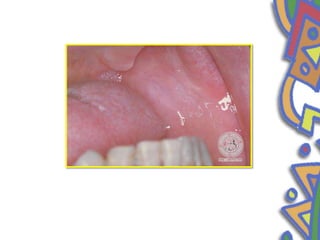
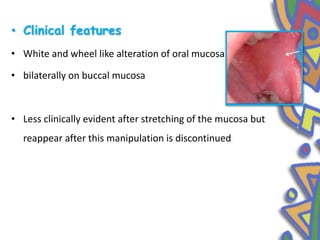
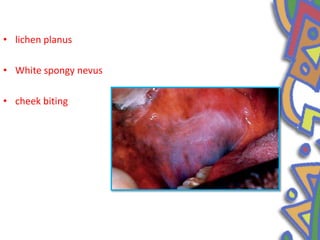
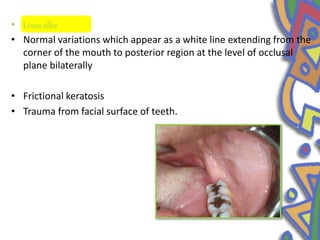
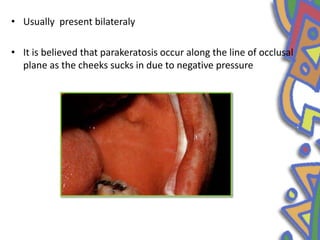
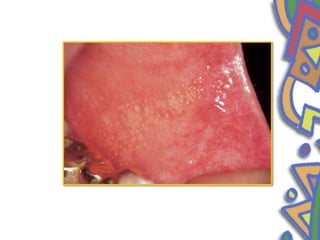
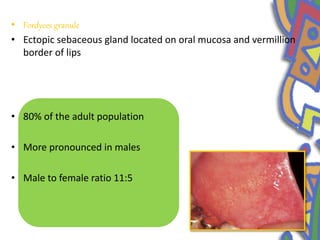
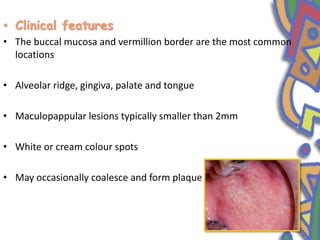
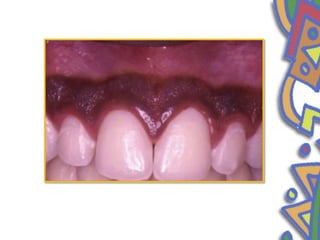
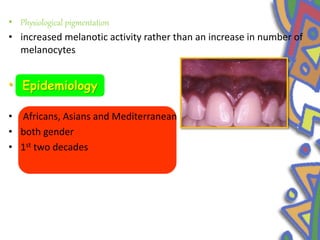
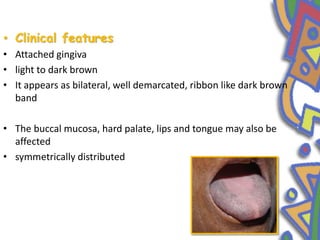
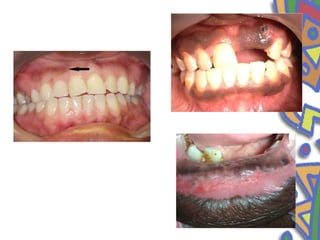
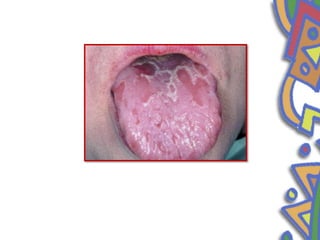
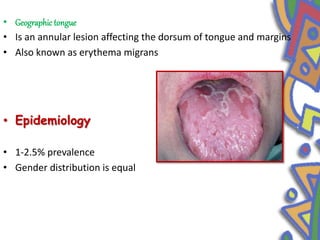
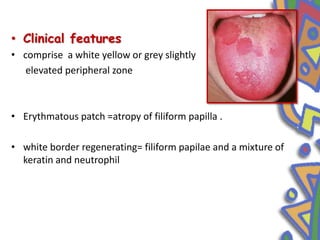
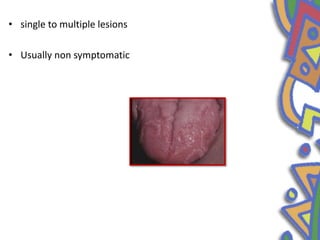
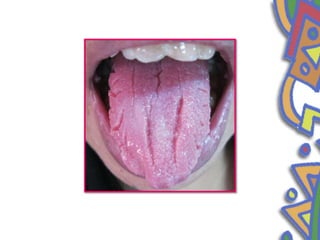
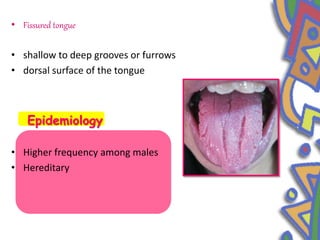
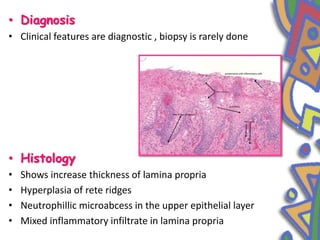
