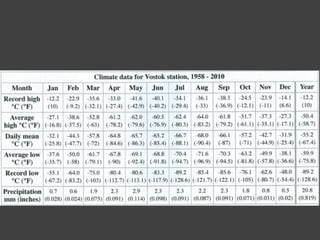
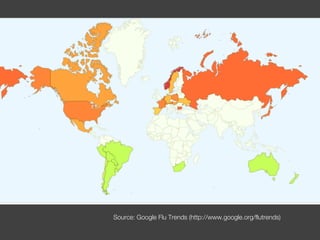
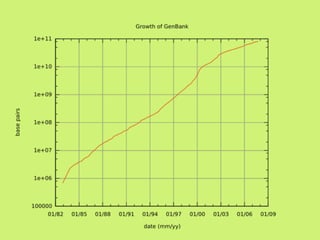
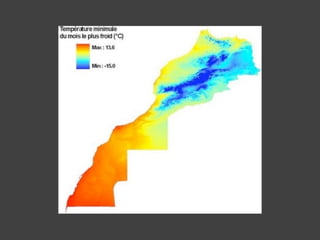
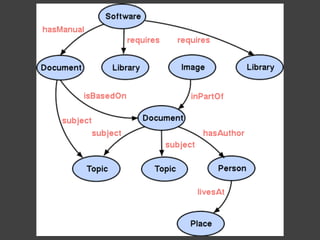
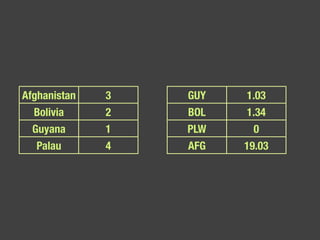
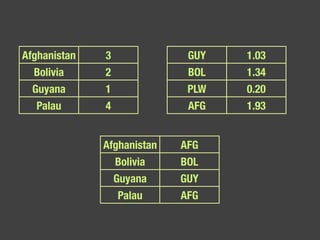
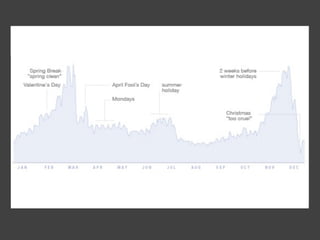
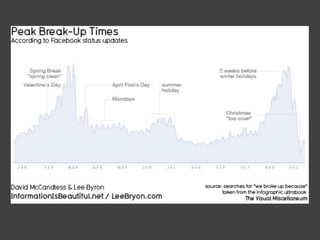
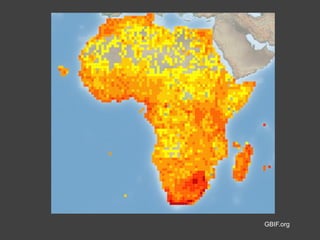
The document discusses data, data science, and finding data sources. It defines data as raw facts about the world and notes that data comes from various sources like government, scientific research, citizens, and private companies. It then discusses the growth of digital data and issues around open data. The document defines data science as using analysis methods to describe facts, detect patterns, and test hypotheses. Finally, it provides tips on finding needed data, such as searching open data sources, APIs, scraping, and joining datasets.