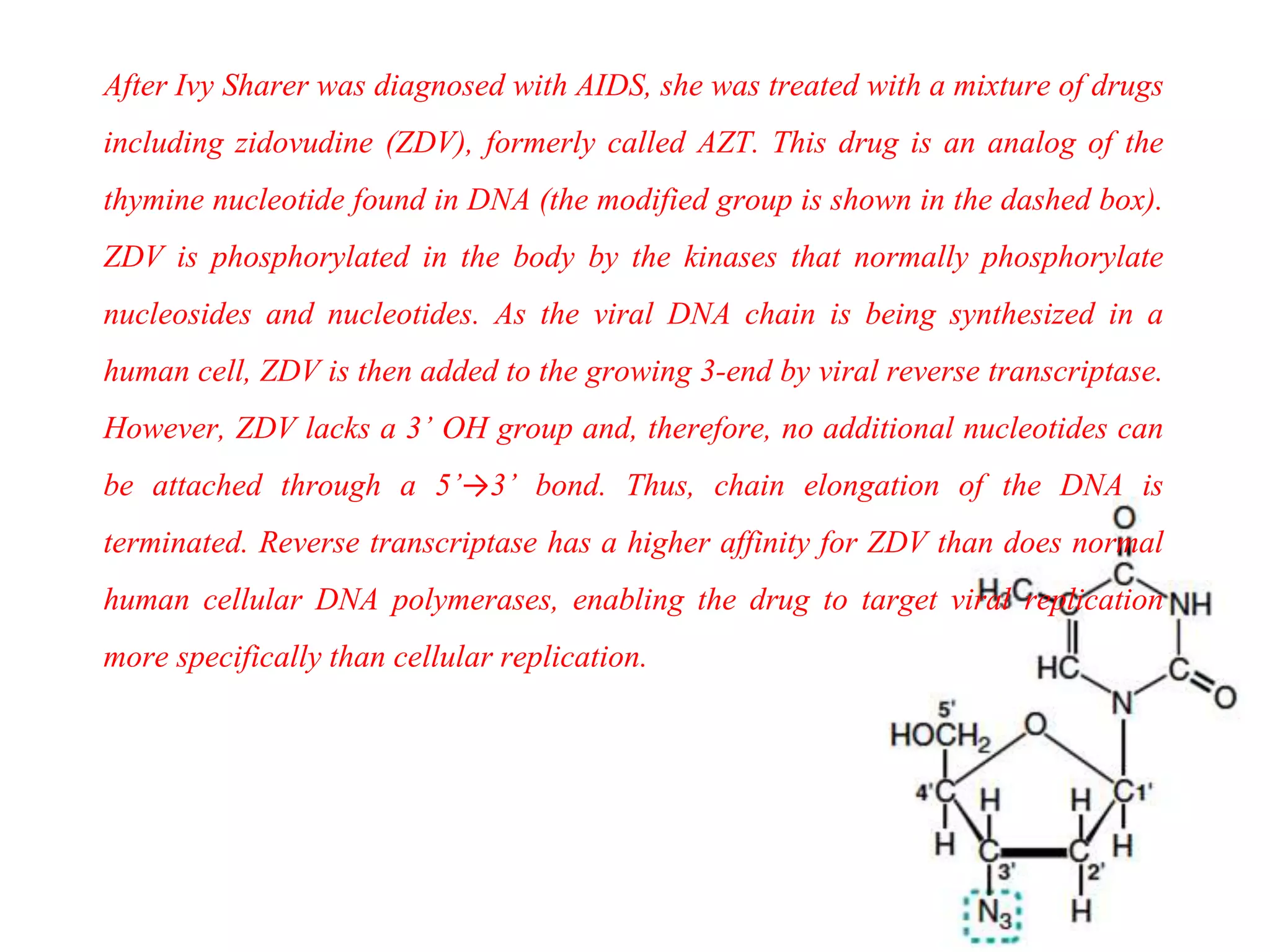
1. The document discusses nucleic acids, their structures and functions. It describes nucleosides, nucleotides, DNA, RNA and their components.
2. Synthetic nucleotide analogs are discussed that are used as chemotherapy drugs and antivirals by interfering with DNA replication. Zidovudine and 5-fluorouracil are highlighted as examples.
3. The clinical cases provided are used to explain how zidovudine works against HIV and how 5-fluorouracil inhibits cancer cell proliferation.