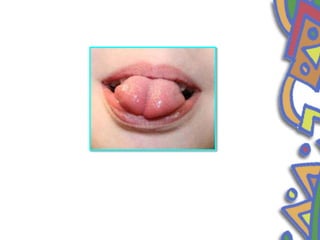
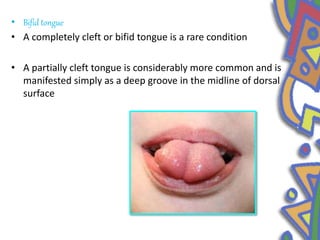
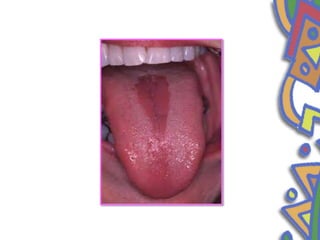
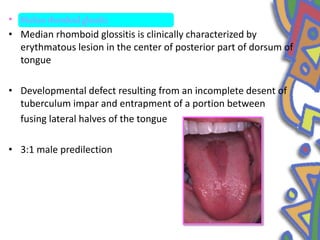
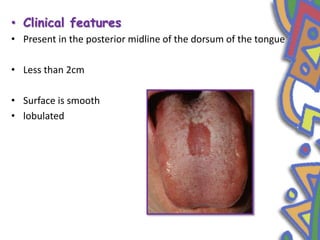
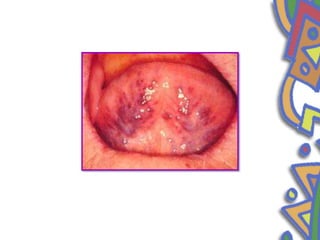
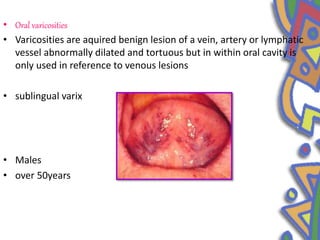
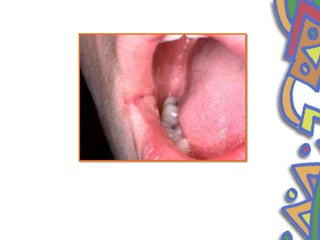
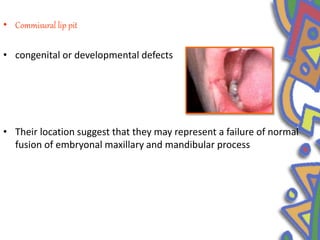
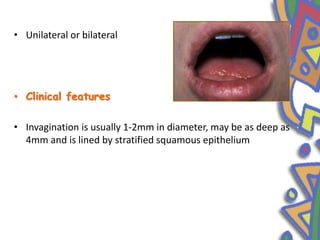
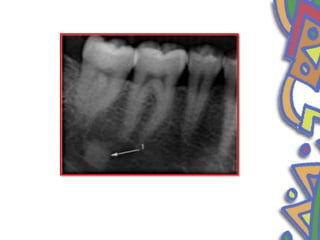
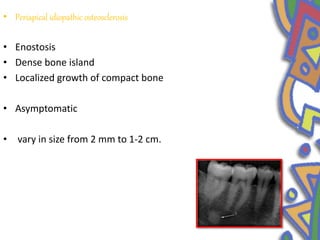
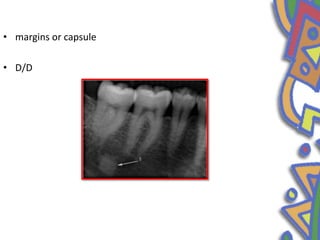
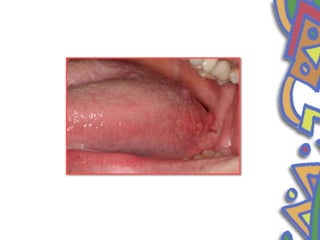
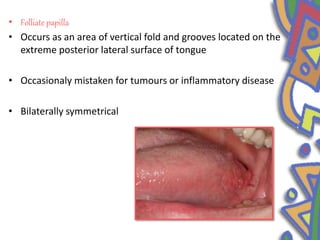
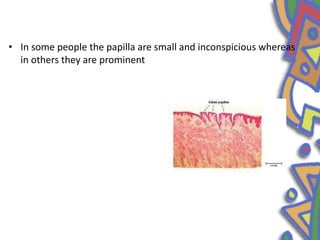
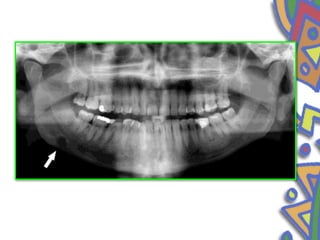
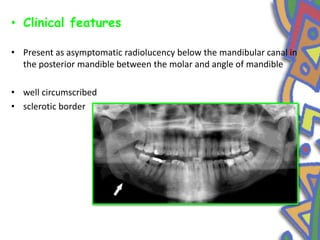
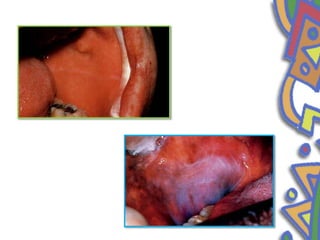
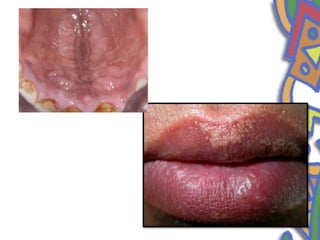
