Amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia by replacing one, two, or all of the hydrogen atoms with alkyl or aryl groups. They are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary based on the number of hydrogens replaced. Amines are found naturally in proteins, vitamins, alkaloids, and hormones, and are also used synthetically in polymers, dyes, drugs like novocaine and antihistamines. Common methods for synthesizing amines include reduction of nitro compounds, reaction of alkyl halides with ammonia, reduction of nitriles and amides, and the Gabriel and Hoffmann reactions. Amines have properties depending on their structure, with lower aliphatic amines being gases and higher ones




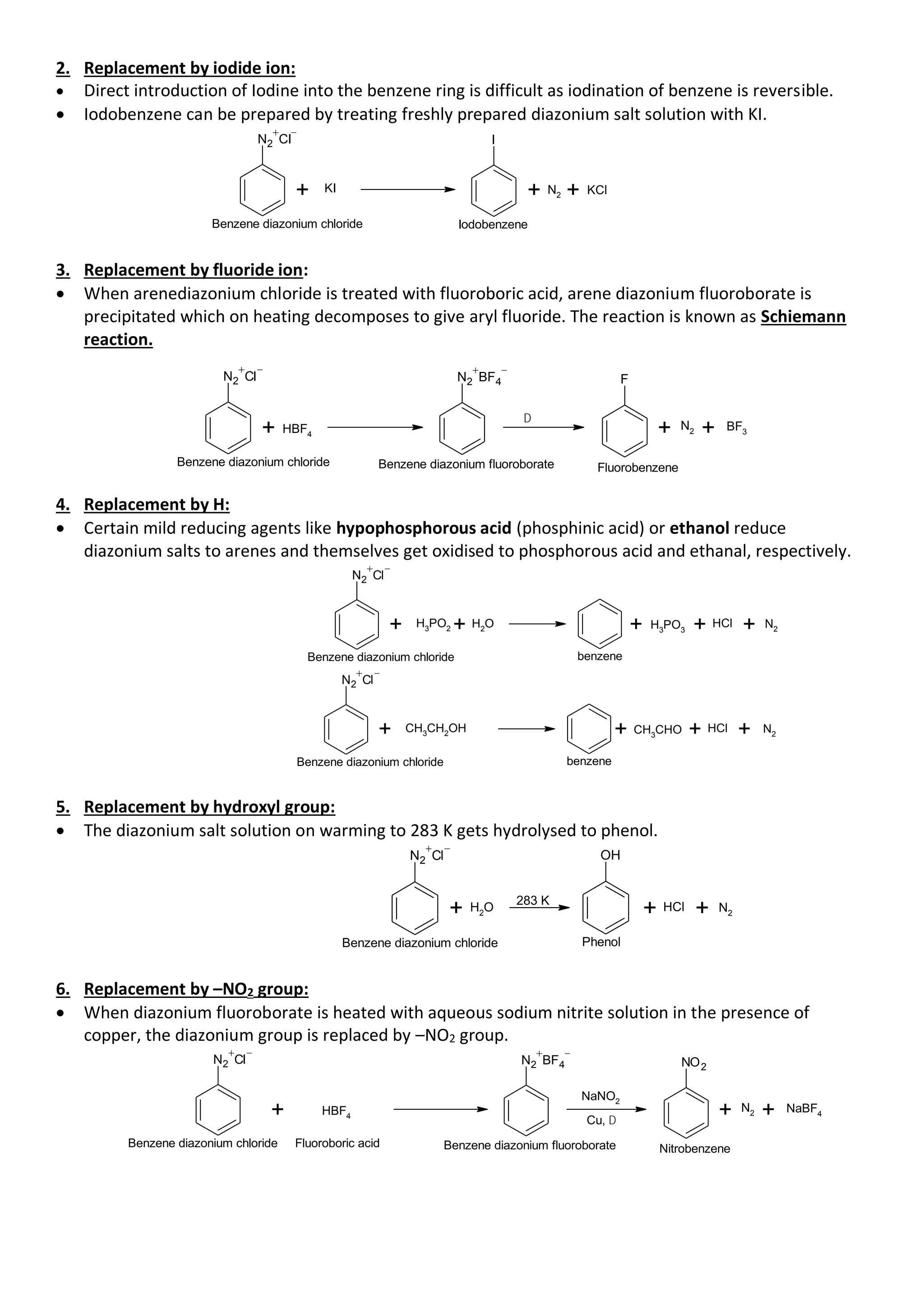
![5. Reaction with nitrous acid:
• Three classes of amines (10
, 20
and 30
amines) react differently with nitrous acid which is prepared in
situ from a mineral acid and sodium nitrite.
