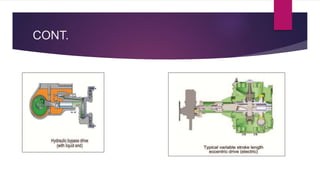
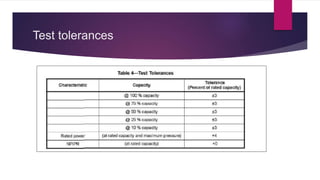
This document provides an overview of API 675 3rd Edition standards for positive displacement pumps with controlled volumes. It defines key terms such as net positive inlet pressure and displacement. It outlines design requirements for pumps, including the ability to adjust flow rates over a specified turndown ratio and incorporating pressure limiting valves. Testing requirements are specified, such as hydrostatic testing pressures and performance tests at multiple flow rates. Annexes provide additional details on data sheets, materials, inspection checklists, drawing requirements, and techniques for analyzing and controlling pulsations and vibrations.