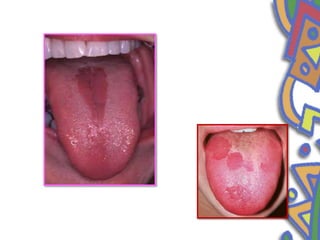
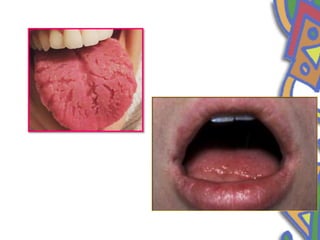
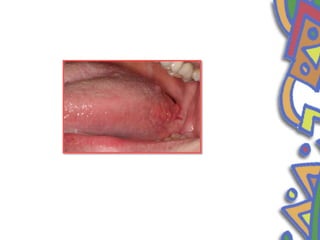
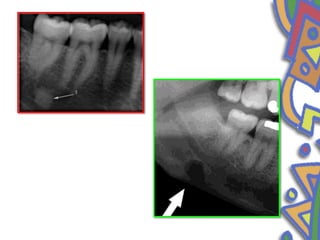
This document summarizes several normal anatomical variations that can occur in the oral cavity. It describes variations that can be seen on the buccal mucosa such as leukedema and Fordyce's granules. Variations of the gingiva, tongue, and lips are also discussed including physiologic pigmentation, fissured tongue, median rhomboid glossitis, and commissural lip pits. Finally, some common radiographic variations like idiopathic osteosclerosis and Stafne bone defects are mentioned. For each variation, the document discusses epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, and differentiation from pathologic conditions.