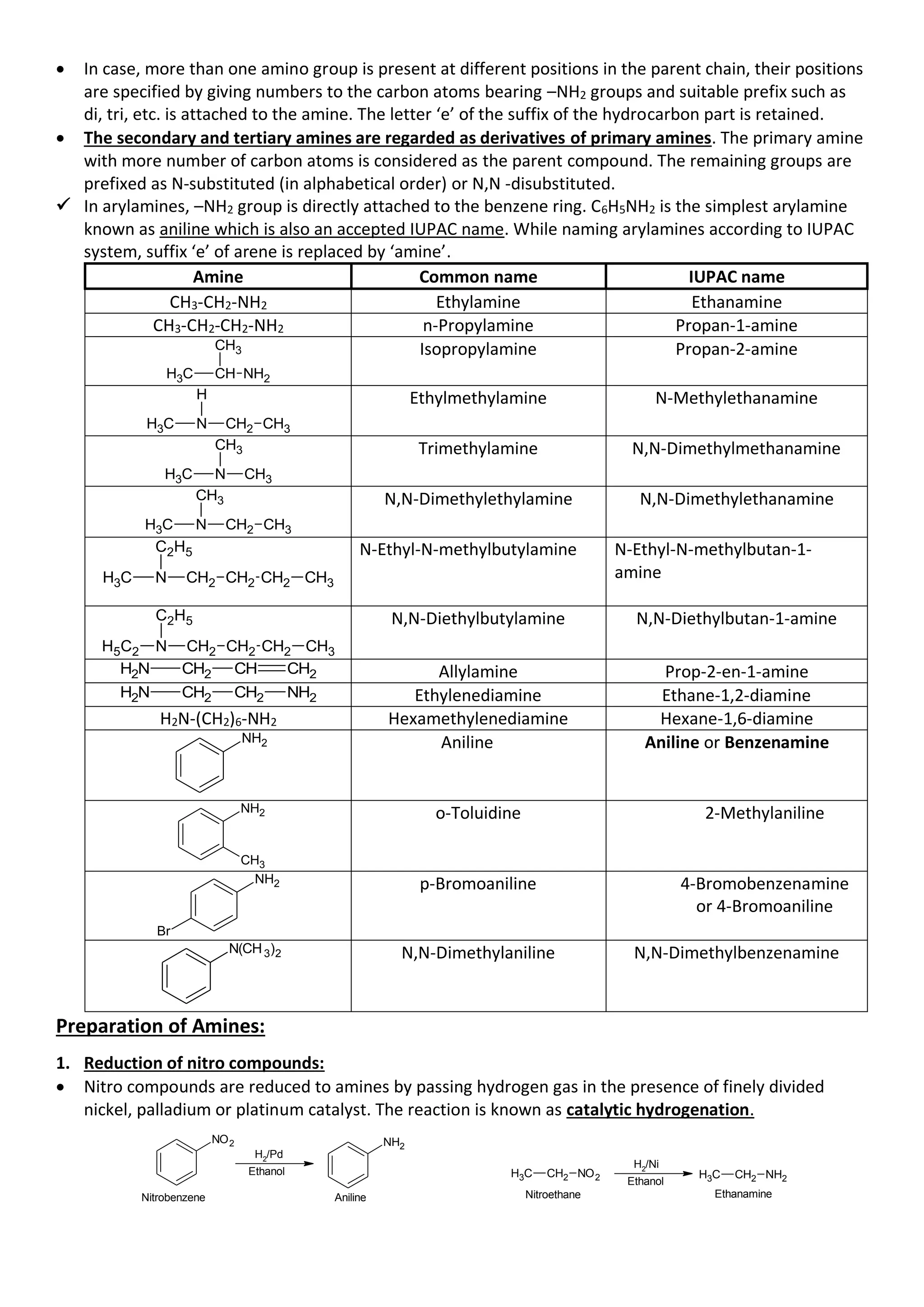
• Primary aliphatic amines react with nitrous acid to form aliphatic diazonium salts which being
unstable, liberate nitrogen gas quantitatively and alcohols. Quantitative evolution of nitrogen is used in
estimation of amino acids and proteins.
