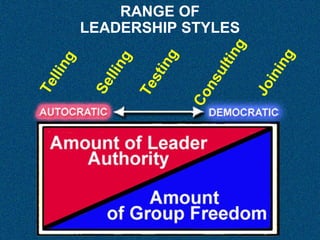
This document discusses different approaches to leadership including authority, responsibility, accountability, leadership styles (autocratic vs democratic), communication skills, and public speaking. It provides definitions of key terms like authority and describes the different components of effective writing, listening, and speech-giving. The document also addresses leadership approaches like telling, selling, testing, consulting and joining, and asks and answers 16 questions to reinforce the concepts.