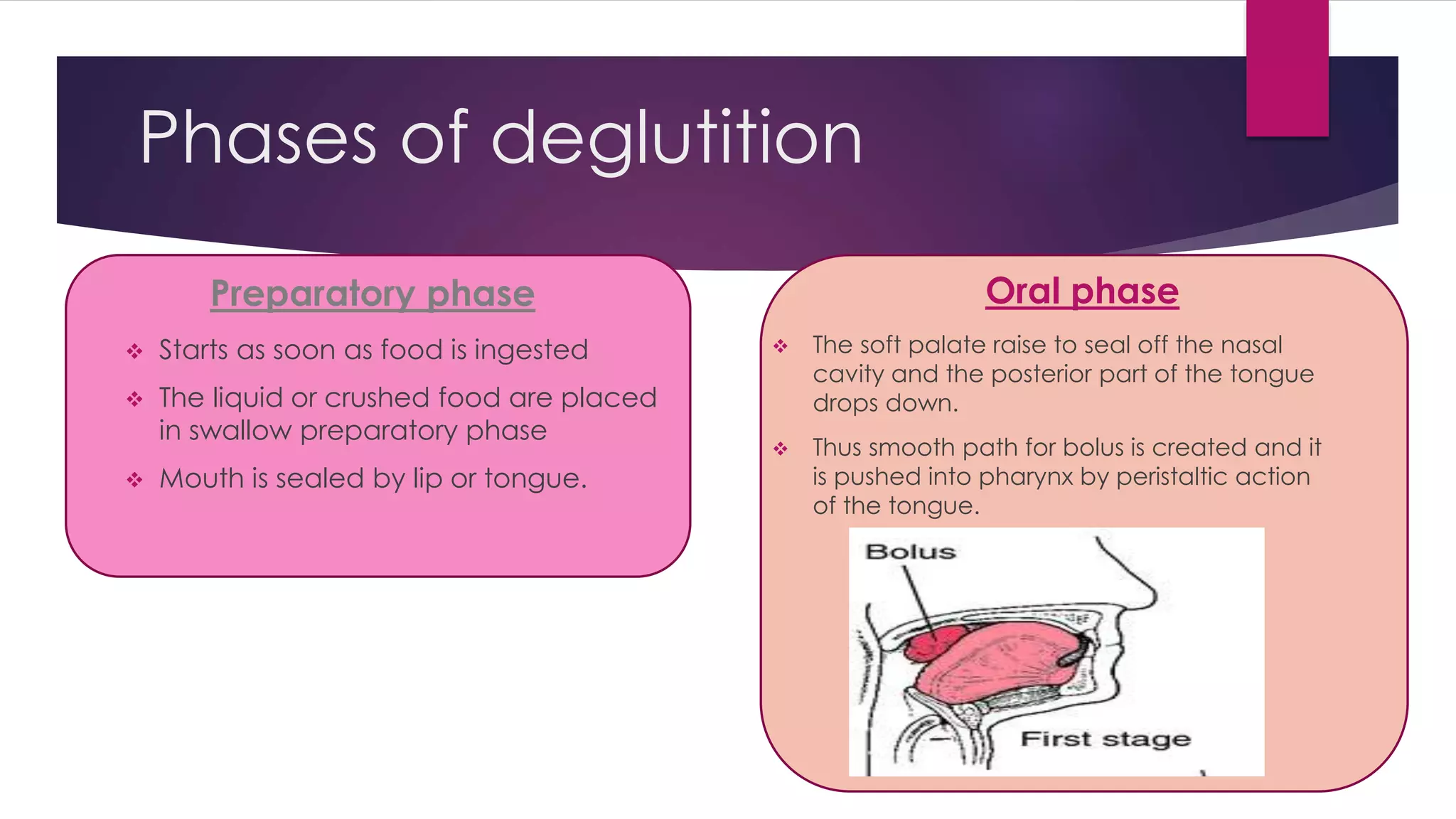
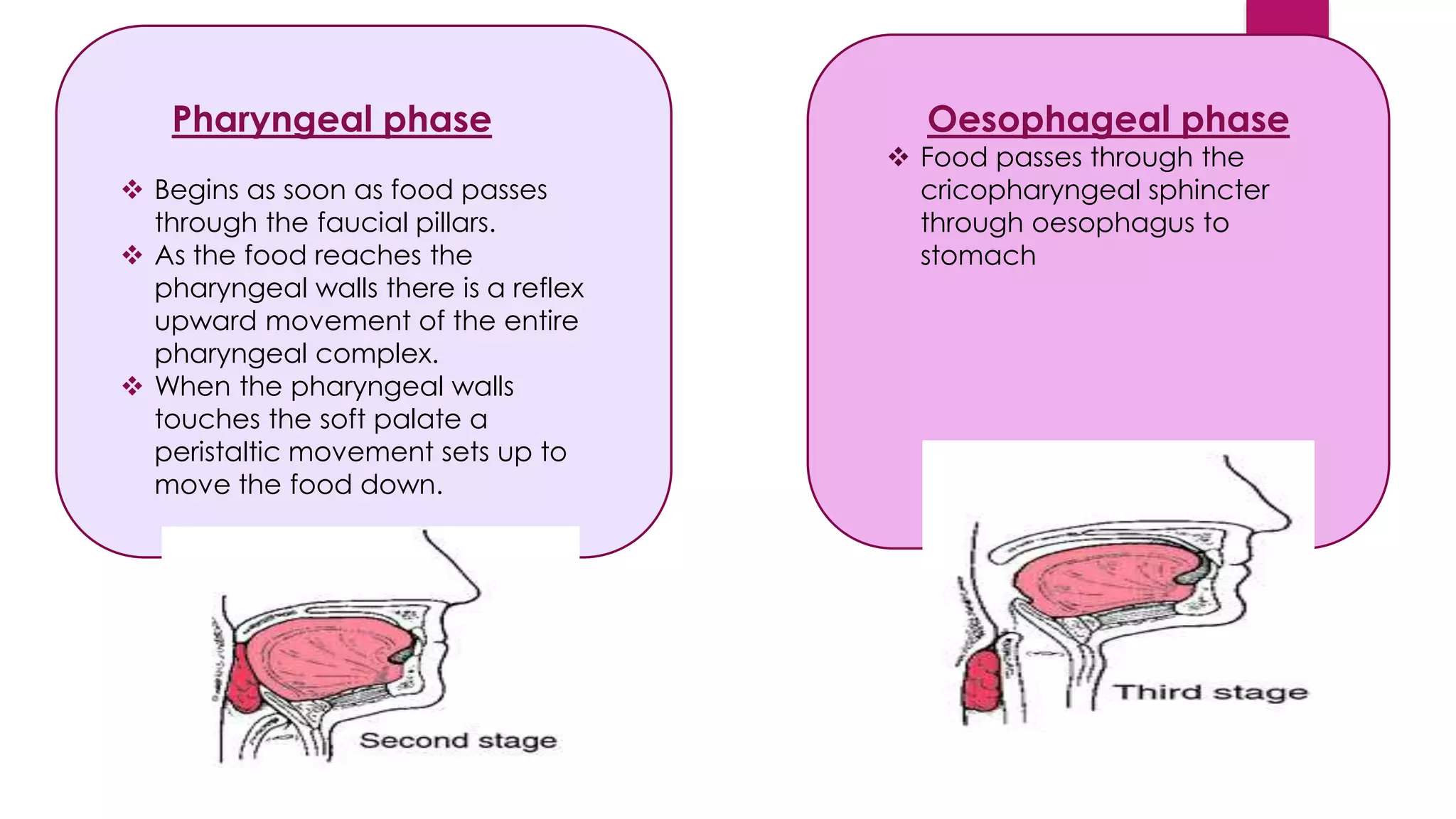
Deglutition, or swallowing, is the coordinated muscle contraction that moves food through the oral cavity, esophagus, and into the stomach. There are two main types of swallowing: infantile swallow and mature swallow. Infantile swallow is an autonomic reflex in infants where suckling and swallowing occur together. Mature swallow develops around ages 4-5 as chewing and swallowing of semisolids and solids is added. It involves relaxation of the lips, placement of the tongue behind the upper teeth, and occlusion of the back teeth during swallowing. The phases of deglutition begin with food in the mouth and involve oral preparation, movement of the bolus into the pharynx by