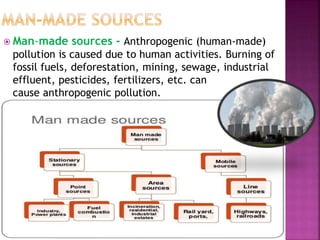
This document defines air pollution and discusses its sources and key pollutants. It identifies two main sources of air pollution as natural sources like volcanoes and fires, and anthropogenic or man-made sources from activities like burning fossil fuels and agriculture. The document categorizes major air pollutants as particulate matter, ozone, carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and volatile organic compounds. It also distinguishes between primary pollutants emitted directly and secondary pollutants formed from chemical reactions of primary pollutants in the atmosphere.