R NH2
NaNO2
+ HCl
R N2
+
Cl
-
[ ] R OH + N2 + HCl
Alkyl diazonium chloride
H2
O
+ HNO2
e.g: Methanamine reacts with nitrous acid to form methyl diazonium salt which decomposes to
methanol liberating nitrogen gas.
C
H3 NH2
NaNO2 + HCl
C
H3 N2
+
Cl
-
[ ] C
H3 OH + N2
+ HCl
methanamine methanol
Methyl diazonium chloride
H2
O
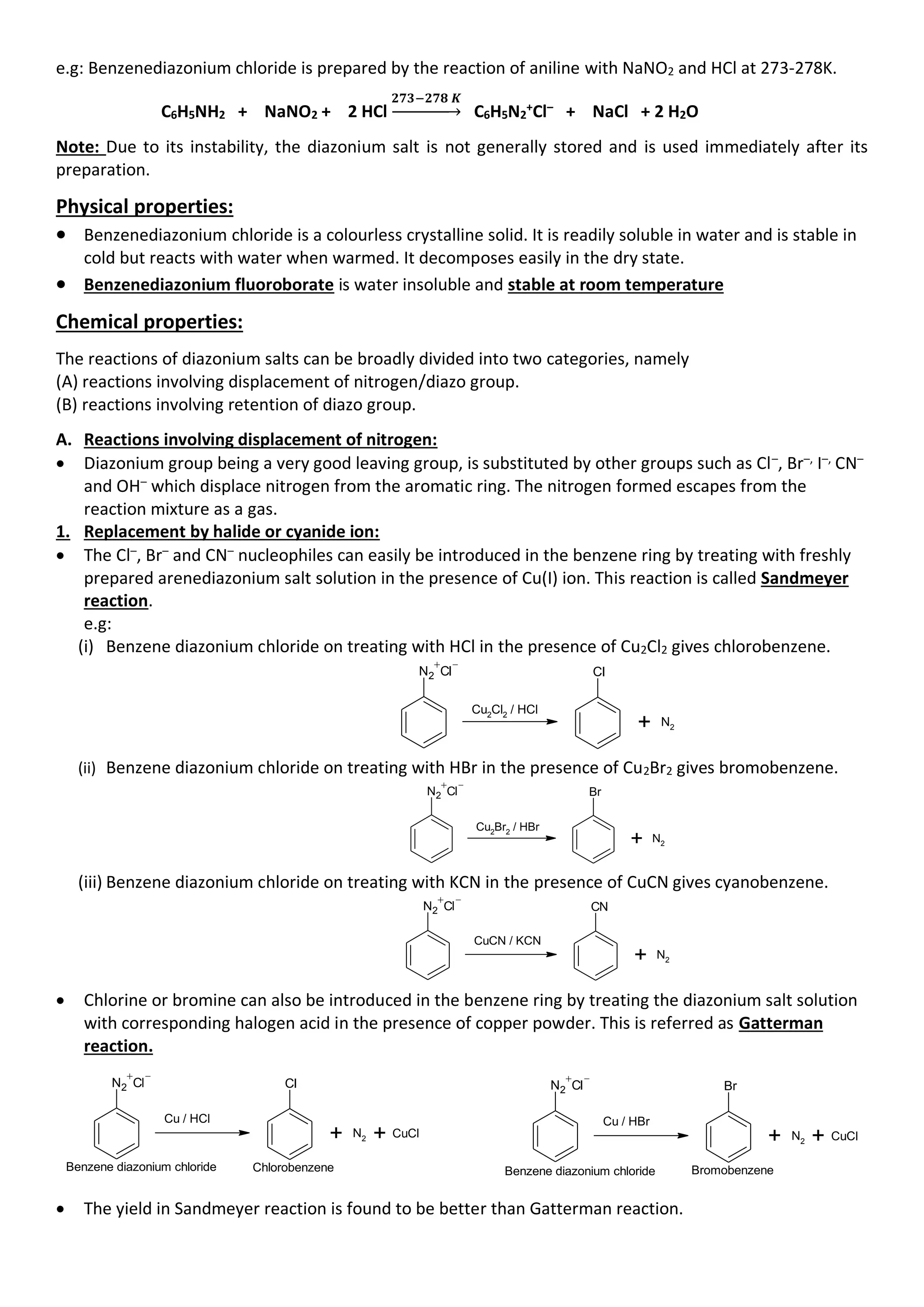
• Aromatic primary amines react with nitrous acid at low temperatures (273-278 K) to form diazonium
salts which are stable at this temperature in solution. Arene diazonium salts are a very important class
of compounds used for synthesis of a variety of aromatic compounds.
NaNO2
+ 2HCl
Benzene diazonium chloride
NH2
273 - 278K
N2 Cl
+ NaCl + O
H2
2
aniline
