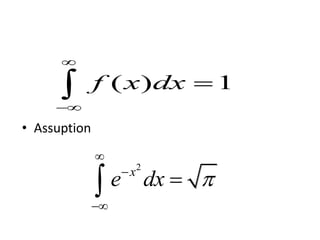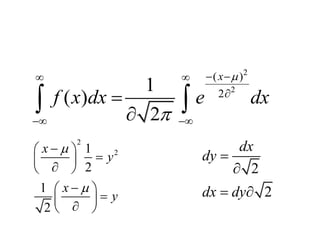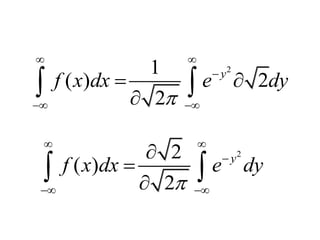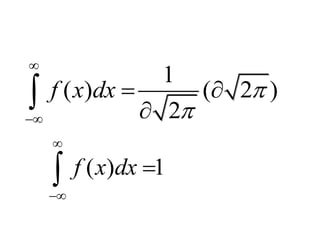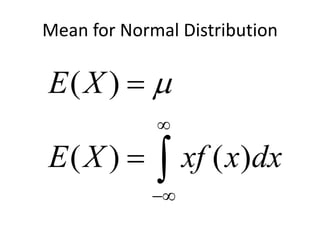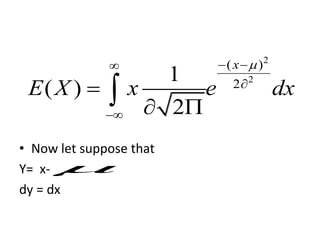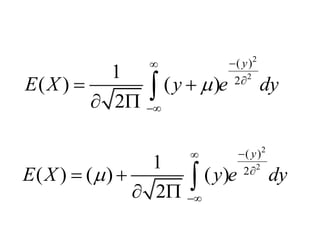Embed presentation
Download to read offline


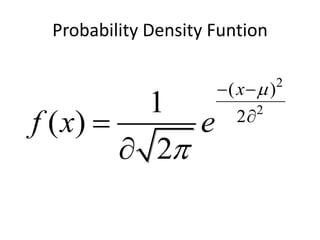
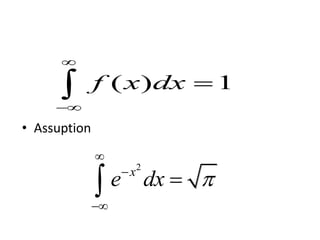
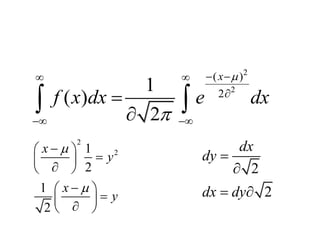
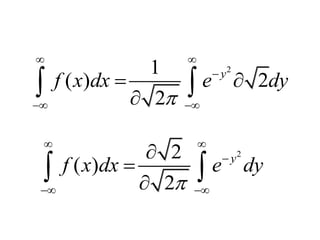
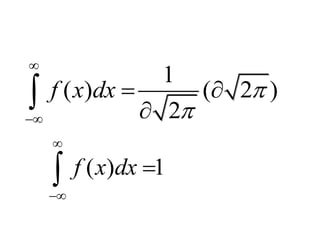
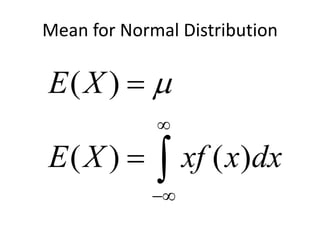
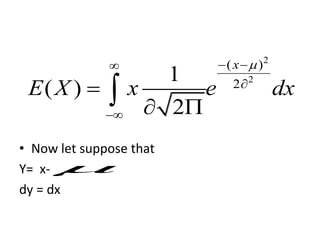
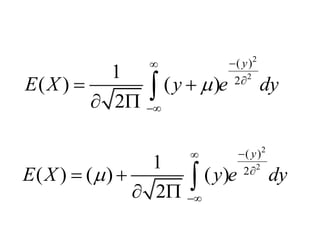


The document discusses the properties of the normal distribution, focusing on the probability density function and the calculation of its mean. It includes mathematical expressions and integrals related to these concepts, illustrating how the probabilities and means are derived. The analysis concludes that the mean of the normal distribution function can be calculated through specific integrals.