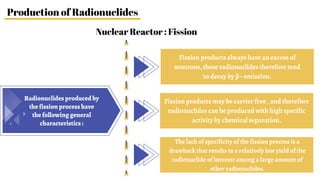
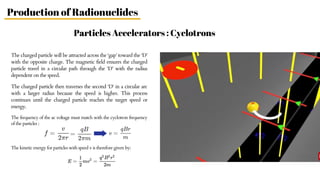
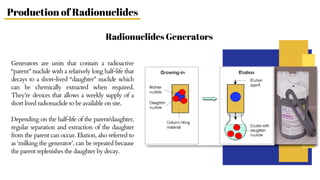
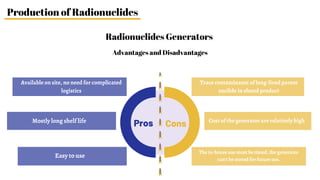
Radiopharmaceuticals are sterile pharmaceutical drugs containing radionuclides used for diagnostic, therapeutic, or sterilization purposes. They are produced using nuclear reactors, particle accelerators like cyclotrons, or generators. Nuclear reactors produce radionuclides via fission or neutron activation, while cyclotrons use charged particles to induce nuclear reactions. Generators contain a long-lived parent nuclide that decays to a short-lived daughter nuclide, allowing weekly extraction of the daughter. Radiopharmaceuticals must have characteristics like specific activity and stability suited to their diagnostic or therapeutic application, while minimizing radiation exposure according to ALARA principles.