• Secondary and tertiary amines react with nitrous acid in a different manner.
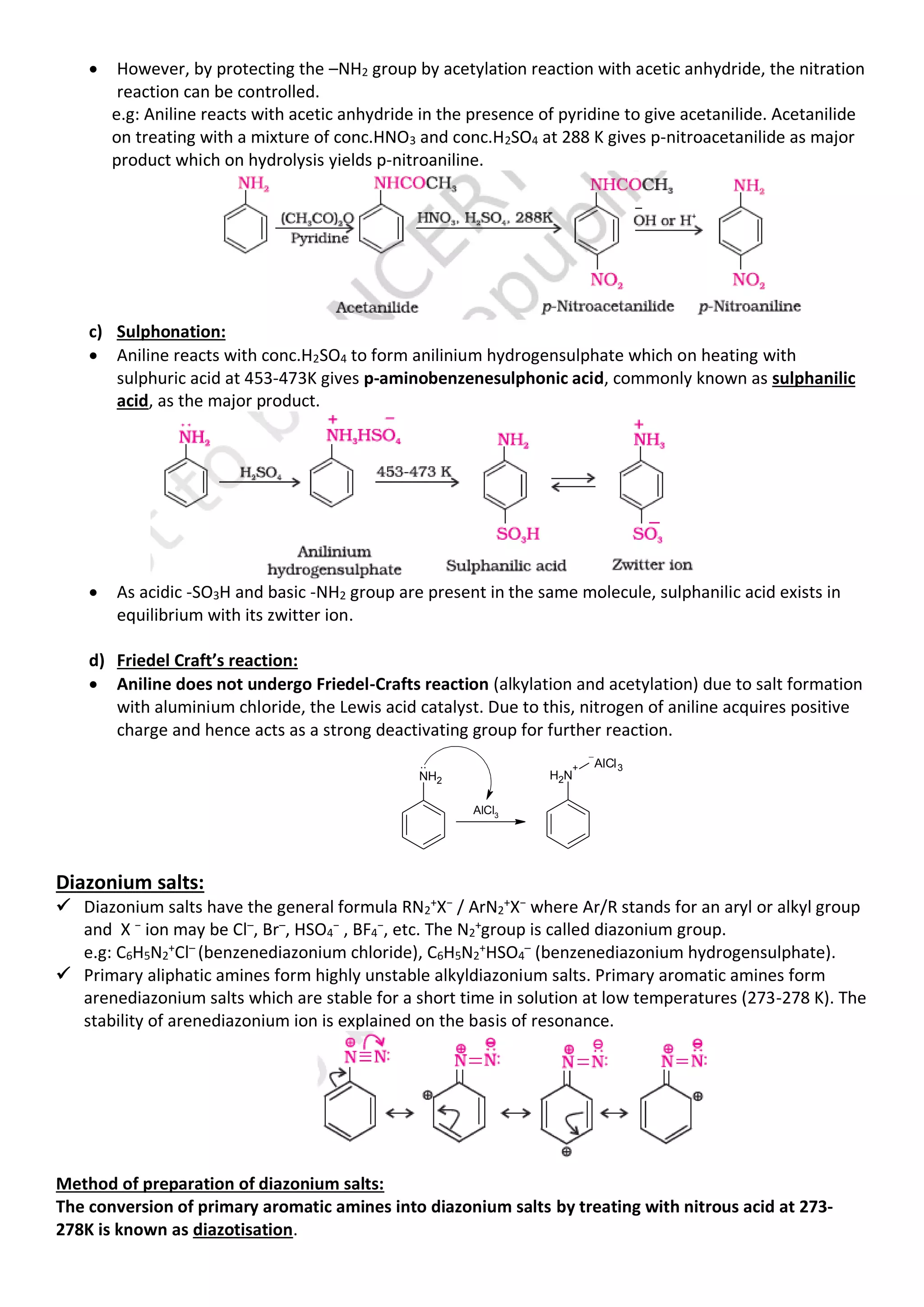
6. Reaction with arylsulphonyl chloride:
• Benzenesulphonyl chloride (C6H5SO2Cl), which is also known as Hinsberg’s reagent, reacts with
primary and secondary amines to form sulphonamides. Tertiary amines do not react with
benzenesulphonyl chloride. This property of amines reacting with benzenesulphonyl chloride in a
different manner is used for the distinction of primary, secondary and tertiary amines and also for the
separation of a mixture of amines.
• These days benzenesulphonyl chloride is replaced by p-toluenesulphonyl chloride.
✓ The reaction of benzenesulphonyl chloride with primary amine yields N-alkylbenzenesulphonamide
which is soluble in alkali.
S
O
O
Cl + H N C2H5
H
Ethanamine
Benzenesulphonyl chloride
S
O
O
NH C2H5 + Cl
H
N-Ethylbenzenesulphonamide
The hydrogen attached to nitrogen in this sulphonamide is strongly acidic due to the presence of strong
electron withdrawing sulphonyl group. Hence, it is soluble in alkali.
✓ The reaction of benzenesulphonyl chloride with secondary amine yields N,N-
dialkylbenzenesulphonamide which is insoluble in alkali.
S
O
O
Cl + H N C2H5
C2H5
N-Ethylethanamine
Benzenesulphonyl chloride
S
O
O
N C2H5
C2H5
+ Cl
H
N,N-Diethylbenzenesulphonamide
Since N,N-dialkylbenzenesulphonamide does not contain any hydrogen atom attached to nitrogen
atom, it is not acidic and hence insoluble in alkali,
✓ Tertiary amines do not react with benzenesulphonyl chloride.
