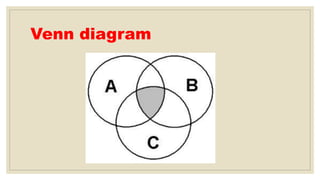
This document discusses key concepts in probability, including experiments, sample spaces, events, and calculating probabilities. It provides examples of identifying the sample space for different experiments like flipping a coin or rolling a die. Events are defined as subsets of the sample space, and probability is calculated as the number of outcomes in the event divided by the total number of outcomes in the sample space. Mutually exclusive events and unions and intersections of events are also introduced.