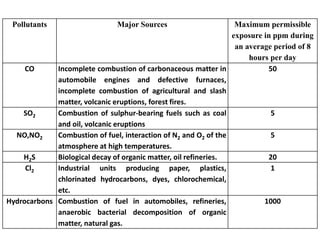
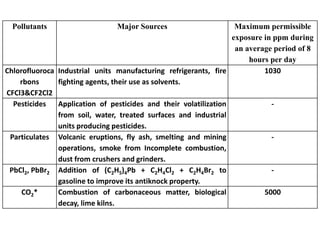
1. The document discusses various types of air pollution including emissions from vehicles, combustion of fossil fuels, and particulate matter. Four major pollutants are highlighted: carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, and particulate matter.
2. The health effects of carbon monoxide and sulfur dioxide are explained. Carbon monoxide deprives the body of oxygen causing headaches, fatigue, and impaired vision. Sulfur dioxide irritates the respiratory system and causes wheezing.
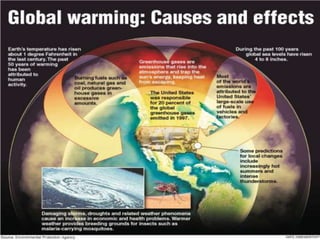
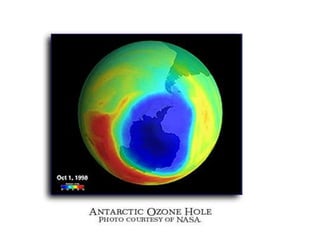
3. The document provides information on reducing air pollution through alternatives to driving, educating others, and encouraging energy conservation. Greenhouse gases and their effect on the environment are also mentioned.