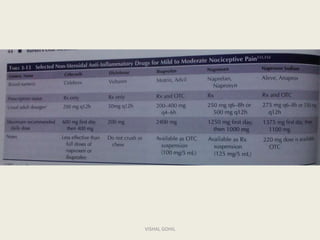
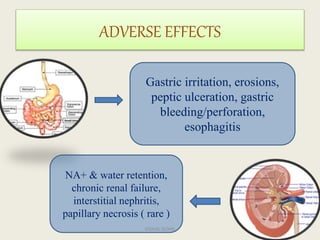
The document summarizes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). It discusses their mechanism of action by inhibiting cyclooxygenase enzymes and reducing prostaglandin formation, leading to analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic effects. NSAIDs are classified based on selectivity for COX-1 and COX-2. Common NSAIDs and their uses for pain relief are described. Adverse effects include gastric irritation and bleeding. Dental considerations advise avoiding NSAIDs if allergic and not using aspirin before and after surgery due to bleeding risk.