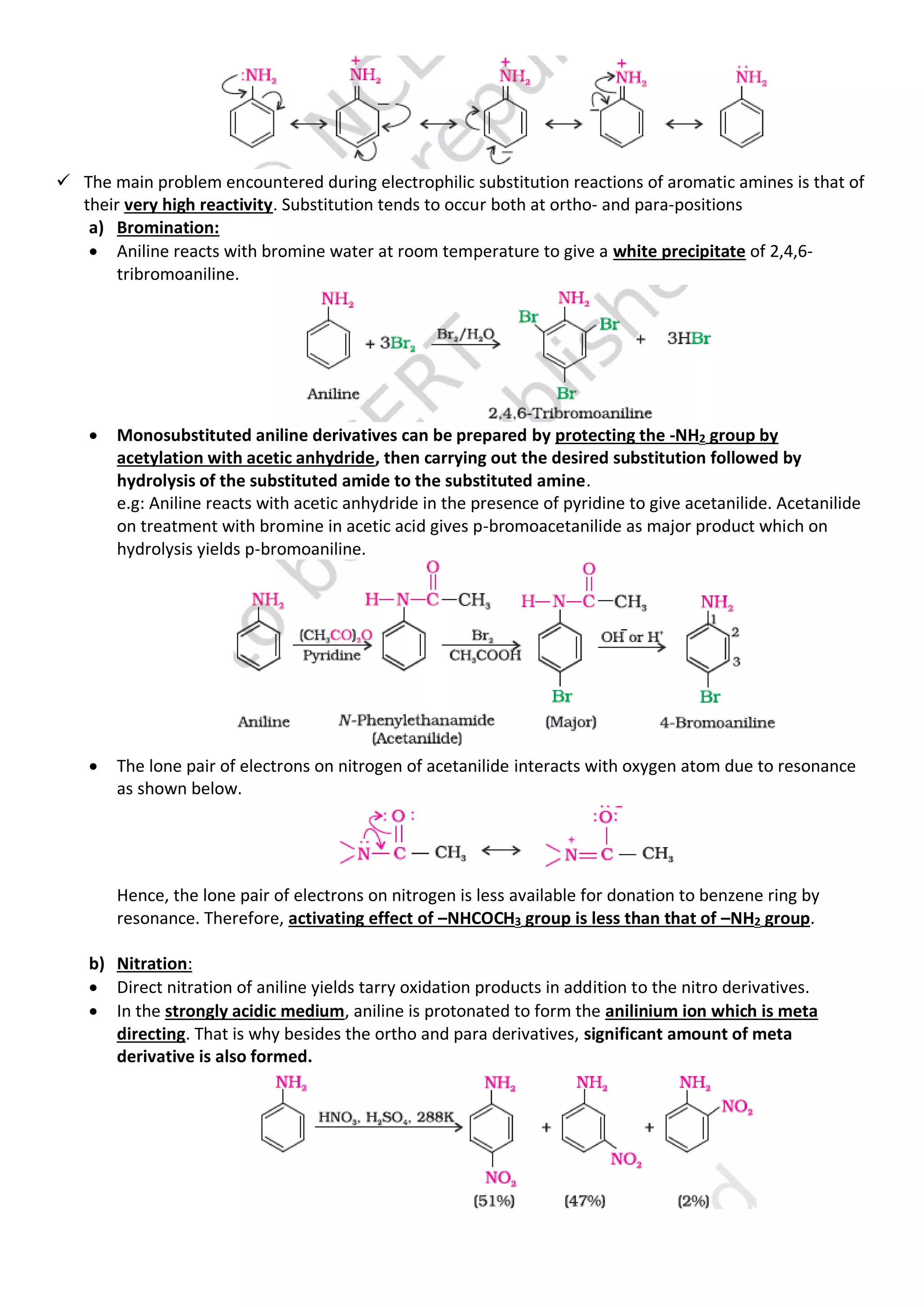
7. Electrophilic substitution:
✓ The –NH2 group is a powerful ring activating and ortho-, para- directing group. It is evident from the
following resonance structures.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notes-amines-230727065412-2ecd4d9a/75/Notes-Amines-pdf-9-2048.jpg)