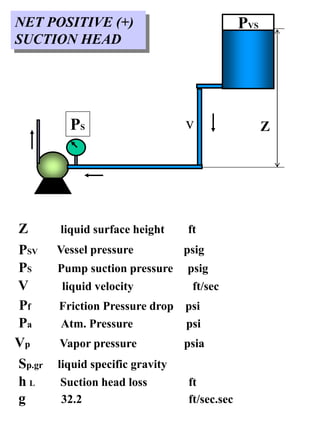
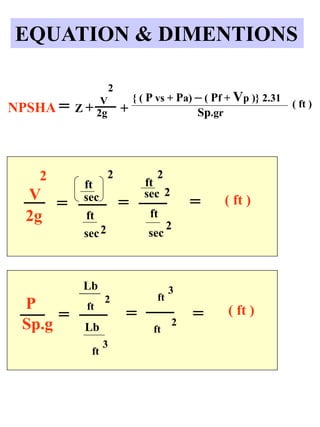
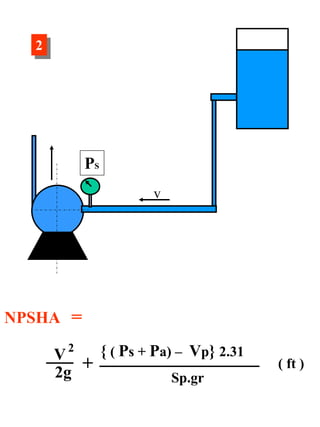
This document discusses Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH) as it relates to centrifugal and positive displacement pumps. It defines NPSH Required (NPSHR) and NPSH Available (NPSHA), explaining that cavitation can occur if NPSHA is less than NPSHR. Methods to improve NPSHA include shortening suction pipe length, increasing pipe size, decreasing suction liquid temperature, and decreasing suction negative altitude. Equations are provided to calculate NPSHA based on factors like suction head, liquid velocity, vapor pressure, and specific gravity. Examples of NPSHA calculations are also given.